Abstract
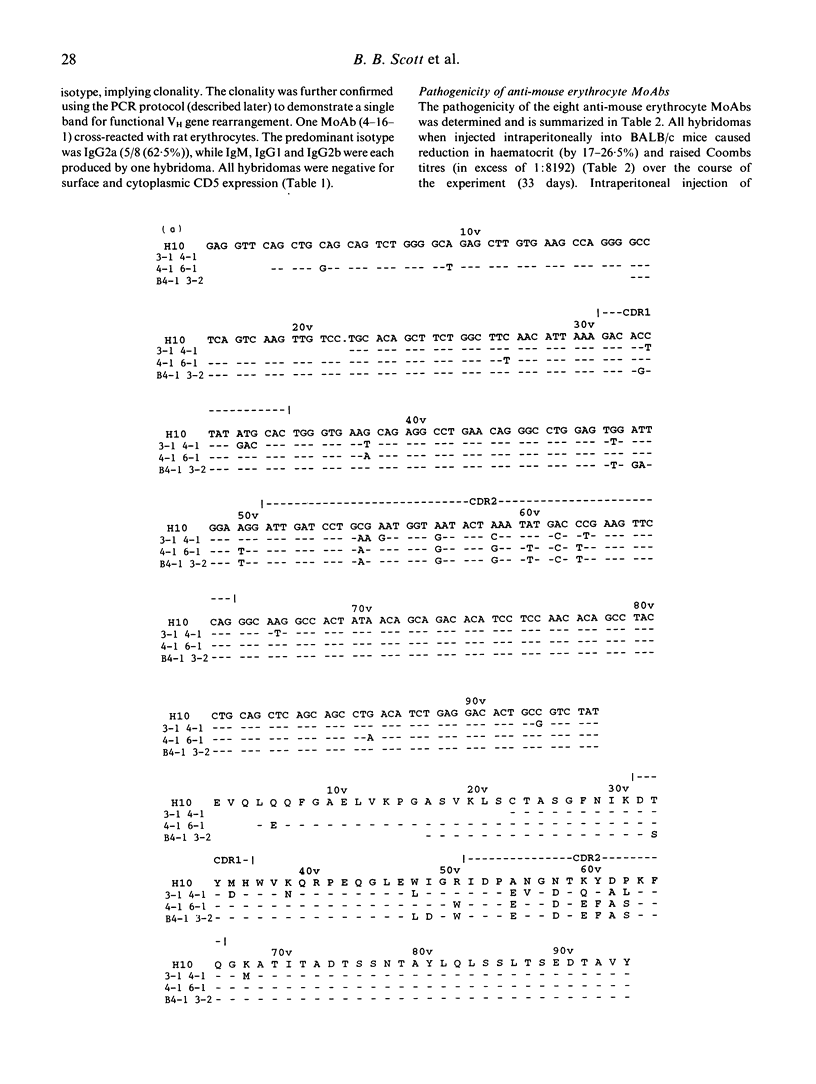
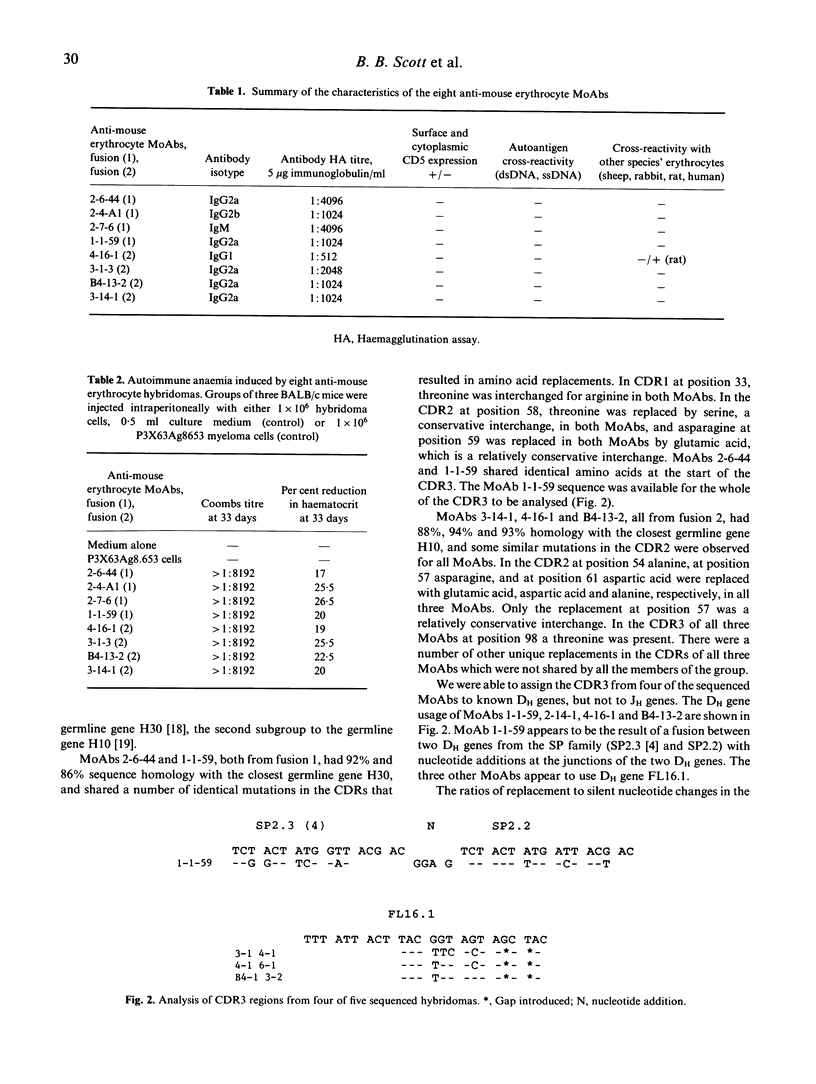
The New Zealand black (NZB) mouse strain is genetically predisposed to develop, at approximately 6 months of age, a spontaneous and severe autoimmune anaemia caused by production of pathogenic anti-mouse erythrocyte autoantibodies. In order to investigate the molecular mechanisms which lead to anti-mouse erythrocyte autoantibody production we have generated eight anti-mouse erythrocyte MoAbs producing hybridomas from splenocytes of 9- and 12-month-old NZB with spontaneous autoimmune anaemia. IgG2a was the predominant isotype, while IgM, IgG1 and IgG2b were each produced by one hybridoma cell line. All anti-mouse erythrocyte MoAbs were characterized for their antigen specificities. None of the MoAbs cross-reacted with ss- or dsDNA or with other species' erythrocytes, with the exception of one MoAb which cross-reacted with rat erythrocytes. None of the eight hybridomas was demonstrated to express surface or cytoplasmic CD5, suggesting that they derived from CD5- B lymphocytes. All hybridomas when implanted intraperitoneally into BALB/c mice caused anaemia. In order to define the genetic basis and investigate the molecular mechanisms resulting in pathogenic anti-mouse erythrocyte autoantibody production, the pattern of immunoglobulin variable region gene use has been studied. Five of the eight MoAbs whose IgVH genes were sequenced all have functionally rearranged genes from the VH J558 gene family. There is evidence for somatic point mutations in the complementarity-determining regions (CDR) of the IgVH genes in all of these five MoAbs when compared with the closest known germline gene. We suggest that these nucleotide sequence changes are likely to reflect selection by an antigen-driven mechanism. Furthermore, the data indicate that pathogenic anti-mouse erythrocytes are not derived from 'natural' autoantibodies.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caulfield M. J., Stanko D. A pathogenic monoclonal antibody, G8, is characteristic of antierythrocyte autoantibodies from Coombs'-positive NZB mice. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2068–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumano A., Rajewsky K. Clonal recruitment and somatic mutation in the generation of immunological memory to the hapten NP. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2459–2468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane M., Norton J. D. Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region family usage is independent of tumor cell phenotype in human B lineage leukemias. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2209–2217. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Krawinkel U., Winter E., Rajewsky K. VH-gene expression in murine lipopolysaccharide blasts distributes over the nine known VH-gene groups and may be random. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1154–1156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchosal M. A., Kofler R., Balderas R. S., Aguado M. T., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genetic diversity of murine rheumatoid factors. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1737–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidanza V., Mayer R., Zaghouani H., DiLiberti M. A., Bona C. A. Autoantibodies, LY-1, and immunoglobulin V gene expression in hybridomas obtained from young and from old New Zealand black mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):711–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. M., Berek C., Kaartinen M., Milstein C. Somatic mutation and the maturation of immune response to 2-phenyl oxazolone. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):271–275. doi: 10.1038/312271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K. Development and physiology of Ly-1 B and its human homolog, Leu-1 B. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:53–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M. Recovery of DNA from agarose gels using liquid nitrogen. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):137–137. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Noonan D. J., Levy D. E., Wilson M. C., Møller N. P., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genetic elements used for a murine lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are closely related to those for antibodies to exogenous antigens. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):805–815. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manheimer-Lory A. J., Monestier M., Bellon B., Alt F. W., Bona C. A. Fine specificity, idiotypy, and nature of cloned heavy-chain variable region genes of murine monoclonal rheumatoid factor antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8293–8297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monestier M., Manheimer-Lory A., Bellon B., Painter C., Dang H., Talal N., Zanetti M., Schwartz R., Pisetsky D., Kuppers R. Shared idiotypes and restricted immunoglobulin variable region heavy chain genes characterize murine autoantibodies of various specificities. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):753–759. doi: 10.1172/JCI112637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi R., Güssow D. H., Jones P. T., Winter G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Kearney J. F., Chang S. P., Hood L. E. Developmentally controlled expression of immunoglobulin VH genes. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1597–1601. doi: 10.1126/science.3975629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radoux V., Chen P. P., Sorge J. A., Carson D. A. A conserved human germline V kappa gene directly encodes rheumatoid factor light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2119–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reininger L., Ollier P., Poncet P., Kaushik A., Jaton J. C. Novel V genes encode virtually identical variable regions of six murine monoclonal anti-bromelain-treated red blood cell autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):316–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reininger L., Shibata T., Ozaki S., Shirai T., Jaton J. C., Izui S. Variable region sequences of pathogenic anti-mouse red blood cell autoantibodies from autoimmune NZB mice. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):771–777. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff C., Milili M., Fougereau M. Functional and pseudogenes are similarly organized and may equally contribute to the extensive antibody diversity of the IgVHII family. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1225–1230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff C., Milili M., Hue I., Rudikoff S., Fougereau M. Genetic basis for expression of the idiotypic network. One unique Ig VH germline gene accounts for the major family of Ab1 and Ab3 (Ab1') antibodies of the GAT system. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):573–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Berney T., Reininger L., Chicheportiche Y., Ozaki S., Shirai T., Izui S. Monoclonal anti-erythrocyte autoantibodies derived from NZB mice cause autoimmune hemolytic anemia by two distinct pathogenic mechanisms. Int Immunol. 1990;2(12):1133–1141. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.12.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Aucoin A. H., Pisetsky D. S., Weigert M. G. Structure and function of anti-DNA autoantibodies derived from a single autoimmune mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Marshak-Rothstein A., Wolfowicz C. B., Rothstein T. L., Weigert M. G. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):805–811. doi: 10.1038/328805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Nemazee D. A., Sato V. L., Van Snick J., Carson D. A., Weigert M. G. Variable region sequences of murine IgM anti-IgG monoclonal autoantibodies (rheumatoid factors). A structural explanation for the high frequency of IgM anti-IgG B cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):407–427. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Nemazee D., van Snick J., Weigert M. Variable region sequences of murine IgM anti-IgG monoclonal autoantibodies (rheumatoid factors). II. Comparison of hybridomas derived by lipopolysaccharide stimulation and secondary protein immunization. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):970–987. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W., Jr, Barrett K. J. Eleven MRL-lpr/lpr anti-DNA autoantibodies are encoded by genes from four VH gene families: a potentially biased usage of VH genes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2323–2331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W., Jr, Maruya A., Barrett K. J. The heavy chain genes of a lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are encoded in the germ line of a nonautoimmune strain of mouse and conserved in strains of mice polymorphic for this gene locus. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3139–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Sugiyama H., Oka Y., Kishimoto S. Estimation of D segment usage in initial D to JH joinings in a murine immature B cell line. Preferential usage of DFL16.1, the most 5' D segment and DQ52, the most JH-proximal D segment. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):4053–4059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutter A., Brodeur P., Shlomchik M., Riblet R. Structure, map position, and evolution of two newly diverged mouse Ig VH gene families. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3215–3223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Desiderio S. V., Paskind M., Kearney J. F., Baltimore D., Alt F. W. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal VH gene segments in pre-B-cell lines. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):727–733. doi: 10.1038/311727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


