Abstract
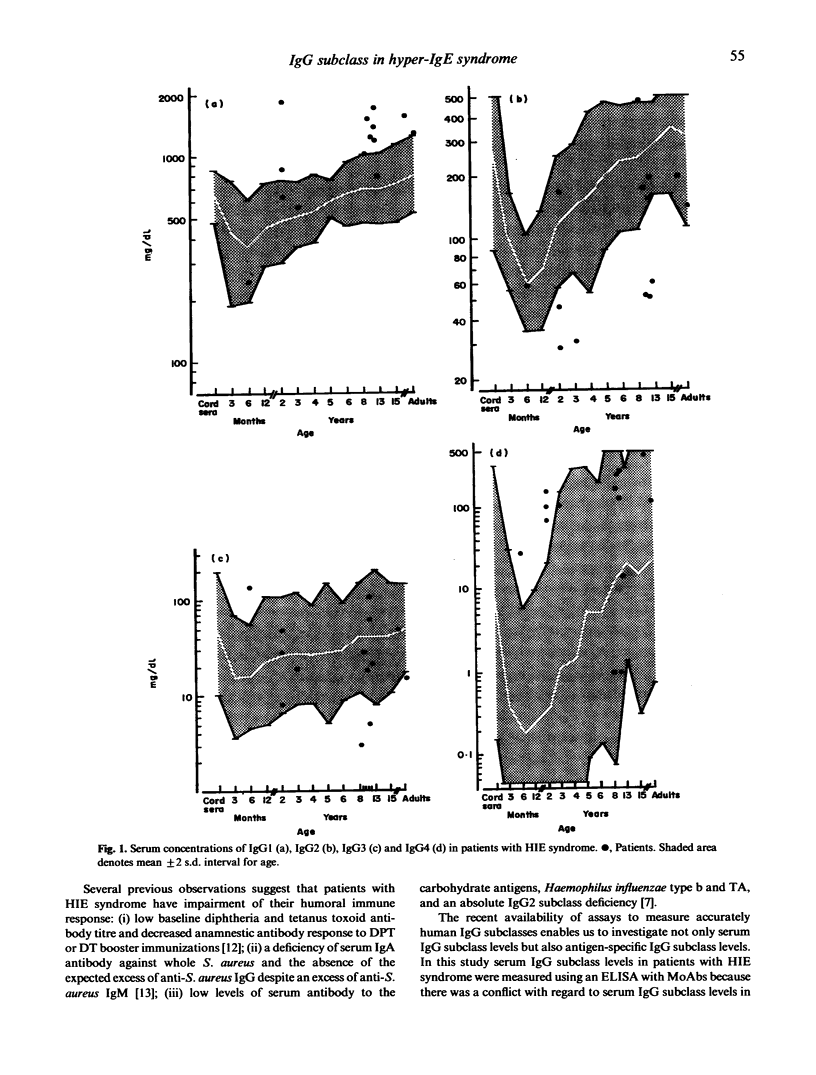
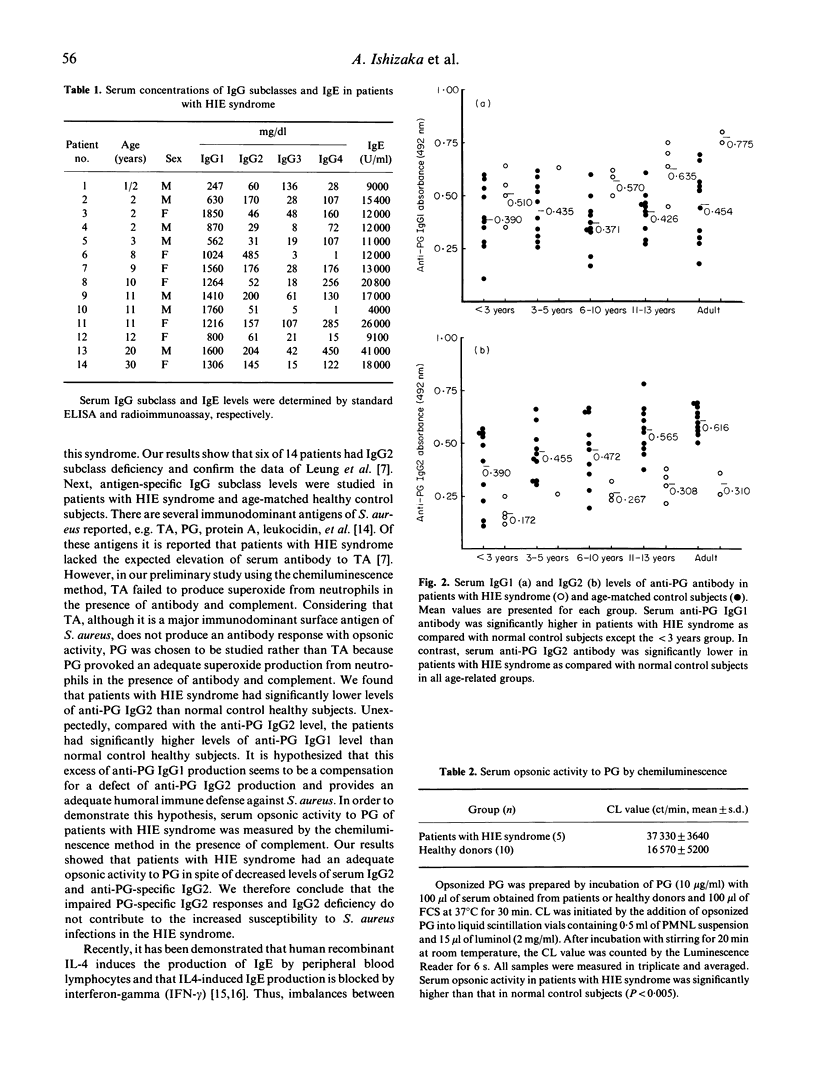
The hyper-IgE (HIE) syndrome is characterized by high IgE serum levels, chronic dermatitis and recurrent infections. To determine whether an impairment of the antibody response to Staphylococcus aureus contributes to infections in this syndrome we measured total serum IgG subclass, specific IgG1 and IgG2 levels against peptidoglycan (PG), the immunodominant cell wall component of S. aureus and serum opsonic activity to PG. Of the 14 patients with HIE syndrome, nine had increased level of serum IgG1 and six had IgG2 subclass deficiency. In regard to specific response of IgG1 and IgG2 antibodies to PG, patients were divided into five groups related to ages and compared with 10 control subjects for each age cohort. Patients with HIE syndrome had significant high levels of serum-specific IgG1 to PG and significant decreased levels of serum-specific IgG2 to PG in all five groups. Additionally, serum opsonic activity in patients was significantly higher than that in normal control subjects. It is concluded that IgG2 deficiency or poor IgG2 antibody response to S. aureus is not the explanation of the abnormal susceptibility to S. aureus infections of HIE patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aucouturier P., Lacombe C., Bremard-Oury C., Lebranchu Y., Griscelli C., Preud'homme J. L. Normal IgG subclass levels in the hyperIgE syndrome. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jun 15;21(4):329–330. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Wang D., Larrick J. W., Dodson R. W., Howard T. H. Enhancement of neutrophil superoxide production by preincubation with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3783–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L. Staphylococcus aureus: biology, mechanisms of virulence, epidemiology. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 2):796–799. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80747-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G., Tiri A., Maggi E., De Carli M., Macchia D., Parronchi P., Rossi M. E., Pietrogrande M. C., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Defective in vitro production of gamma-interferon and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by circulating T cells from patients with the hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1830–1835. doi: 10.1172/JCI114368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. Mononuclear cells from patients with the hyperimmunoglobulin E-recurrent infection syndrome produce an inhibitor of leukocyte chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI110551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreskin S. C., Goldsmith P. K., Gallin J. I. Immunoglobulins in the hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infection (Job's) syndrome. Deficiency of anti-Staphylococcus aureus immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):26–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI111683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Hyper immunoglobulin E syndrome. Immunodefic Rev. 1989;1(2):155–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Ochs H. D., Quie P. G., Clark R. A., Pabst H. F., Klebanoff S. J., Wedgwood R. J. Defect in neutrophil granulocyte chemotaxis in Job's syndrome of recurrent "cold" staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):617–619. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91942-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Quie P. G. Raised serum-IgE levels and defective neutrophil chemotaxis in three children with eczema and recurrent bacterial infections. Lancet. 1974 Feb 9;1(7850):183–187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92493-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Joh K., Shibata R., Wagatsuma Y., Nakanishi M., Tomizawa K., Kojima K., Kandil E., Sakiyama Y., Matsumoto S. Regulation of IgE and IgG4 synthesis in patients with hyper IgE syndrome. Immunology. 1990 Jul;70(3):414–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Nakanishi M., Yamada S., Sakiyama Y., Matsumoto S. Development of hypogammaglobulinaemia in a patient with common variable immunodeficiency. Eur J Pediatr. 1989 Dec;149(3):175–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01958274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Sakiyama Y., Nakanishi M., Tomizawa K., Oshika E., Kojima K., Taguchi Y., Kandil E., Matsumoto S. The inductive effect of interleukin-4 on IgG4 and IgE synthesis in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):392–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. L., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L., Abramson S. L., Nutman T. B. Regulation of immunoglobulin production in hyperimmunoglobulin E recurrent-infection syndrome by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10085–10089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Ambrosino D. M., Arbeit R. D., Newton J. L., Geha R. S. Impaired antibody responses in the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Jun;81(6):1082–1087. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90873-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren M., Persson U., Larsson P., Magnusson C., Smith C. I., Hammarström L., Severinson E. Interleukin 4 induces synthesis of IgE and IgG4 in human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1311–1315. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganelli R., Scala E., Capobianchi M. R., Fanales-Belasio E., D'Offizi G., Fiorilli M., Aiuti F. Selective deficiency of interferon-gamma production in the hyper-IgE syndrome. Relationship to in vitro IgE synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):28–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleman R., Wu J., Fargeas C., Delespesse G. Recombinant interleukin 4 suppresses the production of interferon gamma by human mononuclear cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1751–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Douglas S. D., Quie P. G., Verhoef J. The key role of peptidoglycan in the opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI108971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Bonnefoy J. Y., Spits H., Yokota T., Arai N., Arai K., Banchereau J. IgE production by normal human lymphocytes is induced by interleukin 4 and suppressed by interferons gamma and alpha and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6880–6884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Cunningham-Rundles C., Abrams J. S., Lewis D. B., Meyer J., Schneider L. C., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Regulation of immunoglobulin (Ig)E synthesis in the hyper-IgE syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1666–1671. doi: 10.1172/JCI114618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Lauener R. P., Geha R. S. IL-4 inhibits the synthesis of IFN-gamma and induces the synthesis of IgE in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):570–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., De Weck A. L., Stadler B. M. Effect of recombinant human interleukin 4 on spontaneous in vitro human IgE synthesis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1699–1704. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Velde A. A., Huijbens R. J., Heije K., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Interleukin-4 (IL-4) inhibits secretion of IL-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IL-6 by human monocytes. Blood. 1990 Oct 1;76(7):1392–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


