Abstract
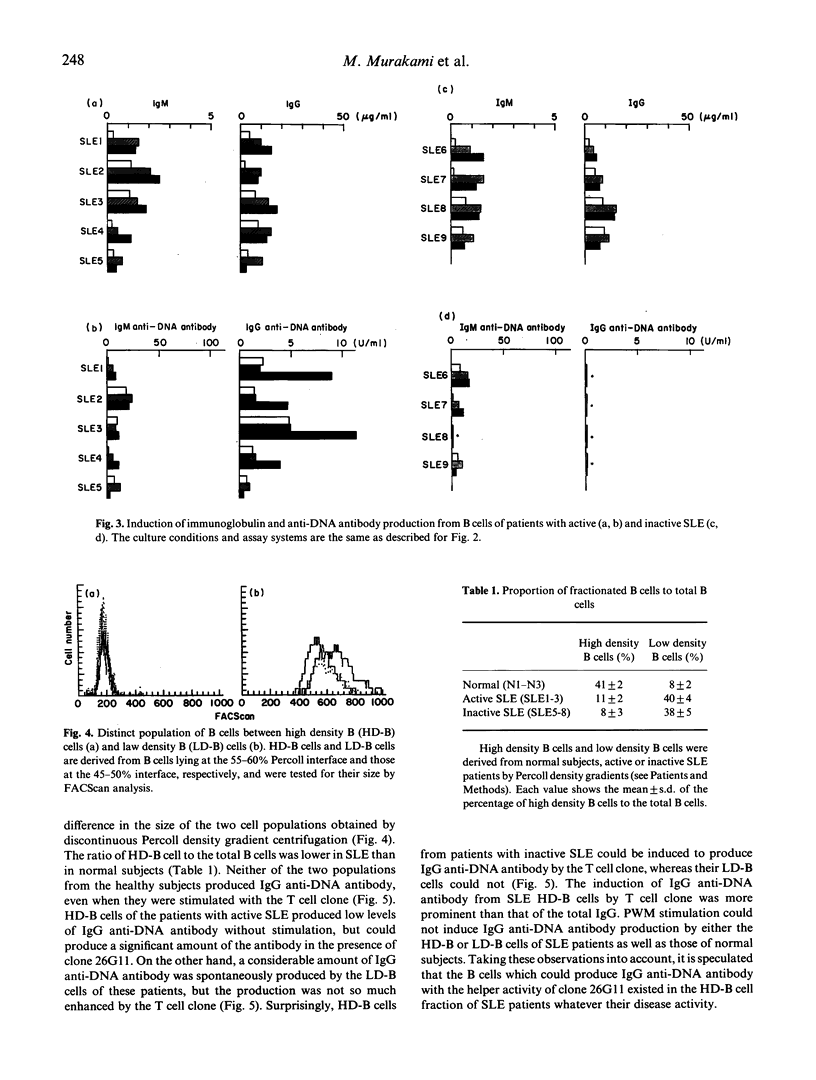
An HLA-DR restricted T cell clone (26G11) which recognized a lymphoid cell-derived autoantigen associated with DR4 molecule was shown to induce not only autologous but also allogenic DR4+ B cells to produce large amounts of antibodies of the IgG and IgM classes. Using the helper activity of this clone, we investigated the mechanism of anti-DNA antibody production in DR-matched patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). When cultured with 26G11 cells, B cells from DR-matched normal control subjects produced large amounts of IgM anti-DNA antibody, but did not produce IgG anti-DNA antibody which is thought to have a pathological role in SLE. In contrast, B cells from DR-matched patients with active SLE spontaneously produced a fairly large amount of IgG anti-DNA antibody, and the production was augmented by the T cell clone. Little IgG anti-DNA antibody was produced by the B cells of patients with inactive SLE in either the presence or absence of T cell clone. We next fractionated B cells into low density B (LD-B) and high density B (HD-B) cells by centrifugation on discontinuous Percoll density gradients. IgG anti-DNA antibody was spontaneously produced by LD-B cells of active SLE patients but not by those either of inactive SLE patients or normal controls. On the other hand, although IgG anti-DNA antibody was not spontaneously produced by the HD-B cells of both active and inactive SLE patients, it could easily be induced by their culture with the T cell clone. Our results clearly show the existence of IgG anti-DNA antibody-producing B cells in the peripheral blood of SLE patients irrespective of their disease activity and suggest that autoreactive T cells may play a pathogenic role in SLE through the induction of autoantibody production.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hahn B. H. Mechanisms of T and B cell collaboration in the in vitro production of anti-DNA antibodies in the NZB/NZW F1 murine SLE model. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3185–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagg M. K., Levitt D. Human B-lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Differentiation of density-separated B lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Oct;21(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Patel H., Berry D. Induction of a cationic shift in IgG anti-DNA autoantibodies. Role of T helper cells with classical and novel phenotypes in three murine models of lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1252–1268. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Segond P., Galanaud P., Wallon C., Massias P., Dormont J. Depressed primary in vitro antibody response in untreated systemic lupus erythematosus. T helper cell defect and lack of defective suppressor cell function. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):141–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI109827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan A., Needleman B. W., Hodes R. J. Function of autoreactive T cells in immune responses. Immunol Rev. 1990 Aug;116:15–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D. Immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Annu Rev Med. 1974;25:149–164. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.25.020174.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan S., Zordan T., Tsokos G. C., Datta S. K. Pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody-inducing T helper cell lines from patients with active lupus nephritis: isolation of CD4-8- T helper cell lines that express the gamma delta T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7020–7024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Tan E. M. An improved ELISA for anti-native DNA by elimination of interference by anti-histone antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 28;63(3):359–366. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki O., Saeki Y., Kishimoto S. Spontaneous immunoglobulin A secretion and lack of mitogen-responsive B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1865–1870. doi: 10.1172/JCI112180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainis K., Datta S. K. CD4+ T cell lines with selective patterns of autoreactivity as well as CD4- CD8- T helper cell lines augment the production of idiotypes shared by pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies in the NZB x SWR model of lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2215–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Amaki S., Takei M., Karasaki M., Amaki I. Impaired B cell proliferation by Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Sep;28(9):1008–1015. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar S., Tsokos G. C., Datta S. K. T cell receptor alpha/beta expressing double-negative (CD4-/CD8-) and CD4+ T helper cells in humans augment the production of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies associated with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Steinberg A. D. Autoimmunity--a perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:175–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., James S. P. Immunoregulatory function of human autoreactive T-cell lines and clones. Immunol Rev. 1990 Aug;116:117–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Kumagai S., Ota M., Inoko H., Tsuji K., Imura H. Demonstration of the requirement for self antigen in the activation of autoreactive T cells. Int Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(2):119–124. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Kumagai S., Umehara H., Iwai K., Sorachi K., Imura H. HLA-DQ-specific autoreactive T cell clone with helper and cytotoxic functions. Immunol Lett. 1990 Dec;26(3):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90157-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Ueda Y., Sakane T. Differential mechanism for differentiation into immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human resting B lymphocyte subsets isolated on the basis of cell density. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):261–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI113304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):226–235. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Schaefer M. E., Finkelman F. D., Scher I., Farrar J., Mond J. J. T cell-derived B cell growth factor(s) can induce stimulation of both resting and activated B cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):369–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Faiferman I., Koffler D. Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antinative DNA antibody with glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):90–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Seaman W. E. Successful treatment of autoimmunity in NZB/NZW F1 mice with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):378–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


