Abstract
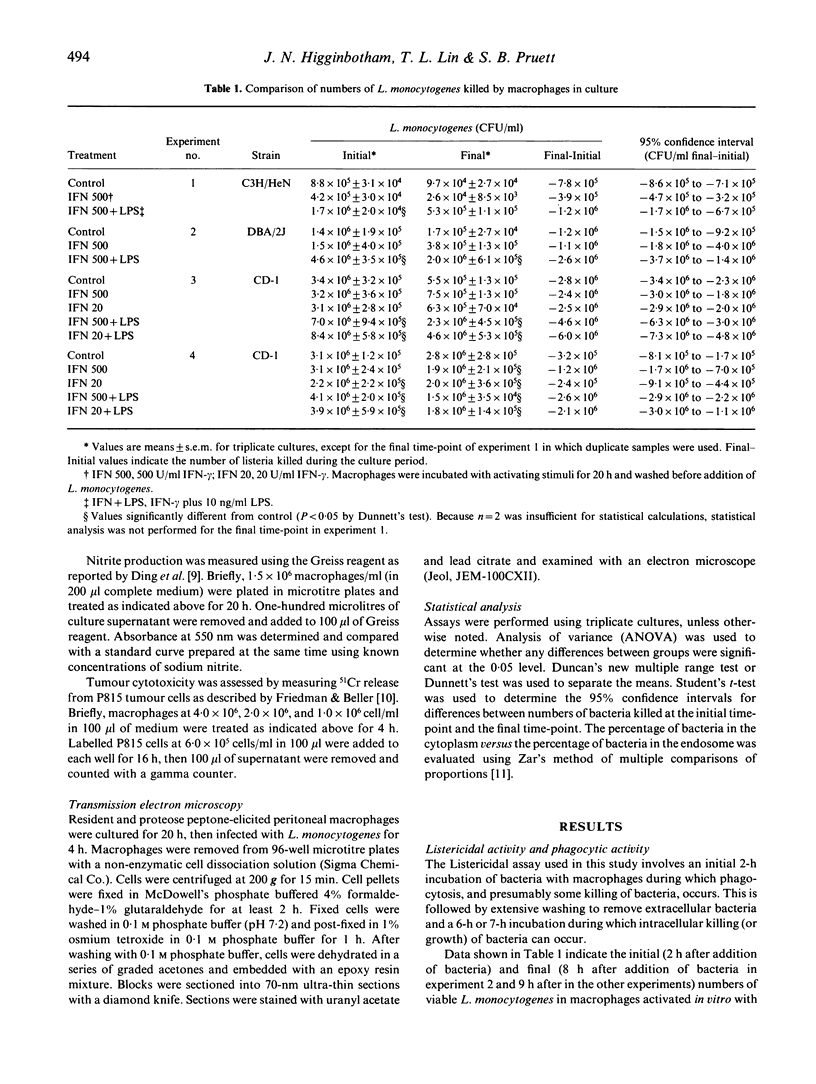
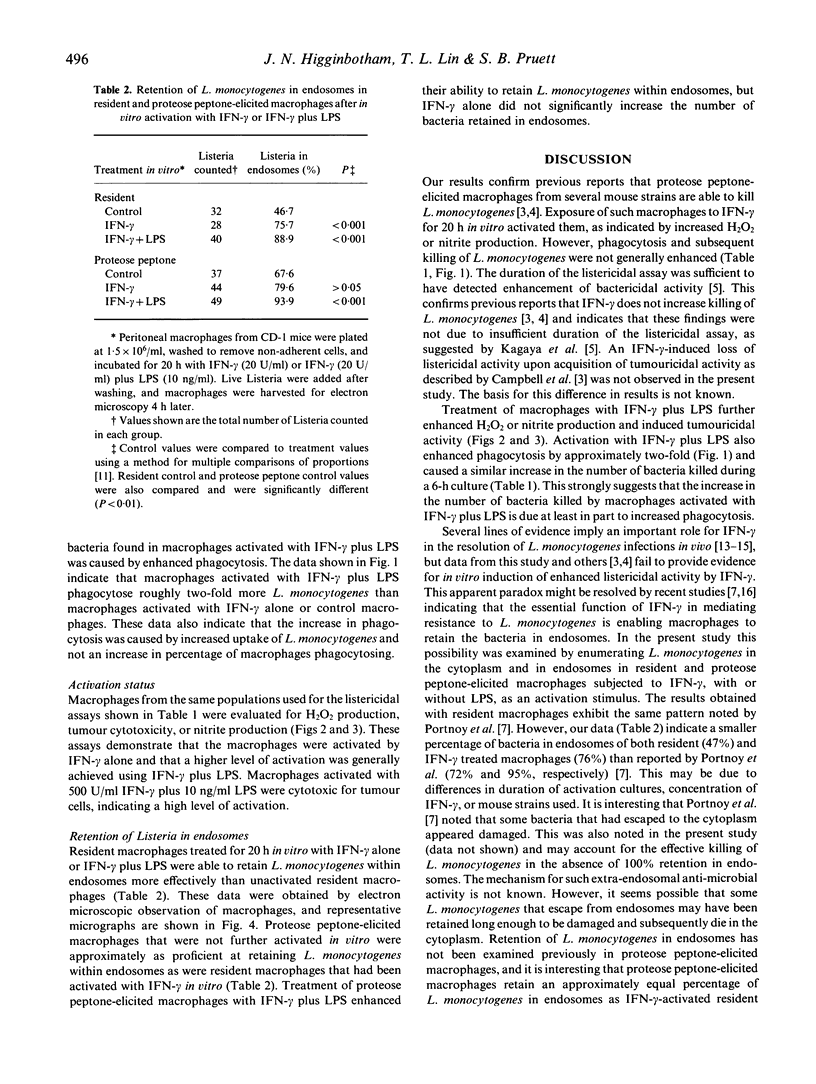
The role of macrophage activation in the killing of L. monocytogenes is unclear. Some studies suggest that activation for enhanced production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates may not be of central importance. Recent data have indicated an important role for interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) induced retention of L. monocytogenes in endosomes. Data from the present study indicate that proteose peptone-elicited macrophages from DBA2/J, CD-1, and C3H/HeN mice are listericidal. Activation of these cells in vitro for 20 h by IFN-gamma (20 or 500 U/ml) increased H2O2 or nitrite production, but did not increase the number of L. monocytogenes killed during a subsequent 6-h or 7-h culture. Incubation of macrophages with IFN-gamma plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) caused greater activation and increased the number of Listeria killed during a 6-h or 7-h culture. However, this seems primarily attributable to enhanced phagocytosis. Proteose peptone-elicited macrophages were significantly more effective than resident macrophages in preventing the escape of L. monocytogenes from endosomes into the cytoplasm. This capability was not significantly enhanced by IFN-gamma in vitro, but was enhanced by IFN-gamma plus LPS. This correlates well with the effects of these activation stimuli on killing of L. monocytogenes by proteose peptone-elicited macrophages. These results indicate that enhanced retention of L. monocytogenes in endosomes is induced by proteose peptone elicitation and that further macrophage activation in vitro by IFN-gamma does not improve listericidal activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. Molecular transductional mechanisms by which IFN gamma and other signals regulate macrophage development. Immunol Rev. 1987 Jun;97:5–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: key components needed in immunity. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Requirement of endogenous interferon-gamma production for resolution of Listeria monocytogenes infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7404–7408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. A., Canono B. P., Cook J. L. Mouse macrophages stimulated by recombinant gamma interferon to kill tumor cells are not bactericidal for the facultative intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1371-1375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F., Pavlov H., Waid C., York J. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: course of listeriosis in resistant or susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. H., Mayer P., Baggiolini M. Stimulation of phagocytosis in bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: correlation with biochemical and functional parameters. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):913–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A., Beller D. I. Simultaneous expression of Ia and cytocidal activity by macrophages, and the consequences for antigen presentation. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):435–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagaya K., Watanabe K., Fukazawa Y. Capacity of recombinant gamma interferon to activate macrophages for Salmonella-killing activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):609–615. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.609-615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaufmann S. H., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Protection of mice against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes by recombinant immune interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):964–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Mizel D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Schreiber R. D., Connelly P., Tilney L. G. Gamma interferon limits access of Listeria monocytogenes to the macrophage cytoplasm. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2141–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran H. T., Cook A. D., Ganas M., Cheers C. Distinction between 'inflammatory' and 'immune' macrophages killing Listeria monocytogenes in murine infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;68(Pt 5):289–297. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dissel J. T., Stikkelbroeck J. J., Michel B. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Inability of recombinant interferon-gamma to activate the antibacterial activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1673–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



