Abstract
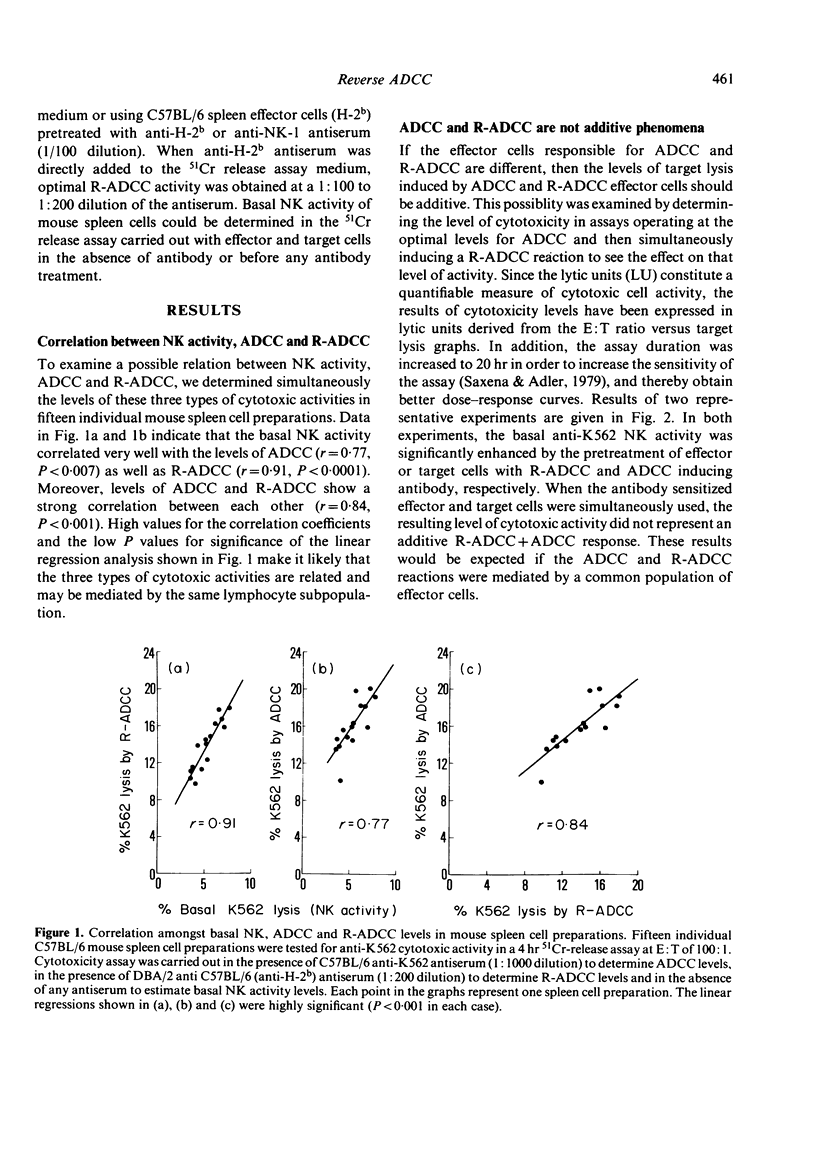
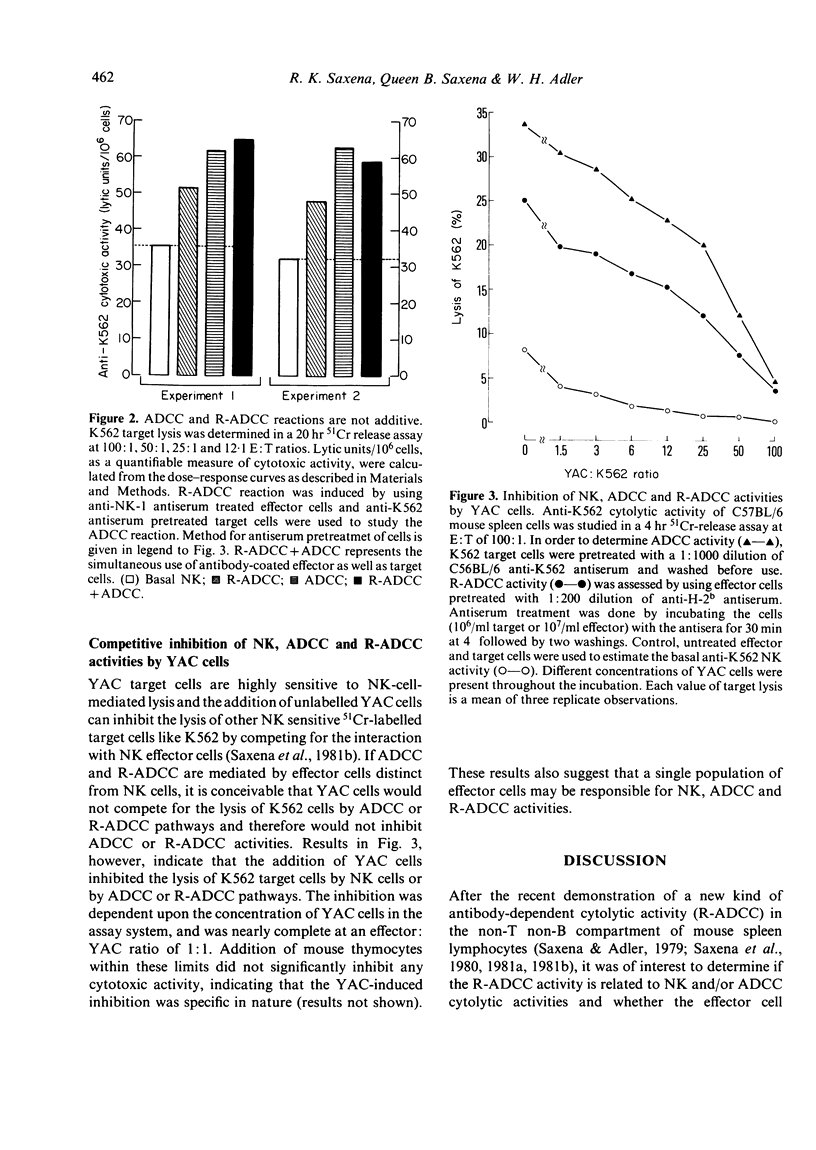
Our previous work has shown that antibody-coated mouse spleen cells express enhanced cytotoxic activity against some Fc-receptor-bearing target tumour cells by a mechanism which appears to be similar to an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) reaction with reversed polarity of the antibody bridge (R-ADCC). In this report we have shown that (i) the levels of basal natural killer (NK), ADCC and R-ADCC cytotoxic activities in mouse spleen cells are strongly correlated with each other, (b) simultaneous induction of ADCC and R-ADCC reactions does not result in an additive cytotoxic response, and (iii) YAC cells which do not bear Fc receptors and are highly sensitive to lysis by NK cells, can specifically and competitively inhibit the ADCC and R-ADCC reactions. These results suggest that the R-ADCC reaction may be mediated by the same effector cell population as mediates NK and ADCC reactions against tumour target cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Glimcher L., Shen F. W., Cantor H. Identification of a cell-surface antigen selectively expressed on the natural killer cell. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):1–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P., Schirrmacher V., Festenstein H. A new sensitive assay for antibody against cell surface antigens based on inhibition of cell-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Specificity and sensitivity. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1348–1363. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R. In vitro and in vivo investigations on antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:65–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Rosén A., Fenyö E. M., Troy F. A. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer cell system: isolation of target structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1405–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena R. K., Adler W. H. Modulation of natural cytotoxicity by alloantibodies. I. Alloantisera enhancement of cytotoxicity of mouse spleen cells toward a human myeloid cell line. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):846–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena R. K., Saxena Q. B., Adler W. H. Modulation of natural cytotoxicity by alloantibodies. III. Augmentation of natural killer activity by alloantisera directed against K, D, and I regions of the murine H-2 complex. Cell Immunol. 1980 Nov;56(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena R. K., Saxena Q. B., Adler W. H. Modulation of natural cytotoxicity by alloantibodies. V. The mechanism of a selective augmenting effect of anti-H-2 antisera on the natural killer activity of mouse spleen cells. Cell Immunol. 1981 Nov 15;65(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


