Abstract
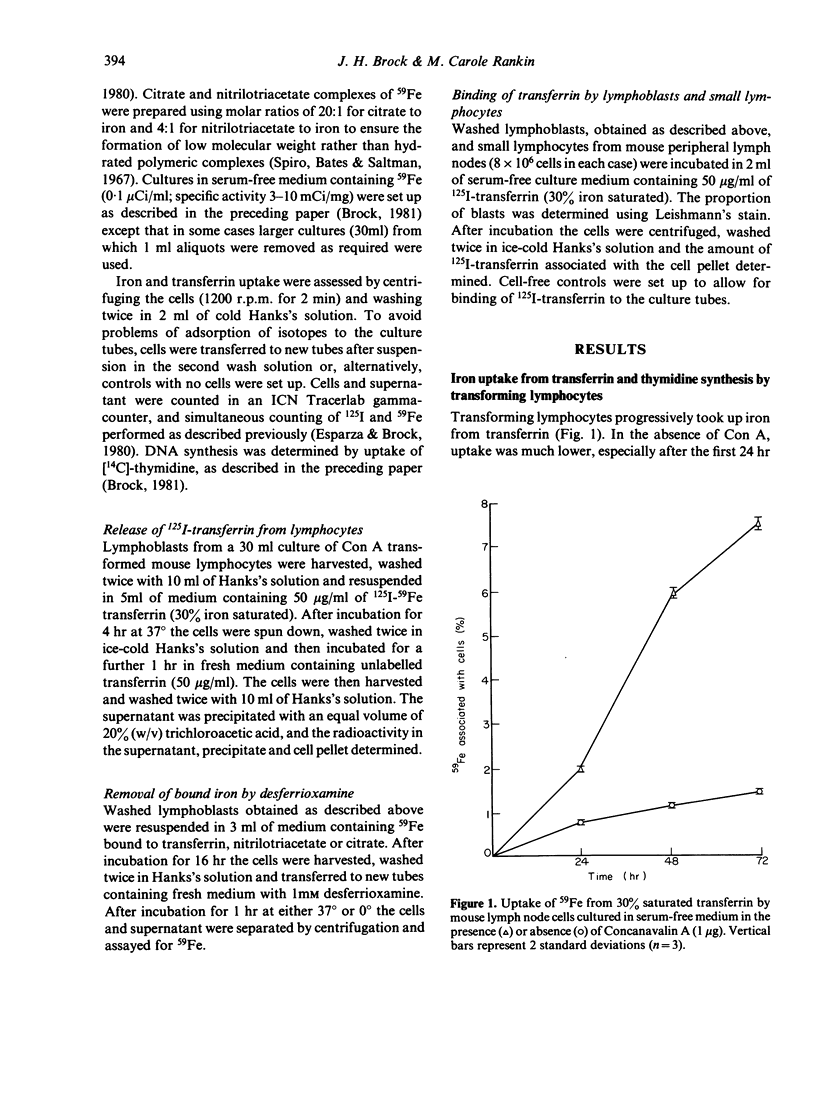
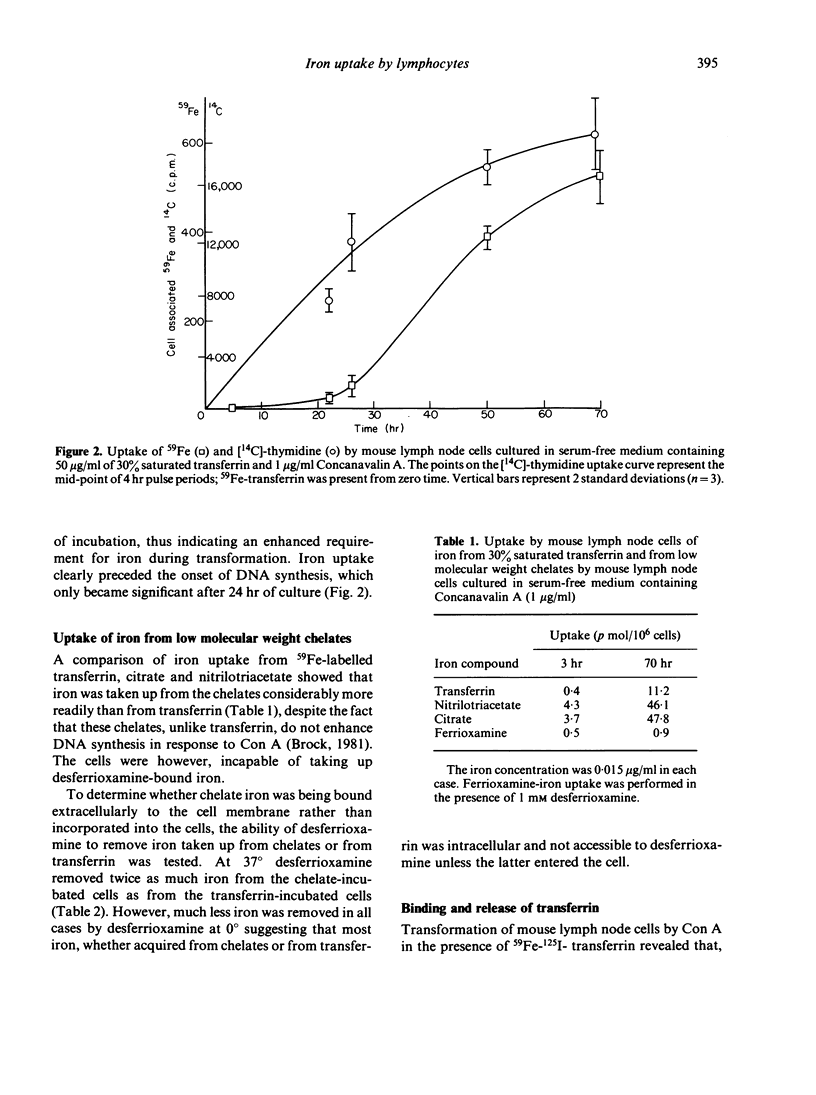
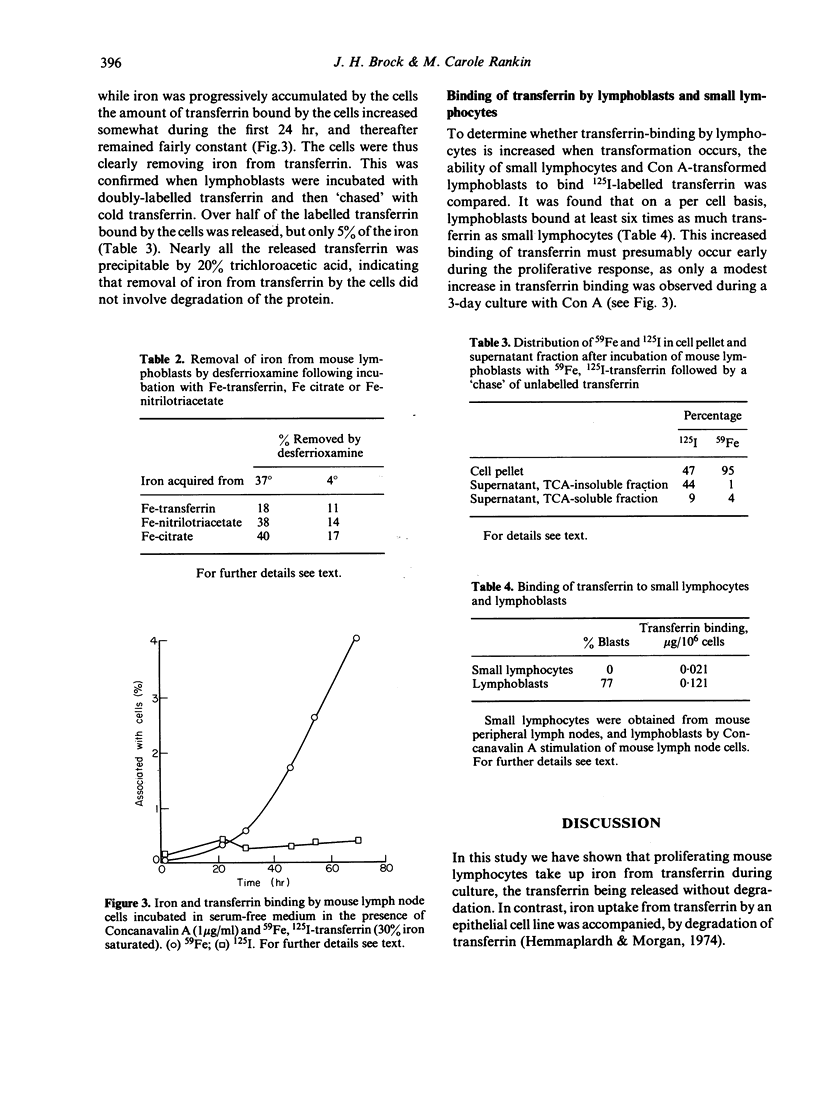
Mouse lymph node cells cultured with Concanavalin A (Con A) in serum-free medium containing 59Fe-transferrin took up 59Fe more rapidly than cells cultured without Con-A. Uptake of iron commenced rapidly and preceded the onset of DNA synthesis in stimulated cells. Total uptake of transferrin during culture was much lower than that of iron, indicating that cells could remove iron from transferrin. The released transferrin appeared to be undergraded. Lymphoblasts bound six times more transferrin per cell than small lymphocytes. Lymphocytes also took up iron from citrate and nitrilotriacetate complexes, and iron so acquired was not readily removed by desferrioxamine, indicating that it was not bound extracellularly.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Brown E. B. The iron-binding function of transferrin in iron metabolism. Semin Hematol. 1977 Jan;14(1):31–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Sato G. Growth of a human mammary tumour cell line in a serum-free medium. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):388–389. doi: 10.1038/281388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Collins S. J., Keene B. R. Replacement of serum by insulin and transferrin supports growth and differentiation of the human promyelocytic cell line, HL-60. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):494–498. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner-Centerlind M. L., Hammarström S., Perlmann P. Transferrin can replace serum for in vitro growth of mitogen-stimulated T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Dec;9(12):942–948. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Brock J. H. The interaction of bovine transferrin and monoferric transferrin fragments with rabbit reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 21;624(2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith G. M., Goust J. M., Mercurio S. M., Galbraith R. M. Transferrin binding by mitogen-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Aug;16(4):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn D., Ganzoni A. M. Critical examination for the presence of a low molecular weight fraction in serum iron. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 7;627(3):250–255. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90454-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmaplardh D., Morgan E. H. Transferrin and iron uptake by human cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jul;87(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffbrand A. V., Ganeshaguru K., Hooton J. W., Tattersall M. H. Effect of iron deficiency and desferrioxamine on DNA synthesis in human cells. Br J Haematol. 1976 Aug;33(4):517–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Cresswell P. Modulation of cell surface iron transferrin receptors by cellular density and state of activation. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):579–586. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Cresswell P. Transferrin receptors on human B and T lymphoblastoid cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. L., Azari P. Effect of iron transferrin on nucleic acid synthesis in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jan;15(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. L. Uptake of transferrin-bound zinc by human lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Feb;35(2):318–329. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Durbin H., Clingan D., de Asua L. J. Iron salts and transferrin are specifically required for cell division of cultured 3T6 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):556–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91508-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. P., Jacobs A. Iron uptake by Chang cells from transferrin, nitriloacetate and citrate complexes: the effects of iron-loading and chelation with desferrioxamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 3;543(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


