Abstract
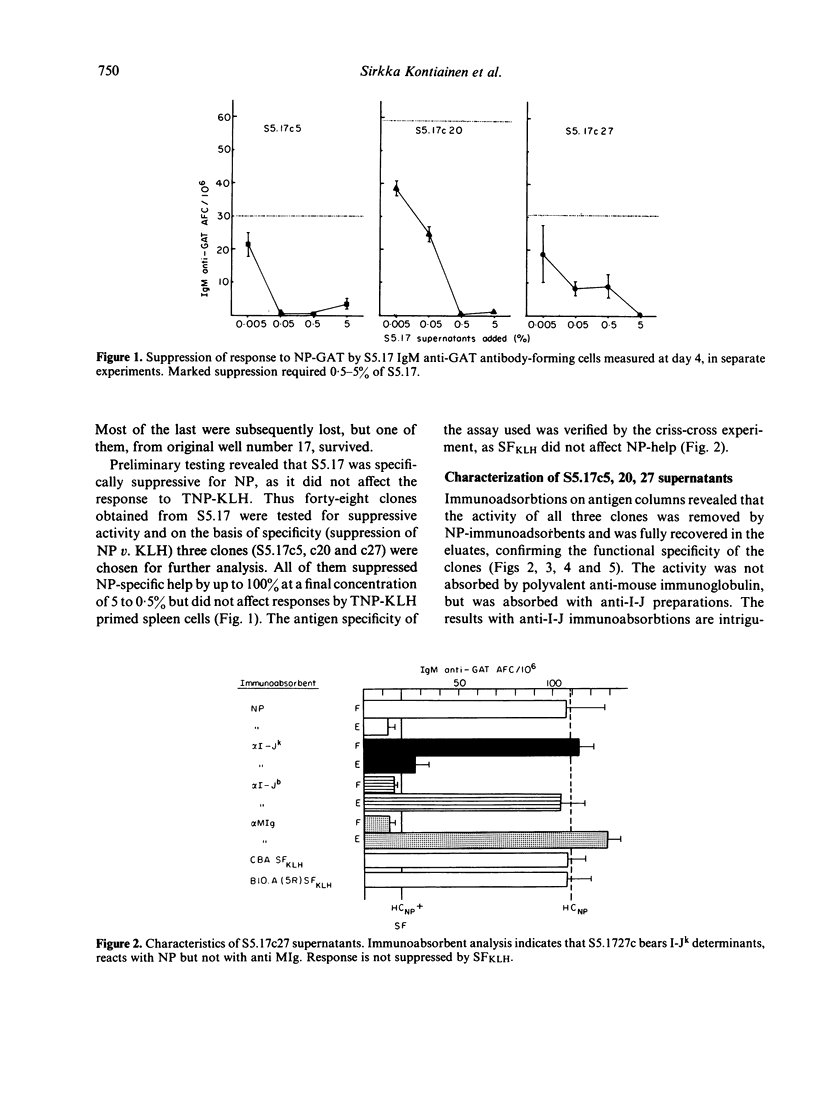
We have made several T-T hybridomas which secrete soluble factors capable of suppressing an in vitro antibody response to nitrophenol (NP), but not other unrelated antigens. These factors bind specifically to NP, and express determinants coded for in the I-J region of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. No determinants that cross-react with the constant regions of mouse immunoglobulins are present on the factors. Three sub-clones originating from the same initial culture well of hybridoma cells secrete factors which carry I-J determinants of different haplotypes. One clone expresses I-J determinants derived from the suppressor cell parent, another expresses I-J determinants derived from the tumour cell parent, and a third expresses both. This correlates exactly with I-J determinants expressed on the cell membrane, and suggests the participation of at least two genes in the determination of suppressor-factor structure.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cramer M., Krawinkel U., Melchers I., Imanishi-Kari T., Ben-Neriah Y., Givol D., Rajewsky K. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. IV. Expression of immunoglobulin variable regions in (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl) acetyl (NP)-specific receptors isolated from murine B and T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):332–338. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M., ZEISS I. M. Chromosome preparation from fresh and cultured tissues using a modification of the drying technique. Nature. 1961 Dec 23;192:1213–1214. doi: 10.1038/1921213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsby R. A., Osborne B. A., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. Hybrid cell lines with T-cell characteristics. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):707–708. doi: 10.1038/267707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J., Liew F. Y. Antigen-specific suppressor factors produced by T cell hybridomas for delayed-type hypersensitivity. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):572–575. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi T., Mäkelä O. Inheritance of antibody specificity. I. Anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl of the mouse primary response. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1498–1510. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack R. S., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K. Idiotypic analysis of the response of C57BL/6 mice to the (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl group. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):559–565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen K., Mäkelä O. A mendelian idiotype is demonstrable in the heteroclitic anti-NP antibodies of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):105–111. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen K. Two major idiotypes in mouse anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitro-phenyl)acetyl (NP) antibodies are controlled by "allelic" genes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Feb;10(2):132–139. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Feldmann M. Specific T helper and suppressor cells and factors induced in vitro to the hapten NP. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1980 May-Jun;131C(3):239–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Feldmann M. Suppressor cell induction in vitro. I. Kinetics of induction of antigen-specific suppressor cells. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):296–301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Feldmann M. Suppressor-cell induction in vitro. IV. Target of antigen-specific suppressor factor and its genetic relationships. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):110–122. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Simpson E., Bohrer E., Beverley P. C., Herzenberg L. A., Fitzpatrick W. C., Vogt P., Torano A., McKenzie I. F., Feldmann M. T-cell lines producing antigen-specific suppressor factor. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):477–480. doi: 10.1038/274477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontianen S., Feldmann M. Induction of specific helper cells in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 31;245(148):285–286. doi: 10.1038/newbio245285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Imanishi-Kari T., Jack R. S., Rajewsky K., Mäkelä O. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. I. Receptors from nylon wool-enriched mouse T lymphocytes lack serological markers of immunoglobulin constant domains but express heavy chain variable portions. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):566–573. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Mage R. G., Kelus A. S., Rajewsky K. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. II. Receptors from nylon wool-enriched rabbit T lymphocytes lack serological determinants of immunoglobulin constant domains but carry the A locus allotypic markers. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):792–801. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Melchers I., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. III. Evidence for idiotypic restriction of T-cell receptors. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1341–1347. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Cieplinski W., Dharmgrongartama B., Gefter M. L., Morrison S. L., Kelly T., Scharff M. D. Regulation of immunoglobulin expression in mouse myeloma cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):781–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico A., Capra J. D. T cell hybrids with arsonate specificity. I. Initial characterization of antigen-specific T cell products that bear a cross-reactive idiotype and determinants encoded by the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1289–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Amkraut A. A. Immunogenicity of trinitrophenyl-hemocyanin: production of primary and secondary anti-hapten precipitins. J Immunol. 1966 Sep;97(3):421–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E., Kontiainen S., Herzenberg L. A., Bohrer E., Torano A., Vogt P., Beverley P., Fitzpatrick W., Feldmann M. T cell hybrids with T cell functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:195–202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Miller J. F. Specific suppressive factors produced by hybridomas derived from the fusion of enriched suppressor T cells and a T lymphoma cell line. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):373–382. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Saito T., Tada T. Antigen-specific suppressive factor produced by a transplantable I-J bearing T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):555–558. doi: 10.1038/278555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Corvalán J. R., Holliman A. Characterization of an antigen-specific factor from a hybrid T-cell line. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:316–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Kimoto M., Maruyama S., Kishimoto T., Yamamura Y. Regulation of antibody response in different immunoglobulin classes. V. Establishment of T hybrid cell line secreting IgE class-specific suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2113–2117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


