Abstract
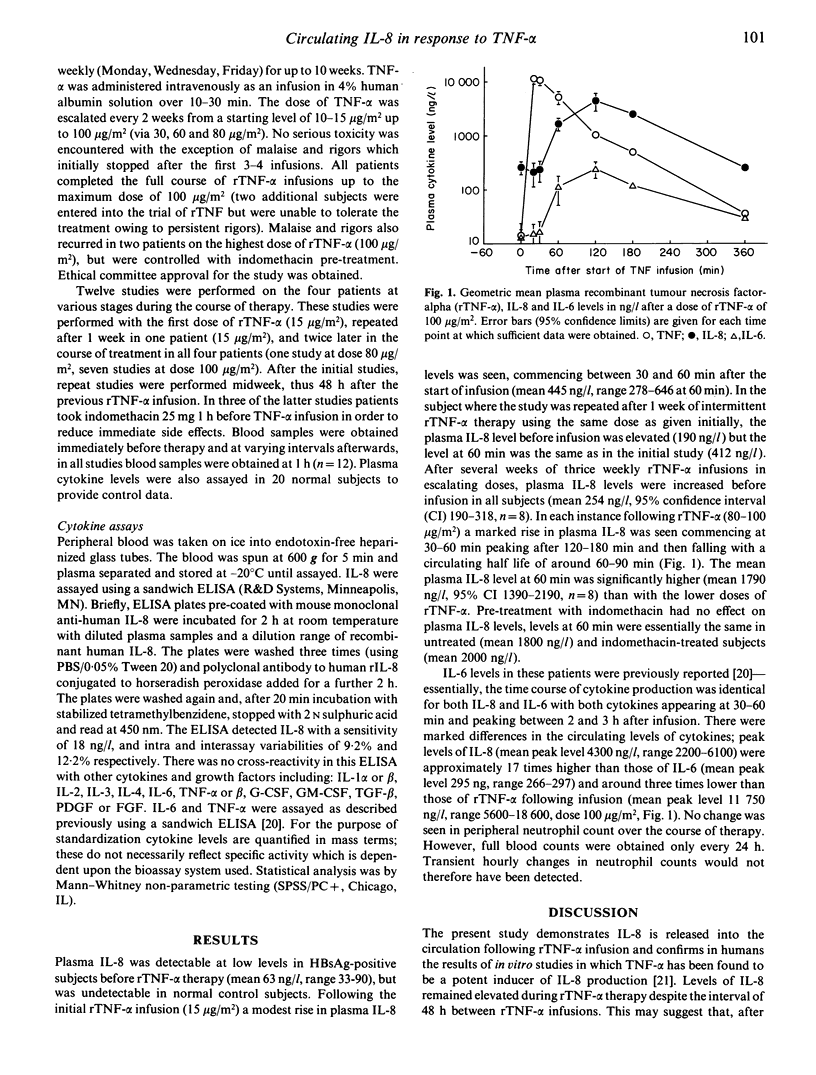
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) is a pivotal cytokine at the centre of a cascade of cytokines and inflammatory mediators which modulate the host response to infection and trauma, and in particular the metabolic changes resulting in shock and subsequent multi-organ failure. The cytokine IL-8--predominantly an activator and chemotactic factor for circulating polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocytes--is produced in response to TNF-alpha in vitro, and high circulating levels of IL-8 are found in septic primates. We have studied the release of IL-8 into the circulation of subjects with chronic hepatitis B undergoing a 10 week pilot trial of recombinant TNF-alpha (rTNF-alpha) therapy in doses of 15-100 micrograms/m2. A marked dose-dependent increase in plasma IL-8 levels was seen commencing at 30-60 min after the start of rTNF-alpha infusion and peaking between 2 and 3 h (mean peak level 4300 ng/l). The temporal pattern of IL-8 production exactly echoed that of IL-6, another component of the cytokine cascade, but peak plasma levels of IL-8 were up to 17 times higher than those of IL-6. This study confirms in vitro data suggesting that IL-8 is a component of the acute circulating cytokine cascade with a potential role in the modulation of the acute immune and metabolic response to infection and trauma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz I., Zwahlen R., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. In vivo inflammatory activity of neutrophil-activating factor, a novel chemotactic peptide derived from human monocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Remick D. G. Kinetics of TNF, IL-6, and IL-8 gene expression in LPS-stimulated human whole blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90478-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A. Interleukin-1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits: synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;286:243–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P. The role of IFN-gamma in the pathology of experimental endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2920–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J., Meyrick B., Jesmok G., Brigham K. L. Human recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha infusion mimics endotoxemia in awake sheep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1448–1454. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Basha M., Standiford T., Ham J., Remick D. G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-8 and chemotactic cytokines. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;349:433–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Hill A. V., Sambou I., Twumasi P., Castracane J., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Brewster D. R., Greenwood B. M. TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1201–1204. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marano M. A., Fong Y., Moldawer L. L., Wei H., Calvano S. E., Tracey K. J., Barie P. S., Manogue K., Cerami A., Shires G. T. Serum cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in critically ill patients with burns correlates with infection and mortality. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 Jan;170(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke V., Bauman J. G., Sticherling M., Ibs T., Zomershoe A. G., Seligmann K., Henneicke H. H., Schröder J. M., Sterry W., Christophers E. Detection of neutrophil-activating peptide NAP/IL-8 and NAP/IL-8 mRNA in human recombinant IL-1 alpha- and human recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human dermal fibroblasts. An immunocytochemical and fluorescent in situ hybridization study. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Dewald B., Gerber N., Baggiolini M. Enhanced production of neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):463–469. doi: 10.1172/JCI115018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Lau J. N., Hofmann J., Williams R., Alexander G. J. Dose-dependent increase in plasma interleukin-6 after recombinant tumour necrosis factor infusion in humans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Dec;82(3):427–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Lau J. Y., Daniels H. M., Webster J., Eddleston A. L., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Tumour necrosis factor to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):321–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91866-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kasahara K., Allen R., Showell H. J., Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L. Human neutrophils exhibit disparate chemotactic factor gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):725–730. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W., Torre-Amione G. Effects of in vivo 'priming' on endotoxin-induced hypotension and tissue injury. The role of PAF and tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):949–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. J., Strieter R. M., Lindley I., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor/IL-8 in human hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2609–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zee K. J., DeForge L. E., Fischer E., Marano M. A., Kenney J. S., Remick D. G., Lowry S. F., Moldawer L. L. IL-8 in septic shock, endotoxemia, and after IL-1 administration. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3478–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


