Abstract
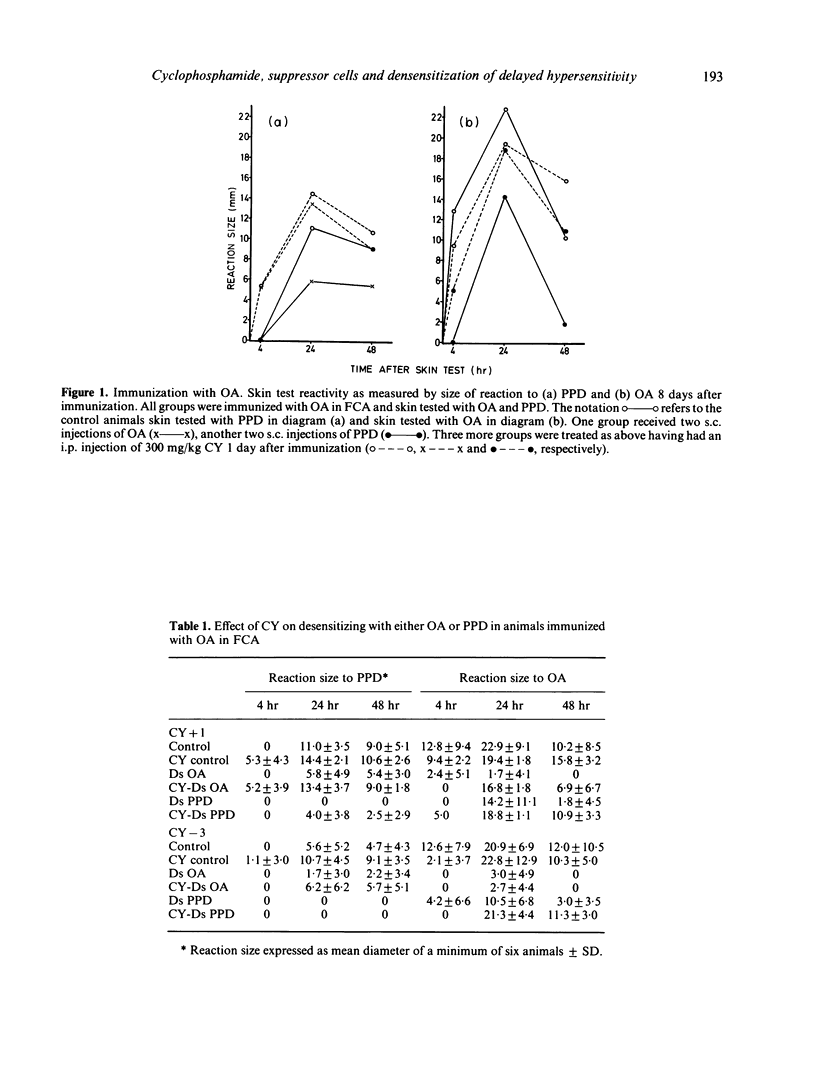
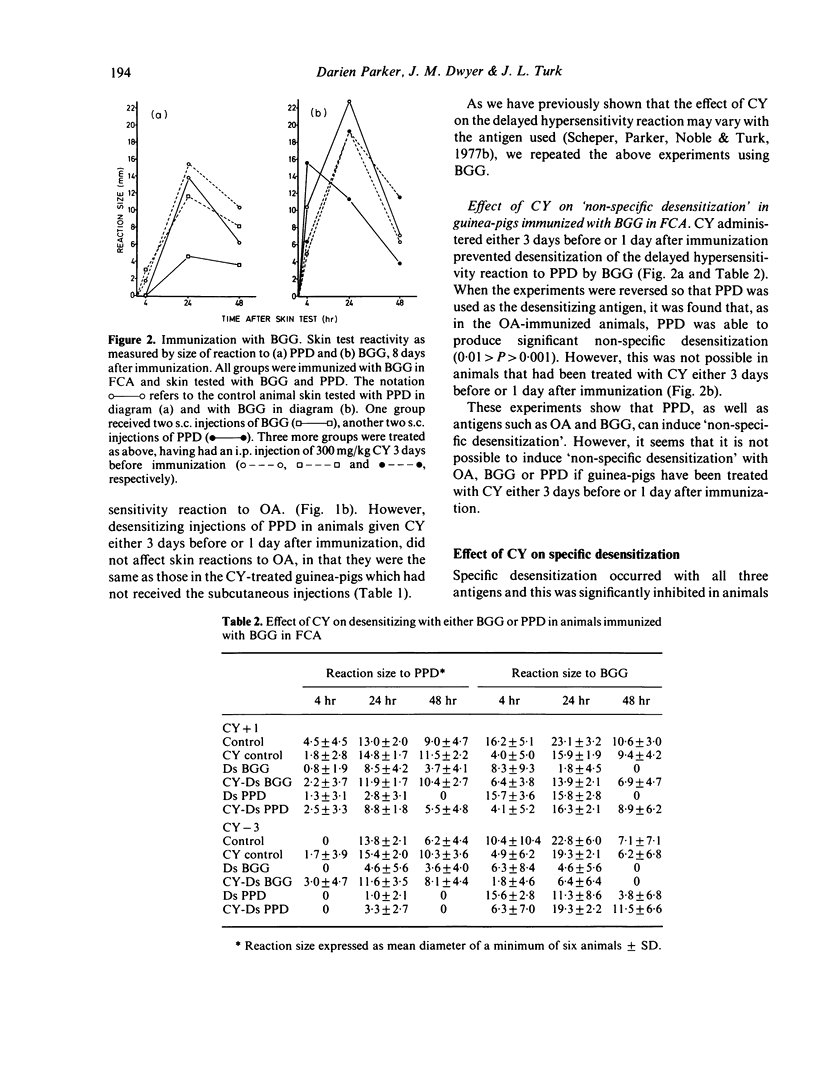
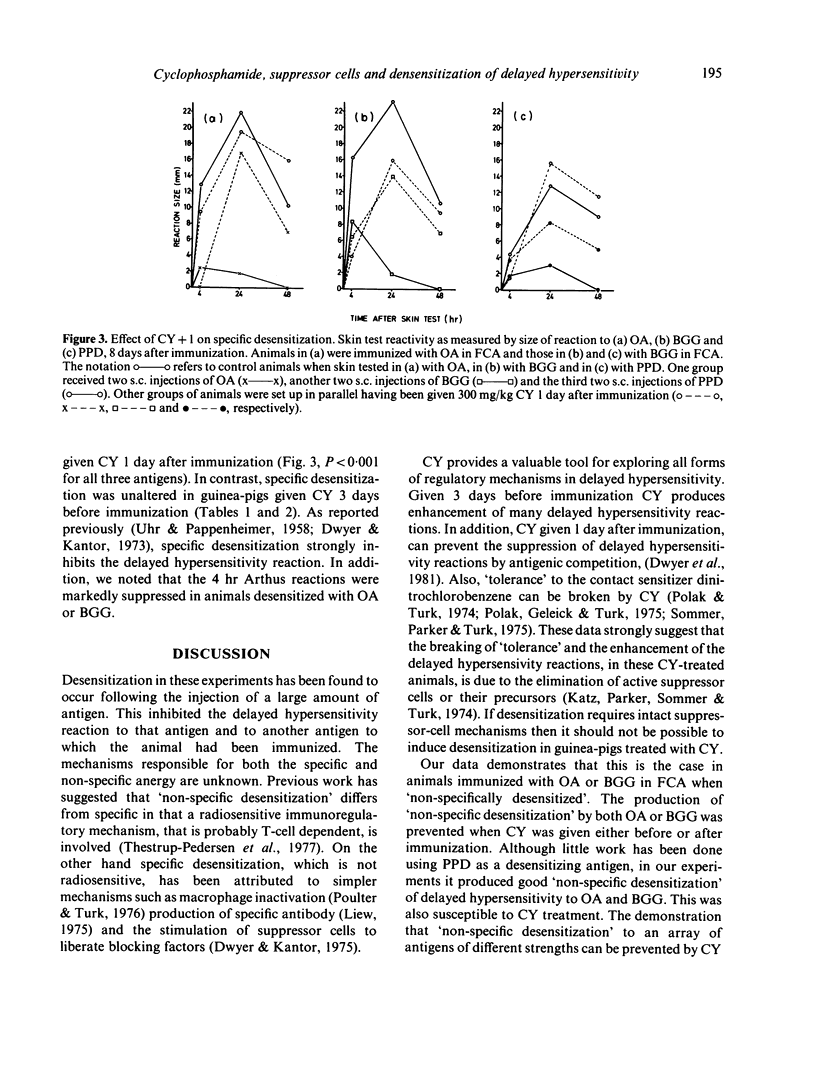
Desensitization of guinea-pigs with ovalbumin (OA) or bovine gamma globulin (BGG) induces strong specific desensitization and is associated with a non-specific energy to tuberculin--PPD. Similarly, it was found that animals receiving desensitizing injections of PPD have suppressed delayed hypersensitivity reactions to OA or BGG. PPD also induced strong specific desensitization. Cyclophosphamide (CY) given in one large dose (300 mg/kg) 3 days before immunization failed to affect the specific desensitization induced by all three antigens. However, if CY was given 1 day after immunization, it was not possible to induce specific desensitization. The induction of non-specific desensitization was prevented in all three antigen systems if CY was given either 3 days before or 1 day after immunization. Desensitization with either OA or BGG markedly suppressed the specific 4 hr Arthus reactions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dwyer J. M., Kantor F. S. In vivo suppression of delayed hypersensitivity: prolongation of desensitization in guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):588–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M., Kantor F. S. Regulation of delayed hypersensitivity. Failure to transfer delayed hypersensitivity to desensitized guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):32–41. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. M., Parker D., Turk J. L. Suppression of delayed hypersensitivity to tuberculin by antigenic competition. A positive immunoregulatory mechanism sensitive to cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):549–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Parker D., Sommer G., Turk J. L. Suppressor cells in normal immunisation as a basic homeostatic phenomenon. Nature. 1974 Apr 12;248(449):612–614. doi: 10.1038/248612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y. Desensitization of delayed-type hypersensitivity by antigen and specific antibody. Cell Immunol. 1975 Sep;19(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak L., Geleick H., Turk J. L. Reversal by cyclophosphamide of tolerance in contact sensitization. Tolerance induced by prior feeding with DNCB. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):939–942. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak L., Turk J. L. Reversal of immunological tolerance by cyclophosphamide through inhibition of suppressor cell activity. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):654–656. doi: 10.1038/249654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Turk J. L. Changes in macrophages in vivo induced by desensitization. Cell Immunol. 1976 Apr;23(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheper R. J., Parker D., Noble B., Turk J. L. The relation of immune depression and B-cell stimulation during the development of delayed hypersensitivity to soluble antigens. Immunology. 1977 Feb;32(2):265–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer G., Parker D., Turk J. L. Epicutaneous induction of hyporeactivity in contact sensitization. Demonstration of suppressor cells induced by contact with 2,4-dinitrothiocyanatebenzene. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):517–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thestrup-Pedersen K., Dwyer J. M., Askenase P. W. Studies on the role of the thymus and T cells in the in vivo suppression of delayed hypersensitivity (desensitization): radiosensitivity of the mechanism inducing nonspecific anergy. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1665–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D. Further studies on B-lymphocyte suppression in delayed hypersensitivity, indicating a possible mechanism for Jones-Mote hypersensitivity. Immunology. 1973 Apr;24(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D., Poulter L. W. Functional aspects of the selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHR J. W., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Delayed hypersensitivity. III. Specific desensitization of guinea pigs sensitized to protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1958 Dec 1;108(6):891–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


