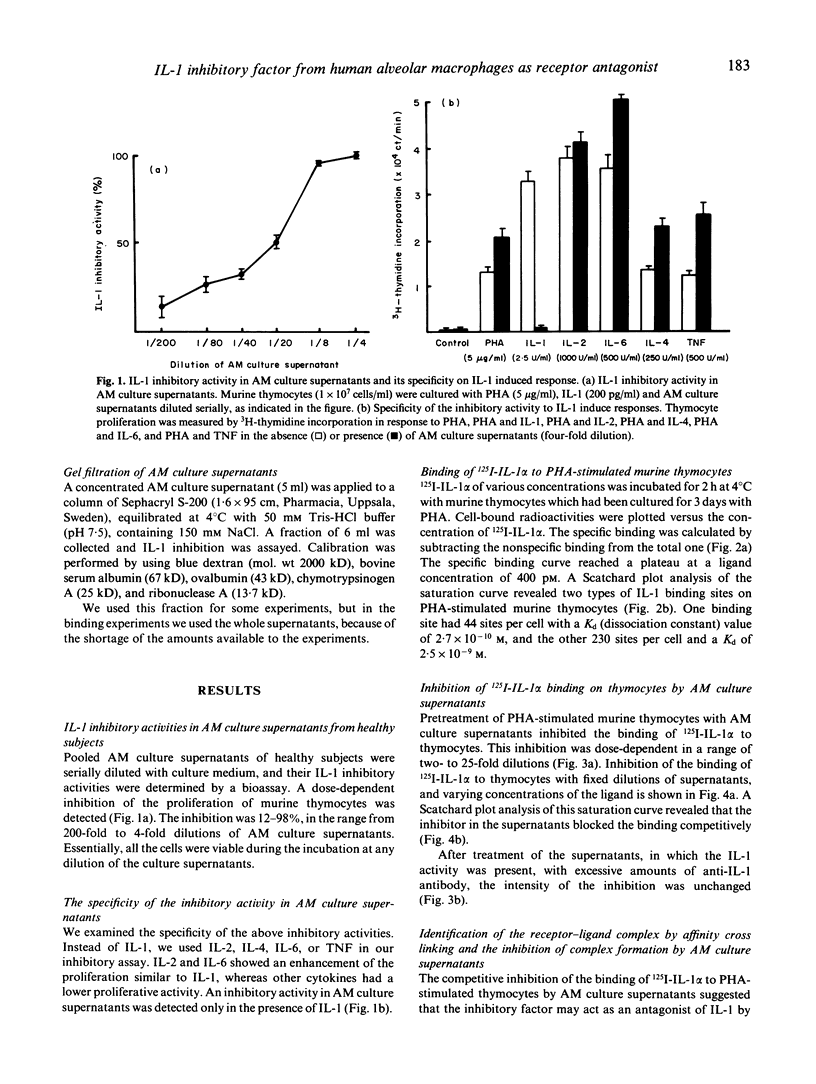
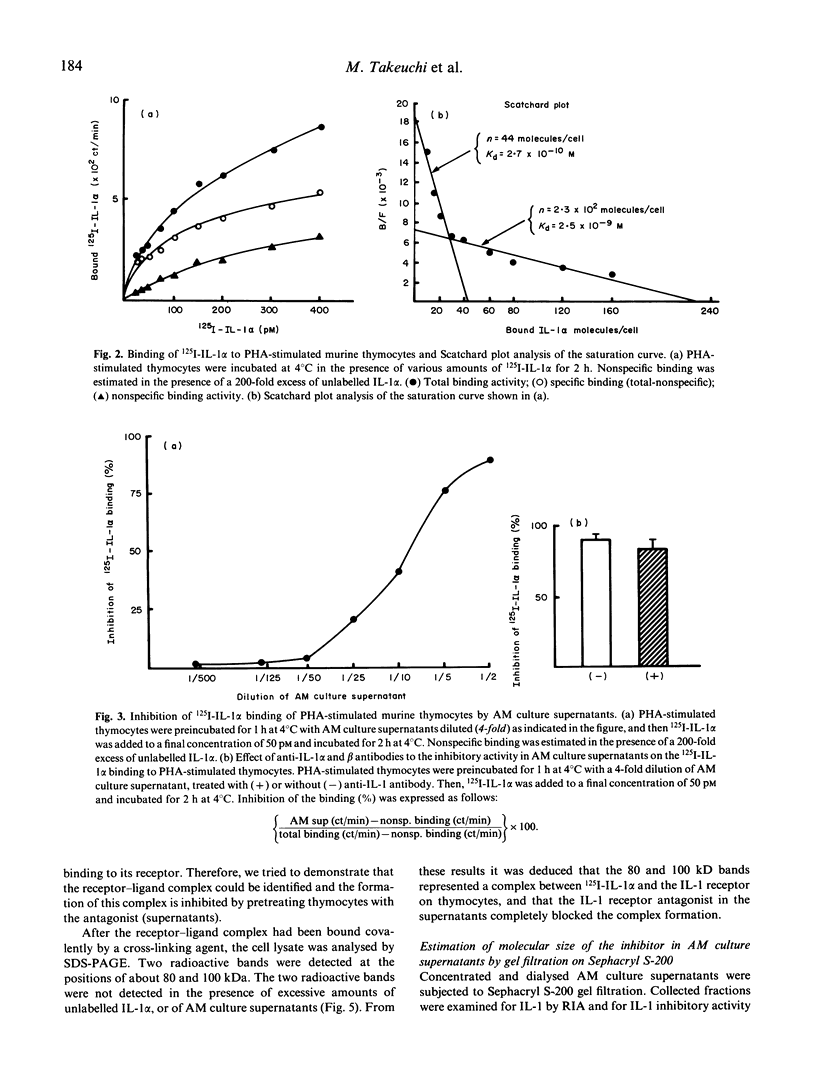
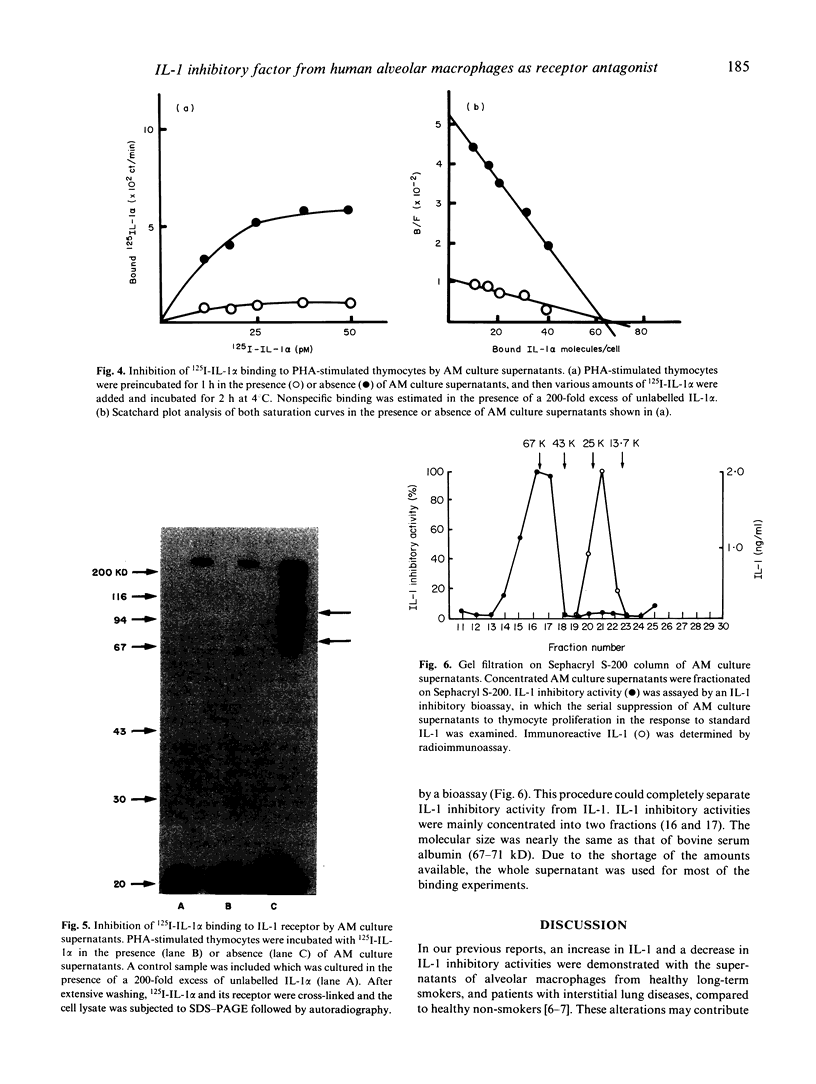
Abstract
IL-1 possesses pleiotropic properties on various cells and its activity may be stringently regulated in several ways. We have previously reported that both IL-1 and its inhibitory factor are concomitantly released from alveolar macrophages in both healthy subjects and patients with chronic inflammatory lung diseases. An increase in IL-1 activities and a decrease in inhibitory activities are characteristics found in both healthy smokers and patients with interstitial lung diseases. In this study, we further examined the biological properties of IL-1 inhibitory factor. The inhibitor exhibited a dose-dependent specific inhibition of an augmentation by IL-1 of PHA-induced murine thymocyte proliferation, while no inhibition of the augmentation by IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, or tumour necrosis factor (TNF) was found. 125I-labelled IL-1 alpha binding on PHA-stimulated murine thymocytes revealed two types of IL-1 binding sites, 44 sites/cell with a Kd of 2.7 x 10(-10) M and 230 sites/cell with a Kd of 2.5 x 10(-9) M. Alveolar macrophage culture supernatants blocked the binding of labelled IL-1 to the IL-1 receptor in a dose-dependent fashion. Scatchard plot analysis revealed that the inhibitory factor in the supernatants blocked the binding competitively. These results indicate that alveolar macrophages produce a specific IL-1 inhibitory factor, functioning as an IL-1 receptor antagonist.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Thompson R. C., Hannum C. H. An IL-1 inhibitor from human monocytes. Production and characterization of biologic properties. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1851–1858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balavoine J. F., de Rochemonteix B., Williamson K., Seckinger P., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Prostaglandin E2 and collagenase production by fibroblasts and synovial cells is regulated by urine-derived human interleukin 1 and inhibitor(s). J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI112669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski M. J., Eessalu T. E., Berger A. E., Truesdell S. E., Shelly J. A., Laborde A. L., Zurcher-Neely H. A., Reardon I. M., Heinrikson R. L., Chosay J. G. Purification and characterization of interleukin 1 receptor level antagonist proteins from THP-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14505–14511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. B., Deibel M. R., Jr, Dunn C. J., Tomich C. S., Laborde A. L., Slightom J. L., Berger A. E., Bienkowski M. J., Sun F. F., McEwan R. N. Purification, cloning, expression and biological characterization of an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):633–638. doi: 10.1038/344633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., de Rochemonteix B., Burrus B., Demczuk S., Dinarello C. A. Human recombinant interleukin 1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):645–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI112350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Kronheim S. R., March C. J., Conlon P. J., Hopp T. P., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Detection and characterization of high affinity plasma membrane receptors for human interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):501–515. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frans A., Van den Eeckhaut J., Garlin P. Isolated cough which responds to inhaled salbutamol and beclomethasone dipropionate. Eur Respir J. 1990 Feb;3(2):243–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galve-de Rochemonteix B., Nicod L. P., Junod A. F., Dayer J. M. Characterization of a specific 20- to 25-kD interleukin-1 inhibitor from cultured human lung macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Oct;3(4):355–361. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosset P., Lassalle P., Tonnel A. B., Dessaint J. P., Wallaert B., Prin L., Pestel J., Capron A. Production of an interleukin-1 inhibitory factor by human alveolar macrophages from normals and allergic asthmatic patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jul;138(1):40–46. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Elias J. A., Kay S. L., Rossman M. D., Nowell P. C., Daniele R. P. Spontaneous production of interleukin-1 by human alveolar macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;29(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W. Native interleukin 1 inhibitors. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Z., Grimshaw R. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Identification of a specific interleukin 1 inhibitor in the urine of febrile patients. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):126–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Warner S. J., Friedman G. B. Interleukin 1: a mitogen for human vascular smooth muscle cells that induces the release of growth-inhibitory prostanoids. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):487–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI113346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Zubler R. H., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Similarities between interleukin-2 receptor number and affinity on activated B and T lymphocytes. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):669–672. doi: 10.1038/315669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei G. J., Seckinger P. L., Dayer J. M., Shaw A. R. Purification and characterization of a 26-kDa competitive inhibitor of interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):683–689. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Aung H., Takeuchi M., Kusume K., Izumi T. IL-1 and IL-1 inhibitory activity in the culture supernatants of alveolar macrophages from patients with interstitial lung diseases. Chest. 1991 Mar;99(3):674–680. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Fujimura N., Hirata T., Izumi T. Differentiation between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial pneumonia associated with collagen vascular diseases by comparison of the ratio of OKT4+ cells and OKT8+ cells in BALF T lymphocytes. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;67(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Takeuchi M., Watanabe K., Aung H., Izumi T. Smoking and interleukin-1 activity released from human alveolar macrophages in healthy subjects. Chest. 1988 Oct;94(4):694–700. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts N. J., Jr, Prill A. H., Mann T. N. Interleukin 1 and interleukin 1 inhibitor production by human macrophages exposed to influenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus. Respiratory syncytial virus is a potent inducer of inhibitor activity. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):511–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Mizel S. B., Cohen D., Green I. Interleukin 1, a potential regulator of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari R., Smithers N., Page K., Bolton E., Champion B. R. Interleukin 1 responsiveness and receptor expression by murine TH1 and TH2 clones. Cytokine. 1990 Mar;2(2):129–141. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90007-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulich T. R., Yin S. M., Guo K. Z., del Castillo J., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. The intratracheal administration of endotoxin and cytokines. III. The interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist inhibits endotoxin- and IL-1-induced acute inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):521–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewers M. D., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Normal human alveolar macrophages obtained by bronchoalveolar lavage have a limited capacity to release interleukin-1. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2208–2218. doi: 10.1172/JCI111647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rochemonteix-Galve B., Dayer J. M., Junod A. F. Fibroblast-alveolar cell interactions in sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence for stimulatory and inhibitory cytokine production by alveolar cells. Eur Respir J. 1990 Jun;3(6):653–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]