Abstract
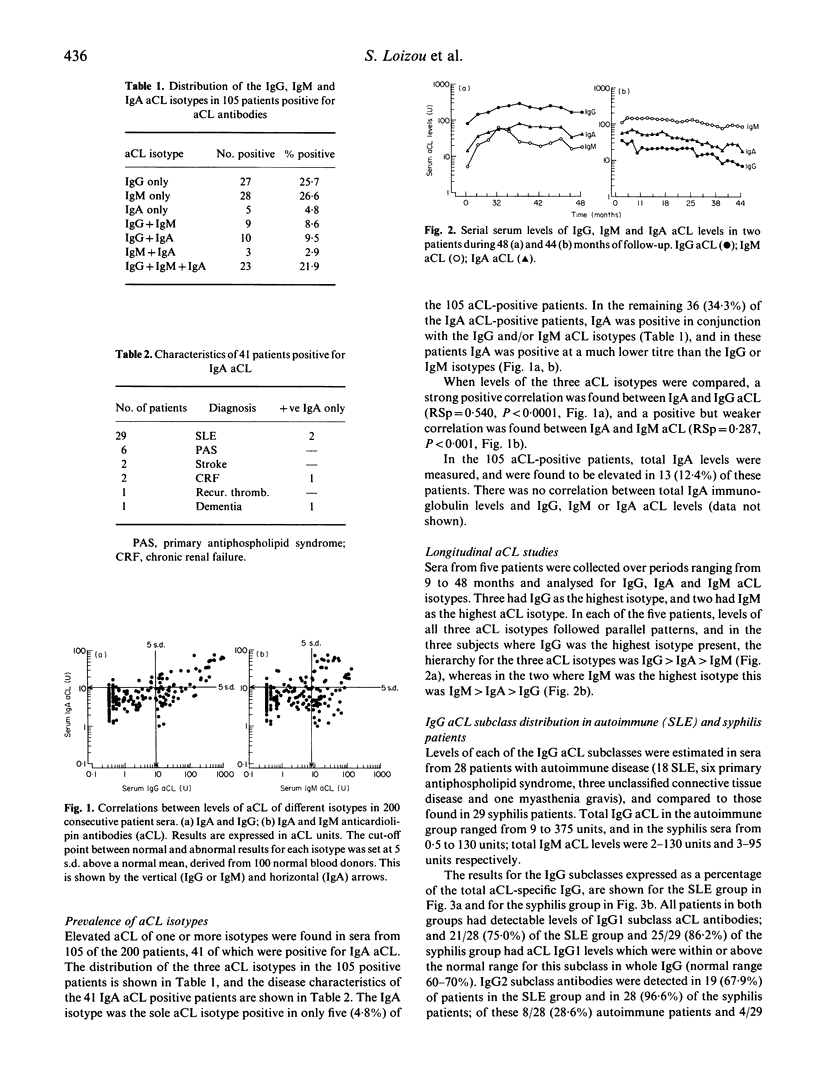
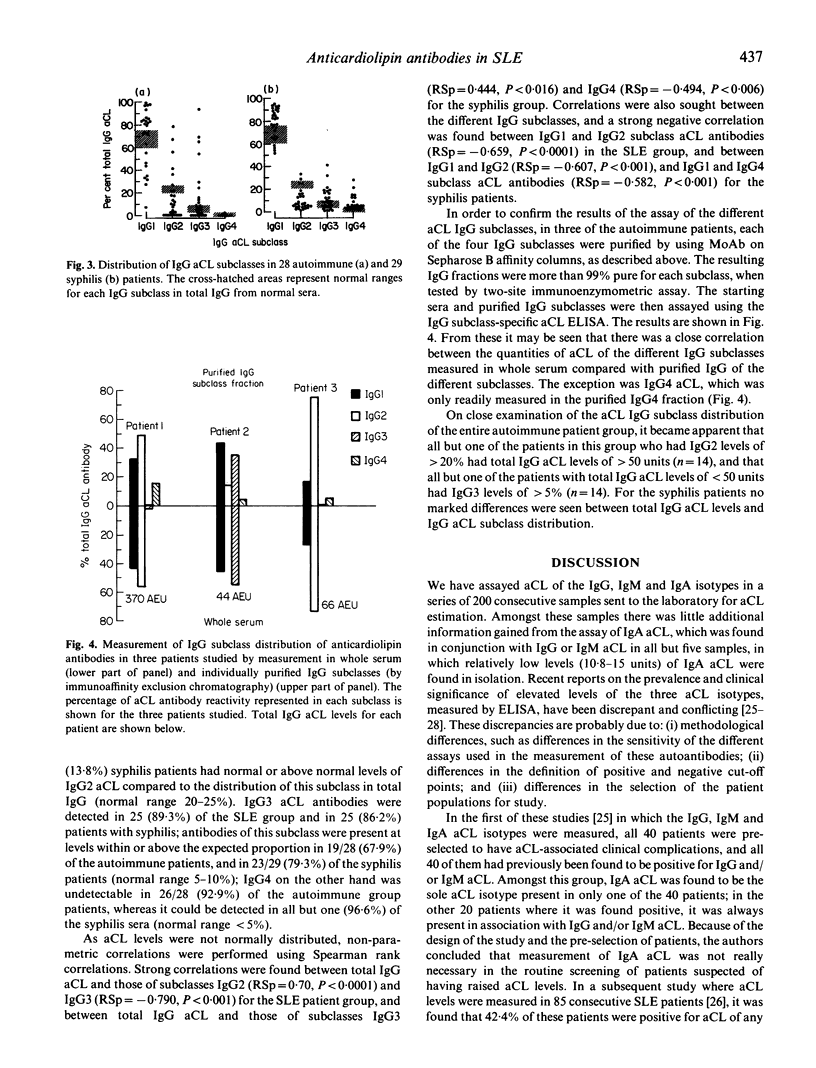
The class and subclass distribution of an antibody response may give insight into the stimulating mechanism and likely effector functions. IgA, IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) were quantified in a consecutive series of 200 samples sent to an autoimmune serology laboratory to determine the relationships between aCL responses of each of these antibody classes and, in particular, whether there was any utility in the measurement of IgA aCL. Positive results for one of the three aCL isotypes were found in 105 samples (53%), and in 41 samples IgA aCL was detected (21%). However, amongst these unselected samples, little additional information was obtained by measurement of IgA aCL, which was found in conjunction with IgM or IgG aCL in all but five samples, and in these the isolated elevation of IgA aCL was only slight, and showed no disease specificity. The levels of each of the four IgG subclasses of aCL were measured in a subgroup of serum samples from 28 patients with autoimmune disease and from 29 patients with syphilis. Amongst the SLE patients IgG1 and IgG3 aCL were the predominant IgG subclasses, consistent with an antigen-driven, T cell-dependent antibody response. However, a subgroup of eight of the autoimmune subjects had predominant elevation of IgG2 aCL, possibly implying a role for T cell-independent antibody production to cardiolipin. Amongst the syphilis patients IgG1 and IgG3 aCL were also the predominant subclasses of aCL but IgG4 aCL were also detected in the majority of subjects, consistent with prolonged antigenic stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Delezé M., Oria C. V., Sánchez-Guerrero J., Gómez-Pacheco L., Cabiedes J., Fernández L., Ponce de León S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective analysis of 500 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Nov;68(6):353–365. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198911000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvieux J., Roussel B., Ponard D., Colomb M. G. Reactivity patterns of anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus sera in relation to erythrocyte binding and complement activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):466–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M., Plikaytis B. D., Wells T. W., Ramirez R. M., Carlone G. M., Chilmonczyk B. A., Reimer C. B. Two-site immunoenzymometric assays for serum IgG subclass infant/maternal ratios at full-term. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleze M., Alarcón-Segovia D., Valdes-Macho E., Oria C. V., Ponce de Leon S. Relationship between antiphospholipid antibodies and recurrent fetal loss in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and apparently healthy women. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;16(6):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delezé M., Oria C. V., Alarcón-Segovia D. Occurrence of both hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenic purpura (Evans' syndrome) in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;15(4):611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostal-Johnson D., Rote N. S., Branch D. W. IgG1 and IgG2 are the predominant subclasses of antiphospholipid antibody in women with the lupus anticoagulant. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;54(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. Y., Loizou S., Boey M. L., Walport M. J. Anticardiolipin antibodies, haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Jul;31(7):453–455. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.7.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton G., Winer J. B., Cameron J. S., Hughes R. A. Severe Guillain-Barré syndrome: an association with IgA anti-cardiolipin antibody in a series of 92 patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Aug;19(1-2):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Lockshin M. D., Hughes G. R., Elkon K. B. IgG subclass and light chain distribution of anticardiolipin and anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Apr;47(4):286–290. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.4.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Chan J. K., Asherson R. A., Aber V. R., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Predictive value of the anticardiolipin antibody test. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Nov;146(11):2153–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalunian K. C., Peter J. B., Middlekauff H. R., Sayre J., Ando D. G., Mangotich M., Hahn B. H. Clinical significance of a single test for anti-cardiolipin antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1988 Nov;85(5):602–608. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. A., Wood K. J., Bernstein R. M., Holt P. J., Pumphrey R. S. An IgG subclass imbalance in connective tissue disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Jul;47(7):536–541. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.7.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M., Simonian N. Lupus anticoagulants, anticardiolipin antibodies, and cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1989 Feb;20(2):225–229. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. H., Wong K. L., Lau C. P., Wong C. K., Liu H. W. Association between antiphospholipid antibodies and cardiac abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1990 Oct;89(4):411–419. doi: 10.1007/BF01453668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Gharavi A. E., Sammaritano L. R., Habina L., Qamar T., Lockshin M. D. Characteristics of IgG antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and syphilis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Aug;17(8):1036–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., Byron M. A., Englert H. J., David J., Hughes G. R., Walport M. J. Association of quantitative anticardiolipin antibody levels with fetal loss and time of loss in systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1988 Jul;68(255):525–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., Mackworth-Young C. G., Cofiner C., Walport M. J. Heterogeneity of binding reactivity to different phospholipids of antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and with syphilis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou S., McCrea J. D., Rudge A. C., Reynolds R., Boyle C. C., Harris E. N. Measurement of anti-cardiolipin antibodies by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): standardization and quantitation of results. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):738–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love P. E., Santoro S. A. Antiphospholipid antibodies: anticardiolipin and the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and in non-SLE disorders. Prevalence and clinical significance. Ann Intern Med. 1990 May 1;112(9):682–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-9-682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Walport M. J. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome: features of patients with raised anticardiolipin antibodies and no other disorder. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 May;48(5):362–367. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.5.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Moore D. D., Galland G. G., Wells T. W., Black C. M., McDougal J. S. Evaluation of thirty-one mouse monoclonal antibodies to human IgG epitopes. Hybridoma. 1984 Fall;3(3):263–275. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Tang F. L., Chan E. K., Pollard K. M., Tsay G., Tan E. M. IgG subclasses of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, and drug-induced autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2528–2534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M., Rothfield N. The gammaG subclass of antinuclear and antinucleic acid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):174–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden N., Wilson P., Pumphrey R. Anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematous. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Jan;48(1):80–82. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.1.80-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi A., Koike T., Ichikawa K., Shimada K., Takabayashi K., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. IgG subclass distribution of anticardiolipin antibody in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;15(12):1764–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaarala O., Palosuo T., Kleemola M., Aho K. Anticardiolipin response in acute infections. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Oct;41(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Nash Z. D., Carinhas R., Musher D. M., Baughn R. E. Immunoglobulin class and subclass restriction of autoimmune responses in secondary syphilis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):381–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Black C. M., Cohen S. B., Tomlinson R., Banga J. P., Reimer C. B. Affinity purification of IgG subclasses and the distribution of thyroid auto-antibody reactivity in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jul;30(1):73–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Cohen S. The IgG subclass distribution of thyroid autoantibodies. Immunol Lett. 1986 Nov 3;13(6):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler T. H., Henschel T. A., Kalies I., Baenkler H. W., Skvaril F., Kalden J. R. Constant isotype pattern of anti-dsDNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):434–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Jefferis R., Eyquem A. IgG subclass distribution of autoantibodies to DNA and to nuclear ribonucleoproteins in autoimmune diseases. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):595–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


