Abstract
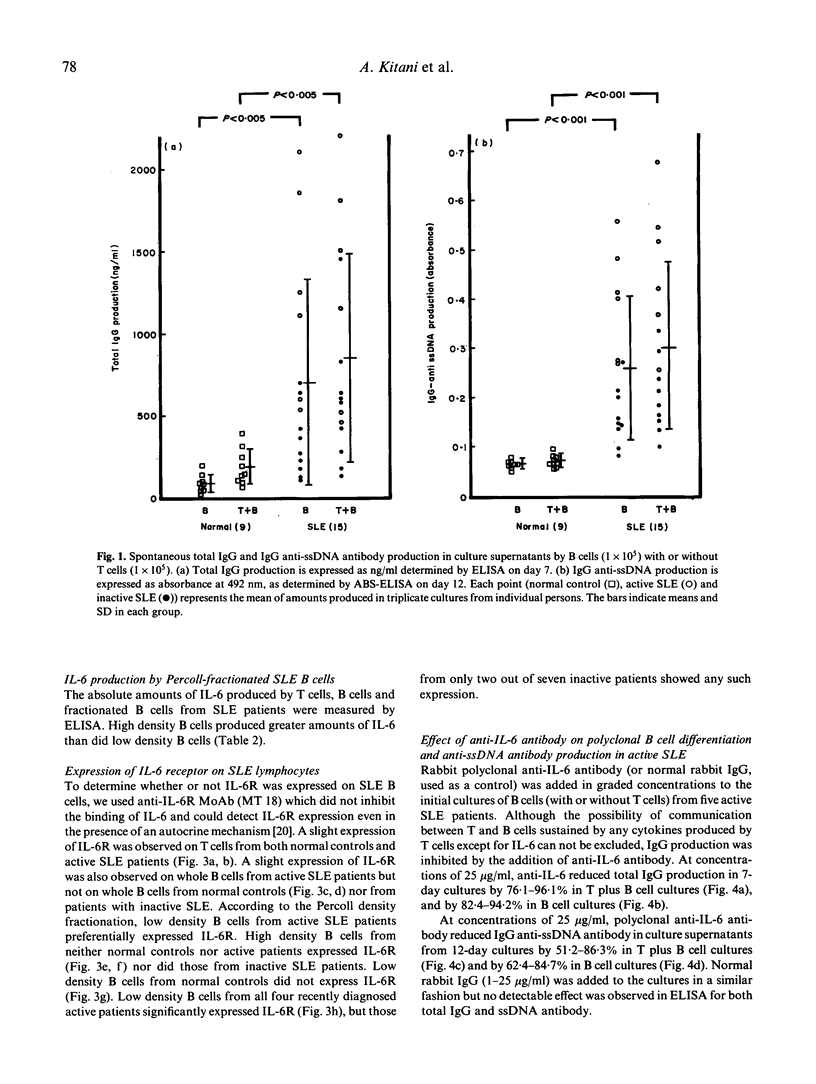
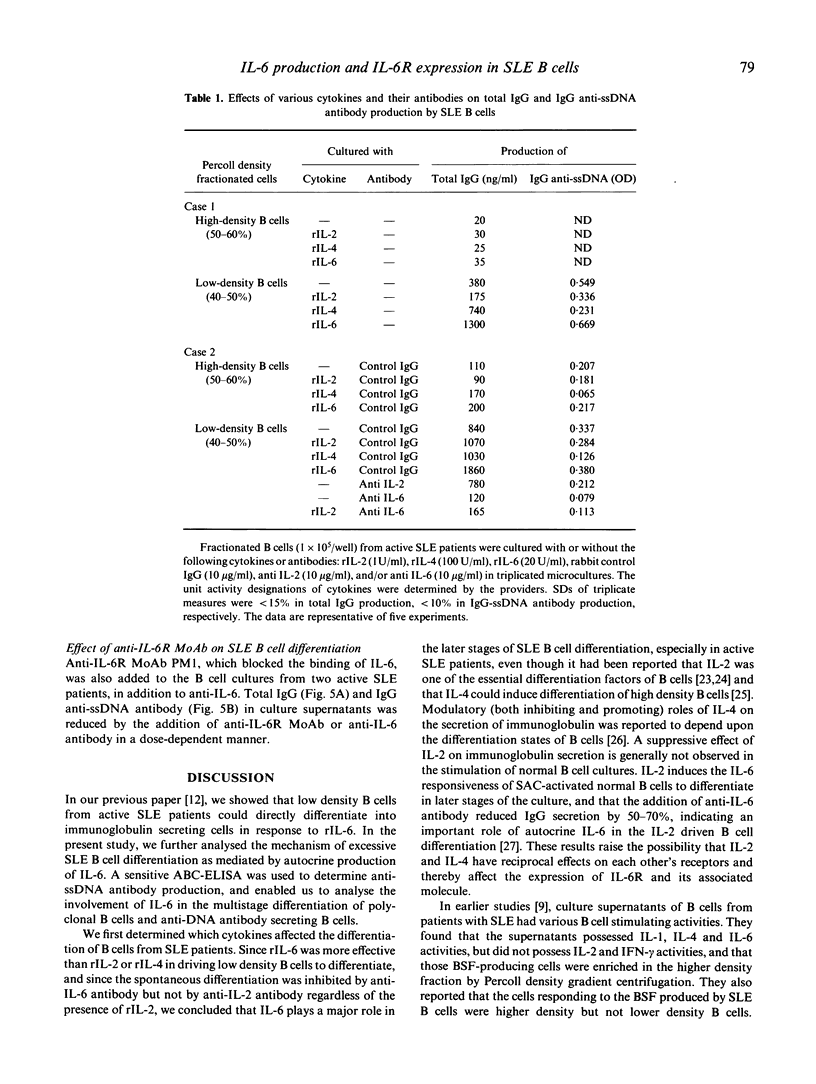
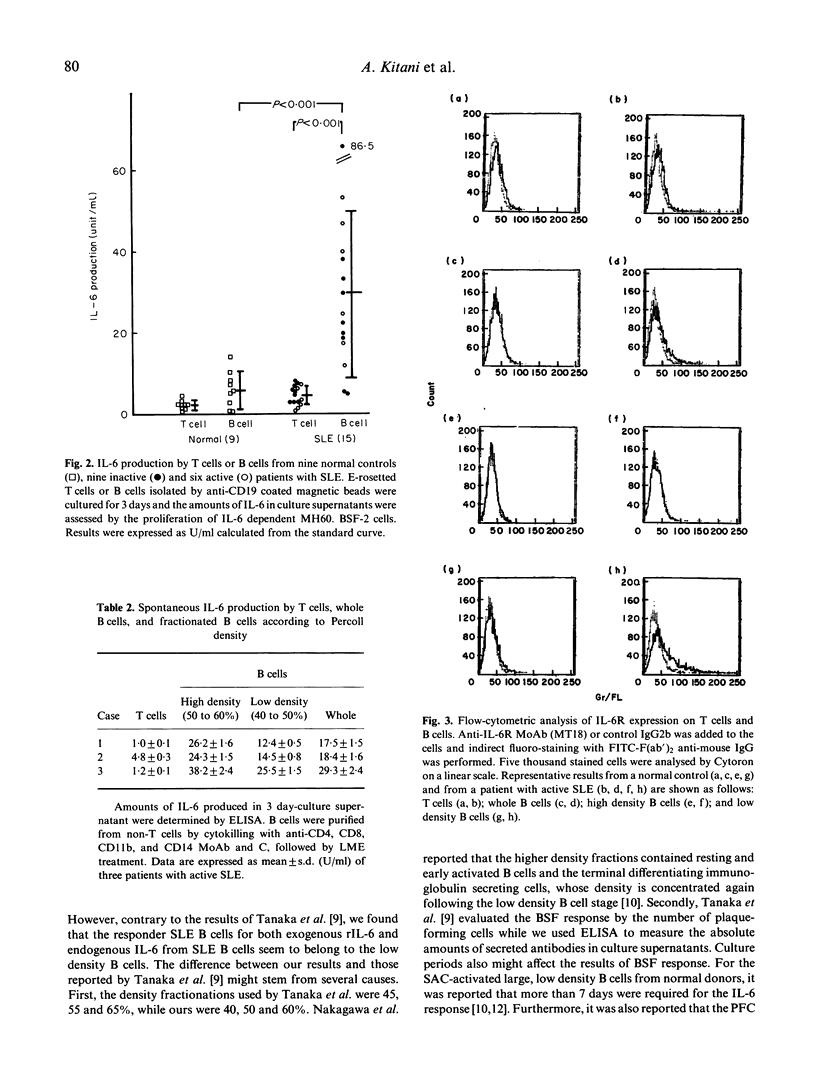
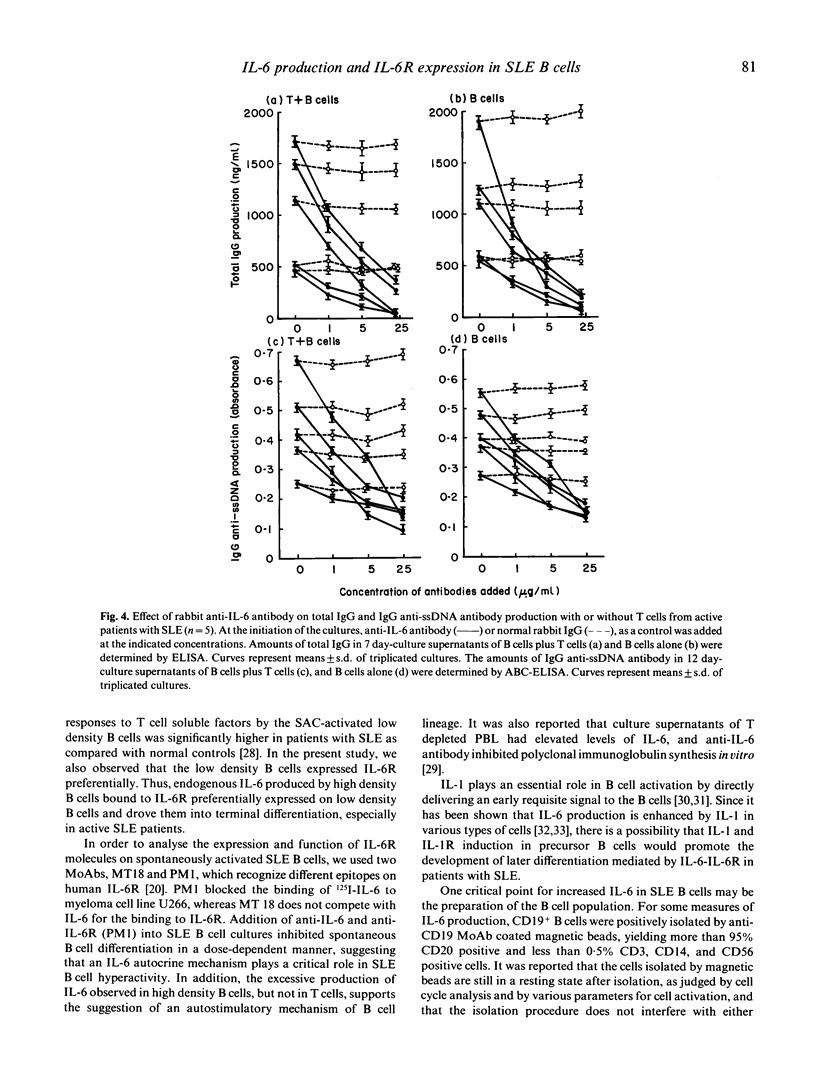
Introducing avidin-biotin complex ELISA for anti-DNA antibody, the mechanism of in vitro production of anti-ssDNA antibody as well as of polyclonal immunoglobulin mediated by an IL-6-IL-6R loop was studied in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Regardless of the presence or absence of T cells, B cells from SLE patients could produce IgG anti-ssDNA antibody as well as total IgG without any stimulation. Low density B cells obtained by Percoll gradient density centrifugation responded to rIL-6 to produce IgG and IgG anti-ssDNA antibody. rIL-2 and rIL-4 had lesser effects on the differentiation of low density B cells. In fact, IL-6R was preferentially expressed on low density B cells from active SLE patients, as detected by anti-IL-6R MoAb, MT18, which did not inhibit IL-6 binding. SLE B cells, especially high density B cells, produced greater amounts of IL-6 in culture supernatants than did T cells, regardless of whether disease was active or inactive. Normal T cells and B cells did not produce significant amounts of IL-6. Thus, endogenous IL-6 produced by high density B cells bound to the IL-6R preferentially expressed on the low density B cells, and drove them into terminal differentiation, especially in active SLE patients. Further, addition of polyclonal anti-IL-6 or anti-IL-6R MoAb (PM1), which inhibited IL-6 binding, both inhibited IgG anti-ssDNA antibody as well as total IgG production by SLE B cells in a dose-dependent manner. These results suggest that interruption of the autocrine IL-6 loop would be of therapeutic value in SLE.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aotsuka S., Okawa-Takatsuji M., Kinoshita M., Yokohari R. Analysis of negatively charged dye-binding antibodies reactive with double-stranded DNA and heparan sulfate in serum from patients with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):436–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Vanbervliet B., Pène J., Banchereau J. Human recombinant IL-4 induces activated B lymphocytes to produce IgG and IgM. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2000–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Autoimmunity: polyclonal activation or antigen induction? Immunol Today. 1988 Nov;9(11):340–342. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funderud S., Erikstein B., Asheim H. C., Nustad K., Stokke T., Blomhoff H. K., Holte H., Smeland E. B. Functional properties of CD19+ B lymphocytes positively selected from buffy coats by immunomagnetic separation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):201–206. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara M., Kitani A., Harigai M., Hirose T., Norioka K., Hirose W., Suzuki K., Kawagoe M., Nakamura H. Differential abnormality in cell-cycle stage of peripheral B cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7(2):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00270312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harigai M., Hara M., Norioka K., Kitani A., Hirose T., Suzuki K., Kawakami M., Masuda K., Shinmei M., Kawagoe M. Stimulation of interleukin 6-like B-cell differentiation factor production in human adherent synovial cells by recombinant interleukin 1. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Mar;29(3):289–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Taga T., Hibi M., Nakano N., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Characterization of IL-6 receptor expression by monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2900–2906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Hara M., Kitani A., Hirose W., Norioka K., Kawagoe M., Nakamura H. Abnormal production of and response to B-cell growth factor and B-cell differentiation factor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Feb;21(2):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R. Autoantibodies in lupus and its variants: experience in 1000 patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Aug 11;289(6441):339–342. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6441.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Podor T. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Loskutoff D. J., Carson D. A., Lotz M. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory mediators augment IL-6 secretion by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TAN E. M. AUTOANTIBODIES AND DISEASE. Adv Immunol. 1964;27:351–395. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60711-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani A., Hara M., Hirose T., Norioka K., Harigai M., Hirose W., Suzuki K., Kawakami M., Kawagoe M., Nakamura H. Heterogeneity of B cell responsiveness to interleukin 4, interleukin 6 and low molecular weight B cell growth factor in discrete stages of B cell activation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jul;77(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klashman D. J., Martin R. A., Martínez-Maza O., Stevens R. H. In vitro regulation of B cell differentiation by interleukin-6 and soluble CD23 in systemic lupus erythematosus B cell subpopulations and antigen-induced normal B cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Mar;34(3):276–286. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Smeland E., Funderud S., Vartdal F., Davies C., Beiske K., Ugelstad J. Characterization of human mononuclear cells after positive selection with immunomagnetic particles. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb03083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Thompson P. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. The role of interleukin 1 in human B cell activation: inhibition of B cell proliferation and the generation of immunoglobulin-secreting cells by an antibody against human leukocytic pyrogen. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2708–2714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Establishment of an interleukin 6 (IL 6)/B cell stimulatory factor 2-dependent cell line and preparation of anti-IL 6 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):951–956. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Hirano T., Nakagawa N., Yoshizaki K., Kishimoto T. Effect of recombinant IL 2 and gamma-IFN on proliferation and differentiation of human B cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Nakagawa N., Goldstein H., Volkman D. J., Fauci A. S. Demonstration that human B cells respond differently to interleukin 2 and B cell differentiation factor based on their stages of maturation. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3175–3182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Suzuki N., Takada S., Ueda Y., Murakawa Y., Tsuchida T., Yamauchi Y., Kishimoto T. B cell hyperactivity and its relation to distinct clinical features and the degree of disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):80–87. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Marshak-Rothstein A., Wolfowicz C. B., Rothstein T. L., Weigert M. G. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):805–811. doi: 10.1038/328805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Steinberg A. D. Autoimmunity--a perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:175–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawski J. B., Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Immunomodulatory role of IL-4 on the secretion of Ig by human B cells. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1569–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawski J. B., McAnally L. M., Lipsky P. E. IL-2 dependence of the promotion of human B cell differentiation by IL-6 (BSF-2). J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):562–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Sakane T. Induction of excessive B cell proliferation and differentiation by an in vitro stimulus in culture in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):937–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI113979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Ueda Y., Sakane T. Differential mechanism for differentiation into immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human resting B lymphocyte subsets isolated on the basis of cell density. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):261–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI113304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Abe T., Koide J., Hosono O., Morimoto C., Homma M. Cellular mechanism of DNA-specific antibody synthesis by lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jul;27(7):766–773. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T. Spontaneous production of antibodies to deoxyribonucleic acids in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Apr;35(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Saito K., Shirakawa F., Ota T., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Production of B cell-stimulating factors by B cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3043–3049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Saito K., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Inhibitory effect of anti-class II antibody on the spontaneous activation of B cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Analysis with IL-1 production and IL-1 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1584–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Shirakawa F., Ota T., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Mechanism of spontaneous activation of B cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Analysis with anti-class II antibody. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):761–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Modulation of human natural killer cell function by L-leucine methyl ester: monocyte-dependent depletion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):786–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia X., Lee H. K., Clark S. C., Choi Y. S. Recombinant interleukin (IL) 2-induced human B cell differentiation is mediated by autocrine IL6. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2275–2281. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


