Abstract
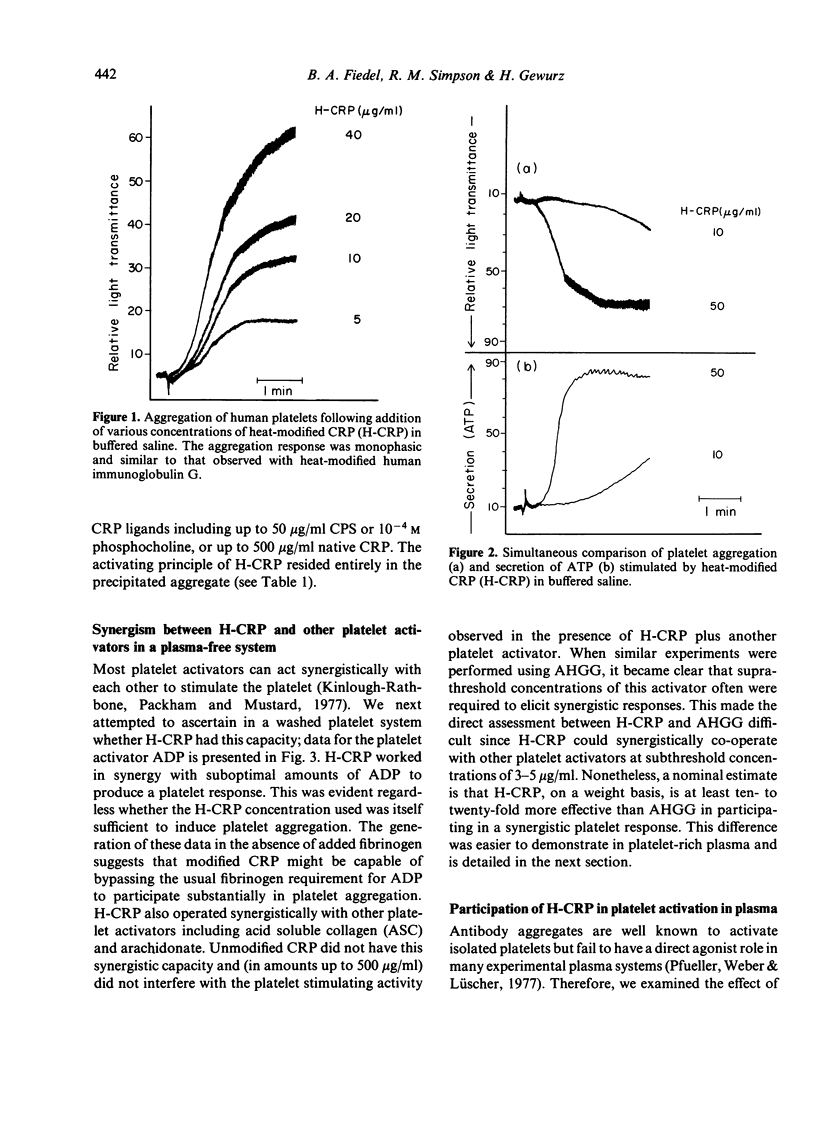
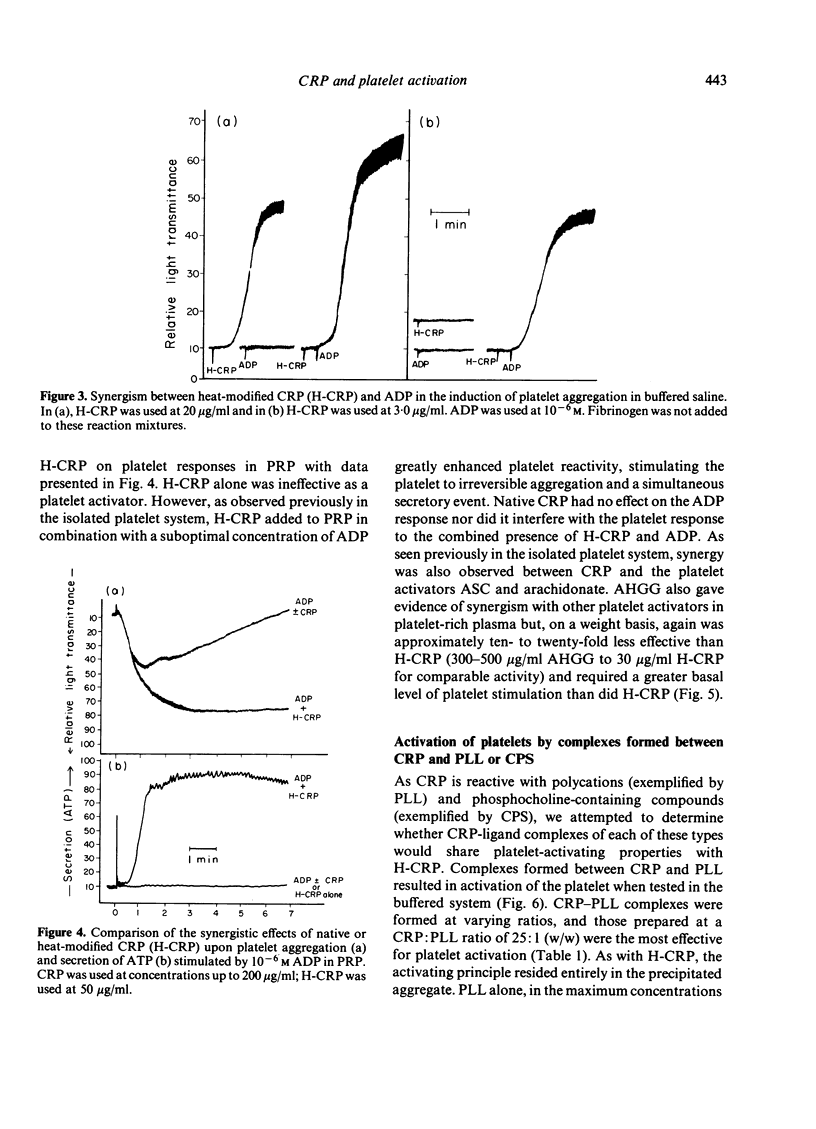
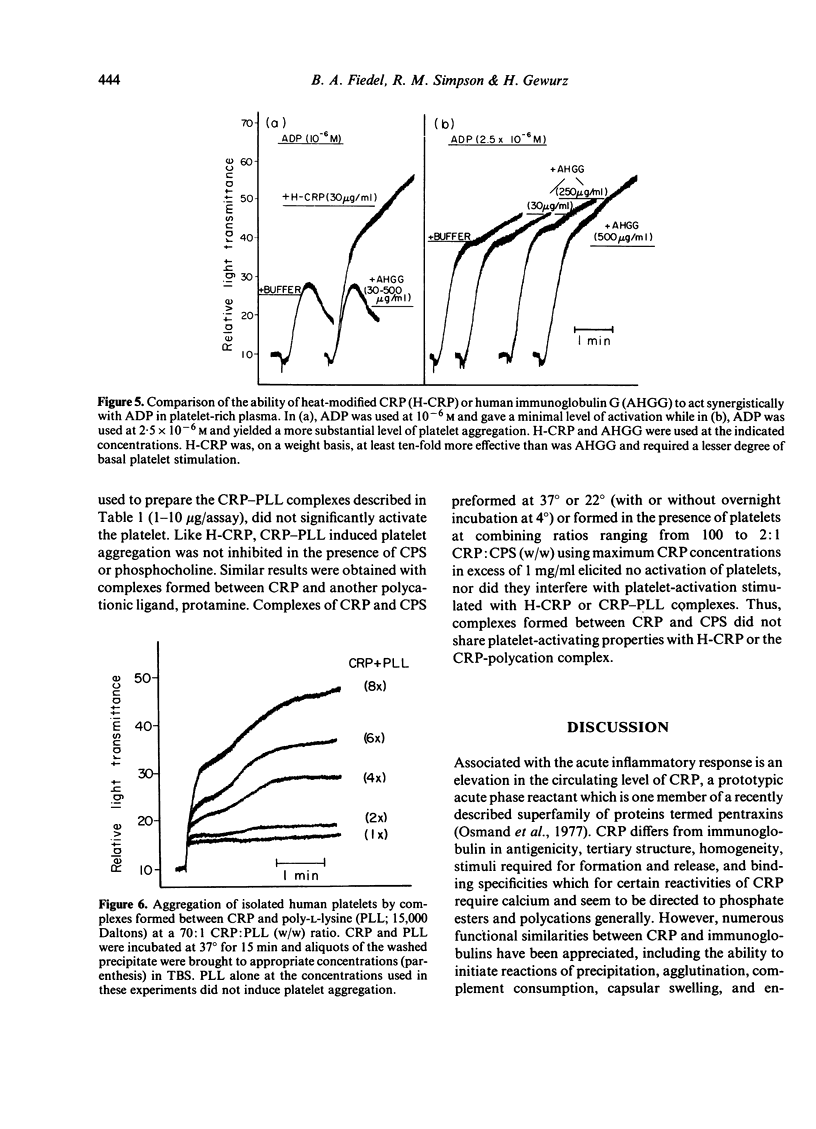
The functional similarities between C-reactive protein (CRP) and immunoglobulin raised the possibility that modified CRP might resemble immunoglobulin in its activating effects upon the human platelet. Thermally-aggregated CRP (H-CRP), but not unmodified CRP, induced reactions of aggregation and secretion from isolated platelets; maximum responses occurred with less than 50 microgram/ml H-CRP and were similar to responses mediated by thermally-aggregated human IgG (AHGG). Platelet activation induced by H-CRP was sensitive to the presence of EDTA and dibucaine, required metabolic energy and was inhibited by increased levels of cAMP. Like AHGG, H-CRP acted synergistically with other platelet stimulators, although on a weight basis H-CRP appeared approximately ten- to twenty-fold more effective than AHGG. Complexes formed between CRP and certain of its polycationic ligands (PLL and protamine) shared platelet activating properties with H-CRP, whereas complexes of CRP and CPS did not. These data point to the ability of appropriately modified CRP to stimulate or enhance platelet responsiveness, and taken together with those reactivities described previously between modified CRP and certain lymphocytes, phagocytes, and the complement system, support the concept that CRP can initiate biological activities similar to those mediated by immunoglobulin.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bills T. K., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Metabolism of [14C]arachidonic acid by human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 23;424(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus D. R., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Radioimmunoassay of human C-reactive protein and levels in normal sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jan;87(1):120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus D. R., Siegel J., Petras K., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the first component of human complement. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. I. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and release reactions. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1289–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. II. Inhibition by CRP of platelet reactivities stimulated by poly-L-lysine, ADP, epinephrine, and collagen. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1073–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Simpson R. M., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on platelet function. III. The role of cAMP, contractile elements, and prostaglandin metabolism in CRP-induced inhibition of platelet aggregation and secretion. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M., Detwiler T. C. Characteristics of the synergistic actions of platelet agonists. Blood. 1981 Apr;57(4):685–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. III. Complement-dependent passive hemolysis initiated by CRP. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits. Association with necrosis in local inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:961–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Synergism between platelet aggregating agents: the role of the arachidonate pathway. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):567–580. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., GOTSCHLICH E. C. The chemical composition of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf L. C., Lyman D. J. The effect of conformational changes on the blood platelet reactivity of polylysine. Thromb Res. 1974 Dec;5(6):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Lint T. F., Gewurz H. Interaction of C-reactive protein with lymphocytes and monocytes: complement-dependent adherence and phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):774–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Mustard J. F., Taichman N. S., Uriuhara T. Platelet aggregation and release of ADP, serotonin and histamine associated with phagocytosis of antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):232–237. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Eckhardt C., Lüscher E. F. Immune reactions of human blood platelets. I. A comparative study on the effects on platelets of heterologous antiplatet antiserum, antigen-antibody complexes, aggregated gammaglobulin and thrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Nov 15;20(1):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich C., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of human C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):489–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Friedenson B., Gewurz H., Painter R. H., Hofmann T., Shelton E. Characterization of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent C1t as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Lüscher E. F. The effects of aggregated immunoglobulins on human blood platelets in relation to their complement-fixing abilities. I. Studies of immunoglobulins of different types. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):517–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Weber S., Lüscher E. F. Studies of the mechanism of the human platelet release reaction induced by immunologic stimuli. III. Relationship between the binding of soluble IgG aggregates to the Fc receptor and cell response in the presence and absence of plasma. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):514–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Rent R., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. I. Protamine-induced consumption of complement in acute phase sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):631–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. M., Williams R. E. Comparison of the secondary structures and binding sites of C-reactive protein and the phosphorylcholine-binding murine myeloma proteins. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1893–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


