Abstract
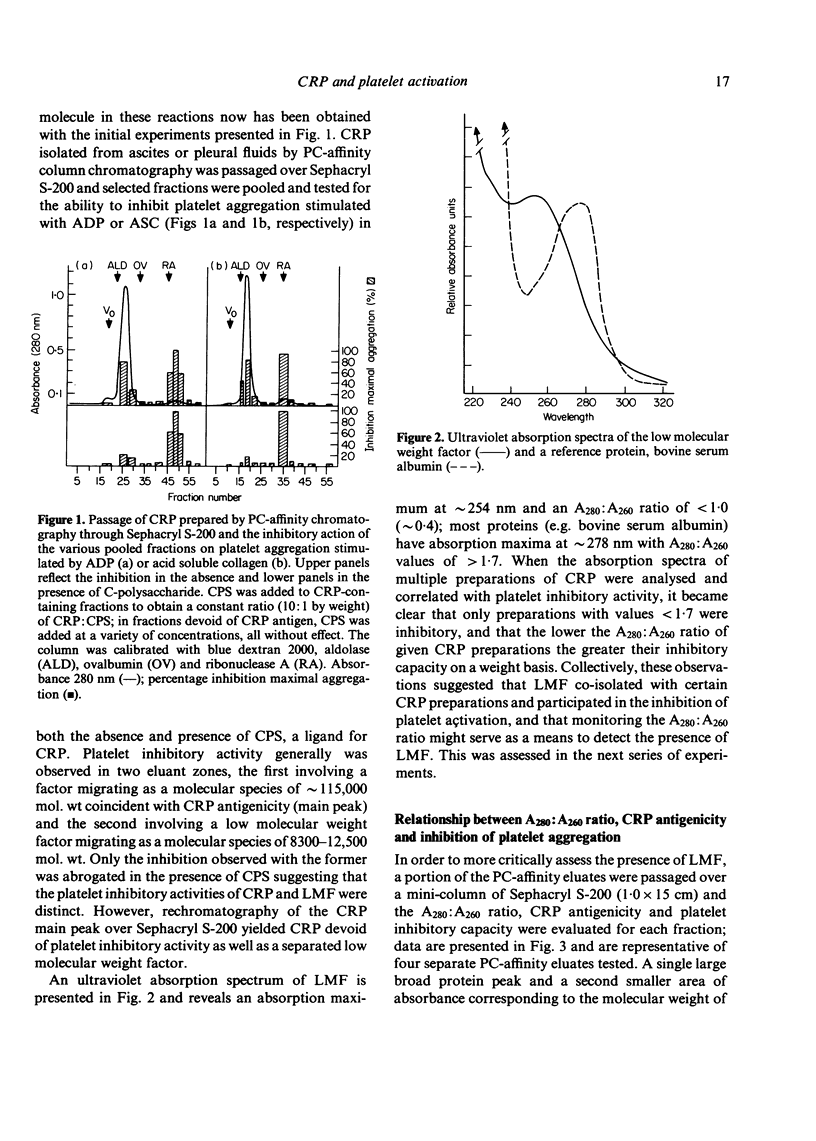
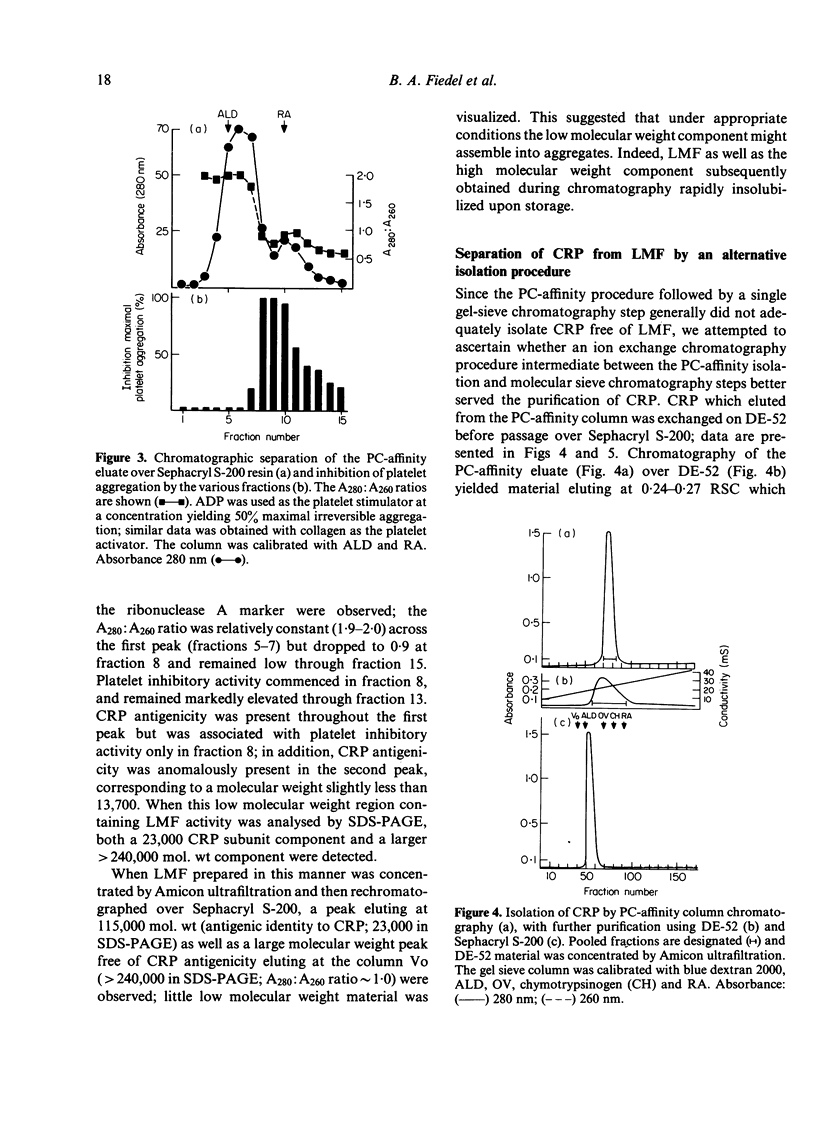
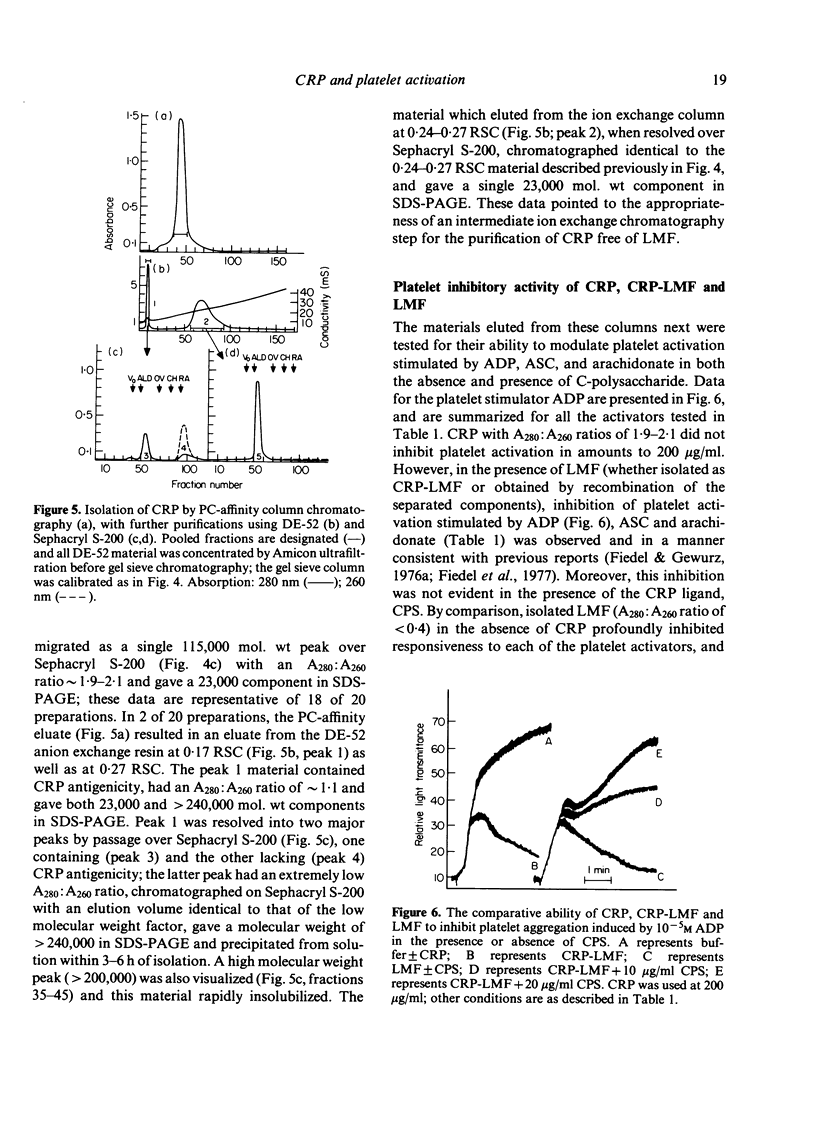
We previously reported that C-reactive protein (CRP), an acute phase reactant, inhibits platelet activation through an effect upon a factor(s) critical to ADP-mediated secondary wave platelet aggregation but independent of a direct effect upon platelet contractile elements. However, a role for an accessory factor in this inhibitory effect became of concern because of an inconsistency in the effects of CRP preparations upon the platelet: inhibition was lost upon storage and CRP preparations differed, on a weight basis, in inhibitory capacity and sensitivity to the presence of the CRP ligand C-polysaccharide (CPS(. The studies presented herein were thus intended to assess whether an accessory factor was involved in the inhibition of platelet activation observed with CRP. We report that the activity of the inhibitory CRP preparations resulted from association with a low molecular weight factor (LMF) with an apparent nominal molecular weight of 8300-12,500 and an A280:A260 ratio of approximately 0.4. Purified CRP did not inhibit platelet responsiveness but CRP with associated LMF (CRP-LMF) did. Moreover, the inhibitory capacity of CRP-LMF but not LMF was substantially reversed in the presence of CPS. These studies indicate that the platelet inhibitory properties of CRP preparations result from and are contingent upon the presence of a co-isolating low molecular weight factor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON H. C., McCARTY M. Determination of C-reactive protein in the blood as a measure of the activity of the disease process in acute rheumatic fever. Am J Med. 1950 Apr;8(4):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber M. M., Fuks Z., Kaplan H. S. E-rosette inhibiting substance in Hodgkin's disease spleen extracts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):369–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus D. R., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Radioimmunoassay of human C-reactive protein and levels in normal sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jan;87(1):120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. I. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and release reactions. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1289–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. II. Inhibition by CRP of platelet reactivities stimulated by poly-L-lysine, ADP, epinephrine, and collagen. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1073–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Simpson R. M., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. III. The role of cAMP, contractile elements, and prostaglandin metabolism in CRP-induced inhibition of platelet aggregation and secretion. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Edelman G. M. C-reactive protein: a molecule composed of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):558–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKAMA Y., RILEY R. F. Purification of C-reactive protein, an acute phase protein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 16;74:305–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokama Y., Coleman M. K., Riley R. F. The nature of C-reactive protein in acute phase serum: evidence for an equilibrium form containing a mucopolysaccharide of serum. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):521–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. III. Complement-dependent passive hemolysis initiated by CRP. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits. Association with necrosis in local inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:961–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., GOTSCHLICH E. C. The chemical composition of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich C., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of human C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):489–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Friedenson B., Gewurz H., Painter R. H., Hofmann T., Shelton E. Characterization of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent C1t as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish W. E. Studies on vasculitis. VII. C-reactive protein as a substance perpetuating chronic vasculitis. Occurrence in lesions and concentrations in sera. Clin Allergy. 1976 Nov;6(6):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Ashley M. J. Isolation of C-reactive protein by affinity chromatography. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. F. CRYSTALLIZATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FOLLOWING REMOVAL OF ASSOCIATED LIPID-CONTAINING MATERIAL BY ANTISERUM TO NORMAL HUMAN BETA LIPOPROTEIN. Yale J Biol Med. 1963 Dec;36:241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. F., McCARTY M., SLATER R. J. The occurrence during acute infections of a protein not normally present in the blood. V. Physical-chemical properties of the C-reactive protein crystallized by a modified technique. J Exp Med. 1954 Jul 1;100(1):71–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. F., McCARTY M. The measurement of C-reactive protein in human sera; comparison of the clinical tests on the basis of a quantitative method. J Clin Invest. 1951 Jun;30(6):616–622. doi: 10.1172/JCI102479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


