Abstract
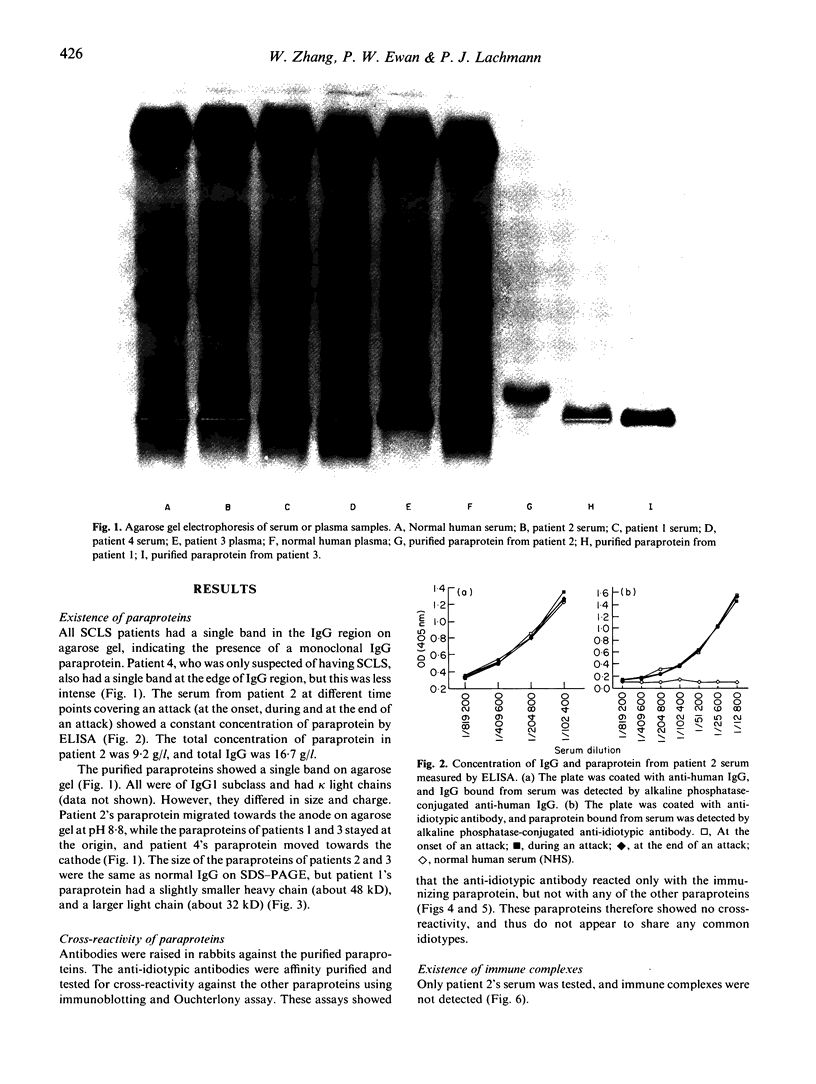
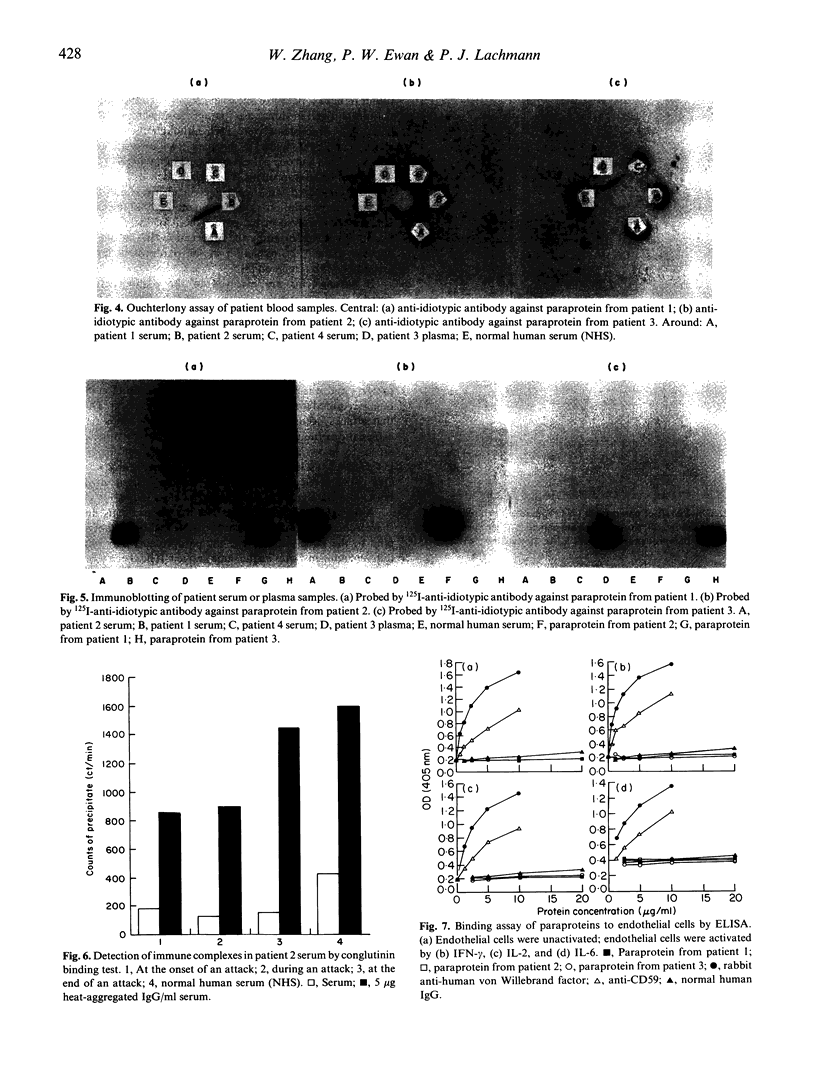
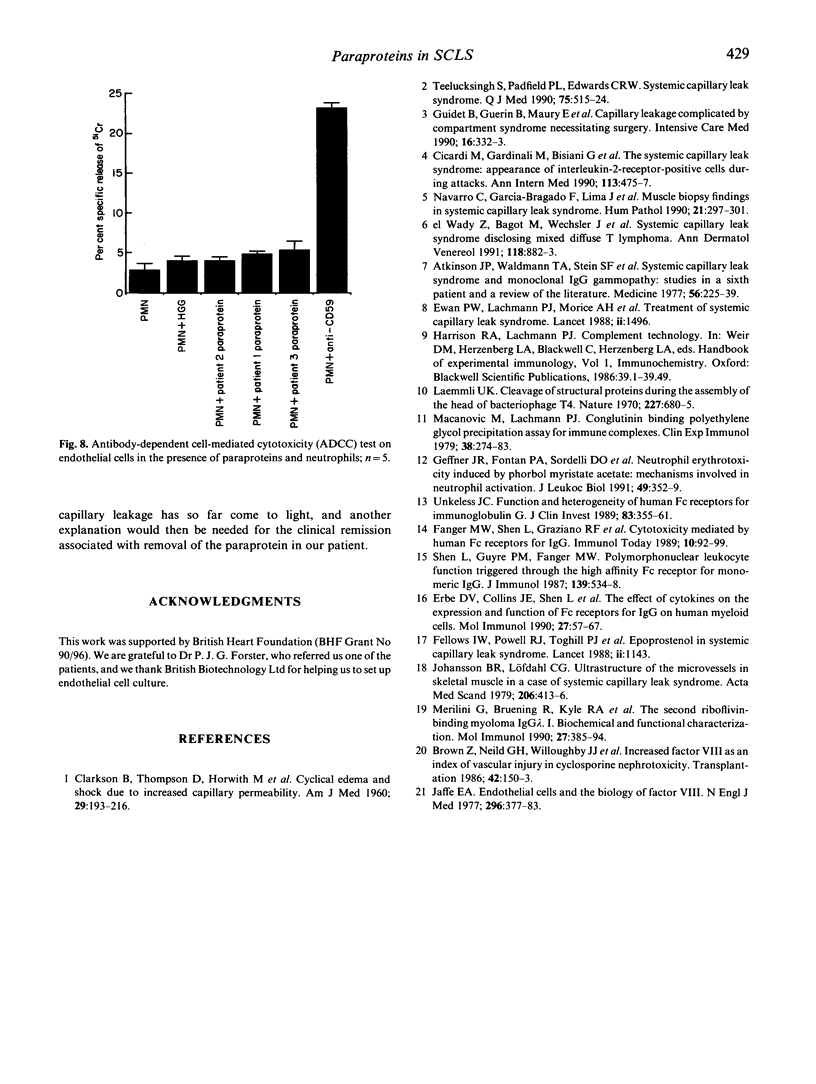
Systemic capillary leak syndrome (SCLS) is a rare disease characterized by episodes of collapse due to rapid transfer of considerable volumes of plasma from the intravascular to the extravascular compartment. The pathogenesis of this disease is unknown. The diagnosis is made largely on clinical grounds, and investigations are unhelpful. The only consistent abnormality is that an IgG paraprotein is found in most patients, raising the possibility that the paraprotein may be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. Reduction of the paraprotein level in our patient was associated with remission. Blood samples from three SCLS patients and one probable SCLS have been studied. All patients had monoclonal IgG paraproteins. The purified paraproteins were all of IgG1 subclass and had kappa light chains. However, they differed in size and charge. Antibodies against each of the paraproteins were raised in rabbits. Affinity-purified anti-idiotypic antibodies were tested for cross-reactivity against the other paraproteins using immunoblotting and Ouchterlony assay. These assays showed that the anti-idiotypic antibodies reacted only with the immunizing paraprotein and not with any of the other paraproteins, i.e. that the paraproteins do not share a common idiotype. Paraproteins did not bind to cultured endothelial cells, either unactivated or following activation with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), IL-2 or IL-6. In addition, we were unable to demonstrate any cytotoxicity towards cultured human endothelial cells by paraprotein alone, or in the presence of neutrophils (pronounced neutrophilia being a feature of attacks). The relationship between the paraproteins and the disease remains unclear. It is likely that additional, as yet unidentified, factors are required for the paraprotein to lead to capillary leak.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., Waldmann T. A., Stein S. F., Gelfand J. A., Macdonald W. J., Heck L. W., Cohen E. L., Kaplan A. P., Frank M. M. Systemic capillary leak syndrome and monoclonal IgG gammopathy; studies in a sixth patient and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 May;56(3):225–239. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197705000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown Z., Neild G. H., Willoughby J. J., Somia N. V., Cameron S. J. Increased factor VIII as an index of vascular injury in cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Transplantation. 1986 Aug;42(2):150–153. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198608000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON B., THOMPSON D., HORWITH M., LUCKEY E. H. Cyclical edema and shock due to increased capillary permeability. Am J Med. 1960 Aug;29:193–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicardi M., Gardinali M., Bisiani G., Rosti A., Allavena P., Agostoni A. The systemic capillary leak syndrome: appearance of interleukin-2-receptor-positive cells during attacks. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 15;113(6):475–477. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-6-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbe D. V., Collins J. E., Shen L., Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. The effect of cytokines on the expression and function of Fc receptors for IgG on human myeloid cells. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jan;27(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90060-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Shen L., Graziano R. F., Guyre P. M. Cytotoxicity mediated by human Fc receptors for IgG. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90234-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows I. W., Powell R. J., Toghill P. J., Williams T. J., Cohen G. F. Epoprostenol in systemic capillary leak syndrome. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1143–1143. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90563-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffner J. R., Fontán P. A., Sordelli D. O., Isturiz M. A. Neutrophil erythrotoxicity induced by phorbol myristate acetate: mechanisms involved in neutrophil activation. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):352–359. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidet B., Guerin B., Maury E., Offenstadt G., Amstutz P. Capillary leakage complicated by compartment syndrome necessitating surgery. Intensive Care Med. 1990;16(5):332–333. doi: 10.1007/BF01706361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Endothelial cells and the biology of factor VIII. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):377–383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702172960707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. R., Löfdahl C. G. Ultrastructure of the microvessels in skeletal muscle in a case of systemic capillary leak syndrome. Acta Med Scand. 1979;206(5):413–416. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb13537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macanovic M., Lachmann P. J. Conglutinin binding polyethylene glycol precipitation assay for immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):274–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlini G., Bruening R., Kyle R. A., Osserman E. F. The second riboflavin-binding myeloma IgG lambdaDOT. I. Biochemical and functional characterization. Mol Immunol. 1990 May;27(5):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90162-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro C., García-Bragado F., Lima J., Fernández J. M. Muscle biopsy findings in systemic capillary leak syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1990 Mar;21(3):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte function triggered through the high affinity Fc receptor for monomeric IgG. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):534–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teelucksingh S., Padfield P. L., Edwards C. R. Systemic capillary leak syndrome. Q J Med. 1990 May;75(277):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Function and heterogeneity of human Fc receptors for immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):355–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI113891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Wady Z., Bagot M., Wechsler J., Kalis B., Rousselot R., Deville J. F., Haioun C., Farcet J. P., Revuz J. Syndrome de fuite capillaire révélant un lymphome T diffus mixte. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1991;118(11):882–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]