Abstract
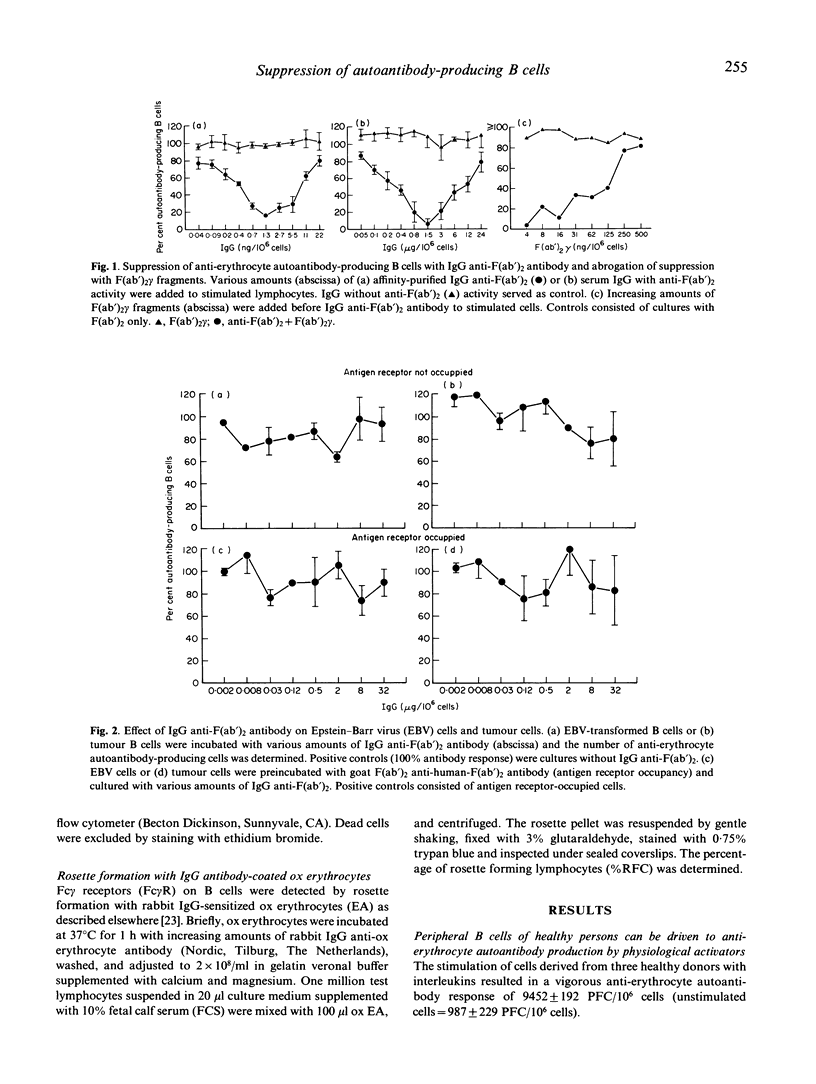
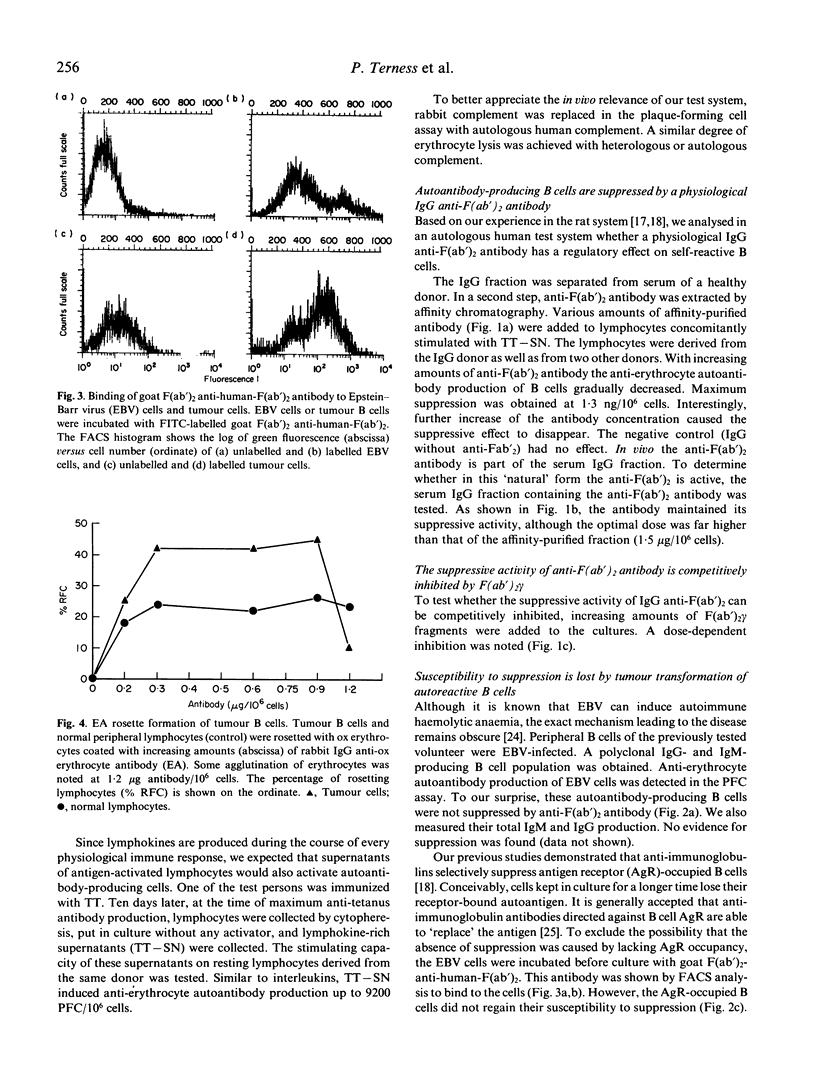
We showed previously that broadly reactive IgG anti-immunoglobulin autoantibodies produced by rats during the immune response suppress the B cell response. We report here on the effect of a similar human antibody on self-reactive human B cells. IgG anti-F(ab')2 was added to cultures of anti-erythrocyte autoantibody-producing B cells derived from healthy donors. A dose-dependent suppression of the antibody response was obtained (maximum at 1.3 ng IgG/10(6) cells). This effect was competitively inhibited by F(ab')2 gamma. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia can be caused by chronic monoclonal B cell proliferation. To reproduce this condition in vitro we immortalized B cells with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and raised a B cell population with anti-erythrocyte autoantibody activity. These cells were electrically fused with CB-F7 tumour cells and an IgG1 cold-reactive anti-erythrocyte autoantibody-producing B cell line was established. Surprisingly, the tumour cells were not suppressed by IgG anti-F(ab')2. It is known that anti-immunoglobulins selectively suppress antigen-receptor (AgR)-occupied B cells by a Fc gamma-receptor (Fc gamma R)-mediated mechanism. To occupy their AgR, we preincubated the tumour cells with anti-AgR antibody. In spite of this, their susceptibility to suppression was not restored. As shown by rabbit IgG-sensitized ox erythrocyte (EA)-rosetting, this refractoriness was not due to a loss of Fc gamma R. Our experiments delineate a mechanism of peripheral B cell suppression to autoantigens, and show a way of escape from control relevant for the pathogenesis of autoimmune haemolytic anaemia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter N. H., Malley A., Mandy W. J. Natural antiglobulin antibodies in primate sera. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):502–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Immunology. Tolerance: a second mechanism. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):340–341. doi: 10.1038/342340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Mitchison N. A. The mechanism of immunological paralysis. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:129–181. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R. W., Jahn S., Grunow R. Development of specific human mab's by a small scale electrofusion technique: the influence of some physical and chemical factors on hybridoma yield of human peripheral blood lymphocytes XCB-F7 fusions. Allerg Immunol (Leipz) 1989;35(2):123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Adelstein S., Basten A. The need for central and peripheral tolerance in the B cell repertoire. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1373–1379. doi: 10.1126/science.2356469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Brink R., Adams E. Breakdown of self-tolerance in anergic B lymphocytes. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):532–536. doi: 10.1038/352532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Adelstein S., Lavoie T. B., Smith-Gill S. J., Brink R. A., Pritchard-Briscoe H., Wotherspoon J. S., Loblay R. H., Raphael K. Altered immunoglobulin expression and functional silencing of self-reactive B lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):676–682. doi: 10.1038/334676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Jorgensen H., Brink R. A., Basten A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):385–391. doi: 10.1038/342385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Crosbie J., Brink R., Kantor A. B., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination from peripheral lymphoid tissues of self-reactive B lymphocytes recognizing membrane-bound antigens. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):765–769. doi: 10.1038/353765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandy W. J., Fudenberg H. H., Lewis F. B. A new serum factor in normal rabbits. I. Identification and characterization. J Immunol. 1965 Sep;95(3):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasu H., Chia D. S., Knutson D. W., Barnett E. V. Naturally occurring human antibodies to the F(ab')2 portion of IgG. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):378–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Sato V. L. Induction of rheumatoid antibodies in the mouse. Regulated production of autoantibody in the secondary humoral response. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):529–545. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Immunologic tolerance: collaboration between antigen and lymphokines. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):147–153. doi: 10.1126/science.2526369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTERLAND C. K., HARBOE M., KUNKEL H. G. Anti-gamma-globulin factors in human sera revealed by enzymatic splitting of anti-Rh antibodies. Vox Sang. 1963 Mar-Apr;8:133–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. Induction and suppression of polyclonal antibody responses by anti-Ig reagents and antigen-nonspecific helper factors: a comparison of the effects of anti-Fab, anti-IgM, and anti IgD on murine B cells. Immunol Rev. 1980;52:115–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Brenig C. Paralysis to serum albumins in T and B lymphocytes in mice. Dose dependence, specificity and kinetics of escape. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Feb;4(2):120–125. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. Cold agglutination. Antibodies and antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Jan;2(2):266–280. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosnek E., Lanzavecchia A. Efficient and selective presentation of antigen-antibody complexes by rheumatoid factor B cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):487–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Dembić Z., Morahan G., Miller J. F., Bürki K., Nemazee D. Peripheral deletion of self-reactive B cells. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):308–311. doi: 10.1038/354308a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Brouet J. C. Antibody activity of human myeloma globulins. Semin Hematol. 1973 Apr;10(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Aucoin A. H., Pisetsky D. S., Weigert M. G. Structure and function of anti-DNA autoantibodies derived from a single autoimmune mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieckmann D. G. The use of anti-immunoglobulins to induce a signal for cell division in B lymphocytes via their membrane IgM and IgD. Immunol Rev. 1980;52:181–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestris F., Bankhurst A. D., Searles R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Studies of anti-F(ab')2 antibodies and possible immunologic control mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Dec;27(12):1387–1396. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süsal C., Guo Z., Terness P., Padányi A., Petrányi G., Opelz G. Induction of anti-F(ab)2 gamma antibodies by buffy coat transfusions and their effect in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1990 Aug;22(4):1893–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terness P., Berteli A., Süsal C., Opelz G. Regulation of antibody response by an IgG-anti-Ig autoantibody occurring during alloimmunization. II. Selective inactivation of antigen receptor-occupied B cells. Transplantation. 1992 Jul;54(1):92–96. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199207000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terness P., Opelz G. Regulation of antibody response by an IgG-anti-Ig autoantibody occurring during alloimmunization. I. A few IgG molecules inactivate one B cell. Transplantation. 1992 Jul;54(1):88–91. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199207000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller M., Richard A. J., Mallory J. Immunochemical and serological studies of enzymaatically fragmented human IgG globulins. II. Hydrolysis with subtilisin, elastase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin. Immunochemistry. 1969 Mar;6(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Immunological unresponsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:61–122. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Fong S., Vaughan J., Carson D. Increased frequency of rheumatoid factor precursor B lymphocytes after immunization of normal adults with tetanus toxoid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):299–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


