Abstract
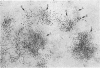
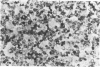
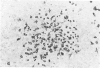
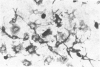
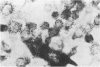
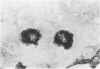
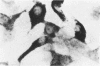
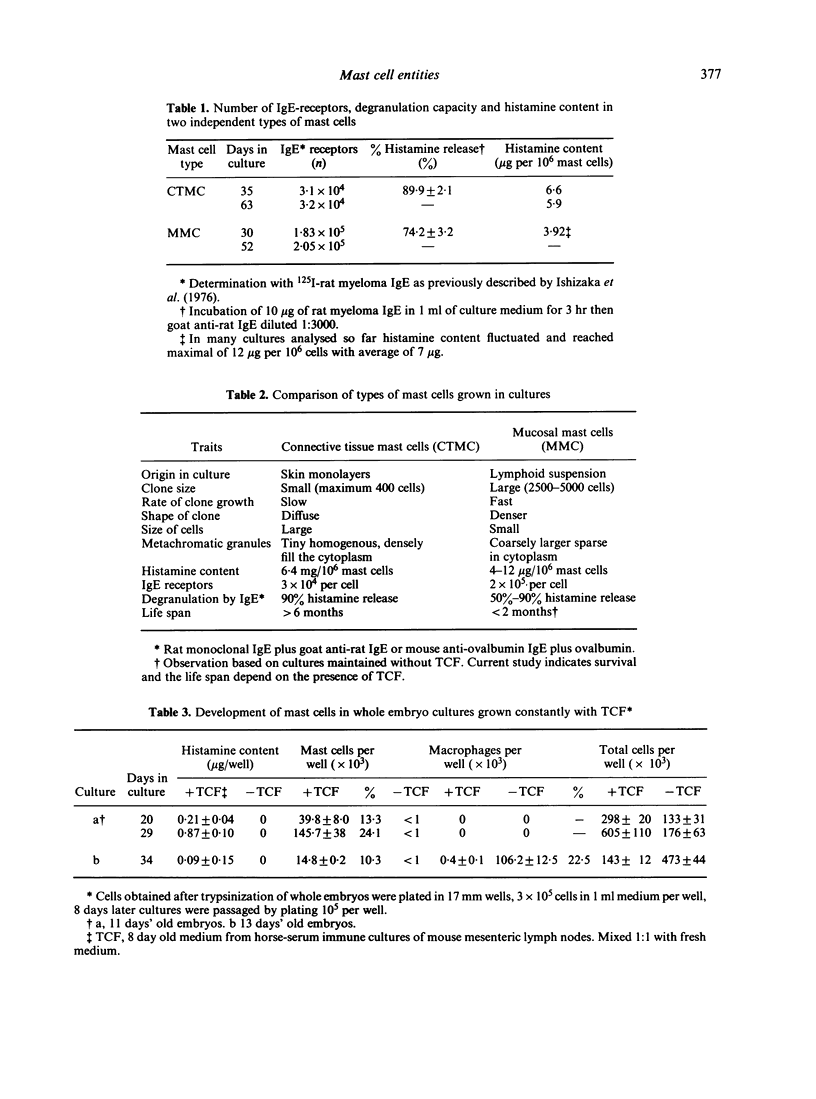
Clonal mast cell differentiation occurs when mesenteric lymph node cells from mice immunized with an antigen are grown in its presence on fibroblast monolayers prepared from mouse embryonic skin. Two types of mast cell clones are identified: the first, originates from a precursor present in the lymphoid cell suspension and the second, from a precursor in the fibroblast monolayer. Clones of the first type fail to appear when T cells are eliminated from the suspension; but they grow luxuriantly in the presence of fluid, harvested from cultures containing the antigen-sensitive T cells exposed to the antigen. The two mast cells differ in the clonal size and rate of growth, life span, cell size, shape and size of the granules and numbers of IgE receptors. It is concluded that the rapidly multiplying lymphoid mast cells associate with the mucosae of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts and appear in large number in response to immunological stimuli; the long lived mast cells derived from the embryonic skin monolayer are found in the general connective tissue.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHIECO-BIANCHI L., FIORE-DONATI L., PENNELLI N., BERTACCINI G. MAST CELL REACTION AND 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE CONTENT IN THE SKIN OF SYRIAN GOLDEN HAMSTERS PAINTED WITH 9:10-DIMETHYL-1:2-BENZANTHRACENE. Nature. 1963 Jul 20;199:293–294. doi: 10.1038/199293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Rousseaux J., Mazingue C., Bazin H., Capron A. Rat mast cell-eosinophil interaction in antibody-dependent eosinophil cytotoxicity to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2518–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaga J. F., Parwaresch M. R., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Die zytochemische Identifikation der Mastzellvorstufen bei der Ratte. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;121(2):292–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dye-binding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):303–312. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 4. Monoamine storing capacity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;67(3):365–379. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.67.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIORE-DONATI L., DE BENEDICTIS G., CHIECO-BIANCHI L. Development of mast cell reaction during chemical skin carcinogenesis of mouse. Nature. 1962 Jan 20;193:287–288. doi: 10.1038/193287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG H., SACHS L. FORMATION OF PURE SUSPENSIONS OF MAST CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE BY DIFFERENTIATION OF LYMPHOID CELLS FROM THE MOUSE THYMUS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Jul;31:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG H. The in vitro differentiation and culture of normal mast cells from the mouse thymus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 26;103:20–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Ben-Shahar D., Hammel I., Ben-David E. Degranulation capacity of cultured mast cells in the presence of histamine releaser. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):151–153. doi: 10.1038/280151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Lagunoff D. The in vitro differentiation of mast cells. Cultures of cells from immunized mouse lymph nodes and thoracic duct lymph on fibroblast monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1967 Dec;35(3):685–697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nir I., Hammel I., Eren R., Weissman B. A., Naot Y. Differentiation and activity of mast cells following immunization in cultures of lymph-node cells. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):485–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Mechanisms of reaginic hypersensitivity and IgE antibody response. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:109–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Adachi T., Chang T-H, Ishizaka K. Development of mast cells in vitro. II. Biologic function of cultured mast cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Okudaira H., Mauser L. E., Ishizaka K. Development of rat mast cells in vitro. I. Differentiation of mast cells from thymus cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Matsuda H., Hatanaka K. Clonal nature of mast-cell clusters formed in W/Wv mice after bone marrow transplantation. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):154–155. doi: 10.1038/281154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Go S., Matsuda H., Hatanaka K., Seki M. Distribution of mast-cell precursors in hematopoeitic and lymphopoietic tissues of mice. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):482–490. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Hatanaka K., Miyano Y. Development of mast cells from grafted bone marrow cells in irradiated mice. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):442–443. doi: 10.1038/268442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D. Contributions of electron microscopy to the study of mast cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 May;58(5):296–311. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Bazin H., Gowans J. L. Nature of cells binding anti-IgE in rats immunized with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: IgE synthesis in regional nodes and concentration in mucosal mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):537–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Fisher R. Mast cells in severely T-cell depleted rats and the response to infestation with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):145–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G. The nature of the thymus dependency of mucosal mast cells. II. The effect of thymectomy and of depleting recirculating lymphocytes on the response to Nippostrongylus brasilliensis. Cell Immunol. 1979 Oct;47(2):312–322. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R. Immune reactions in mucous membranes. 3. The discharge of intestinal mast cells during helminth expulsion in the rat. Lab Invest. 1971 May;24(5):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa Y., Miller H. R. Adoptive transfer of the intestinal mast cell response in rats infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Cell Immunol. 1979 Feb;42(2):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira H., Ishizaka K. Reaginic antibody formation in the mouse. V. Adoptive antihapten IgE antibody response of dinitrophenyl-keyhole limpet hemocyanin-primed spleen cells cultured with dinitrophenyl heterologous carrier conjugates. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):615–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Lima M. S., Javierre M. Q. Active anaphylactic reaction in mouse peritoneal mast cells in vitro. Life Sci. 1966 Feb;5(4):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Elgersma A. Absence of intestinal mast cell response in congenitally athymic mice during Trichinella spiralis infection. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):258–260. doi: 10.1038/264258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Elgersma A. Response of intestinal globule leucocytes in the mouse during a Trichinella spiralis infection and its independence of intestinal mast cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1979 Jun;60(3):246–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]