Abstract
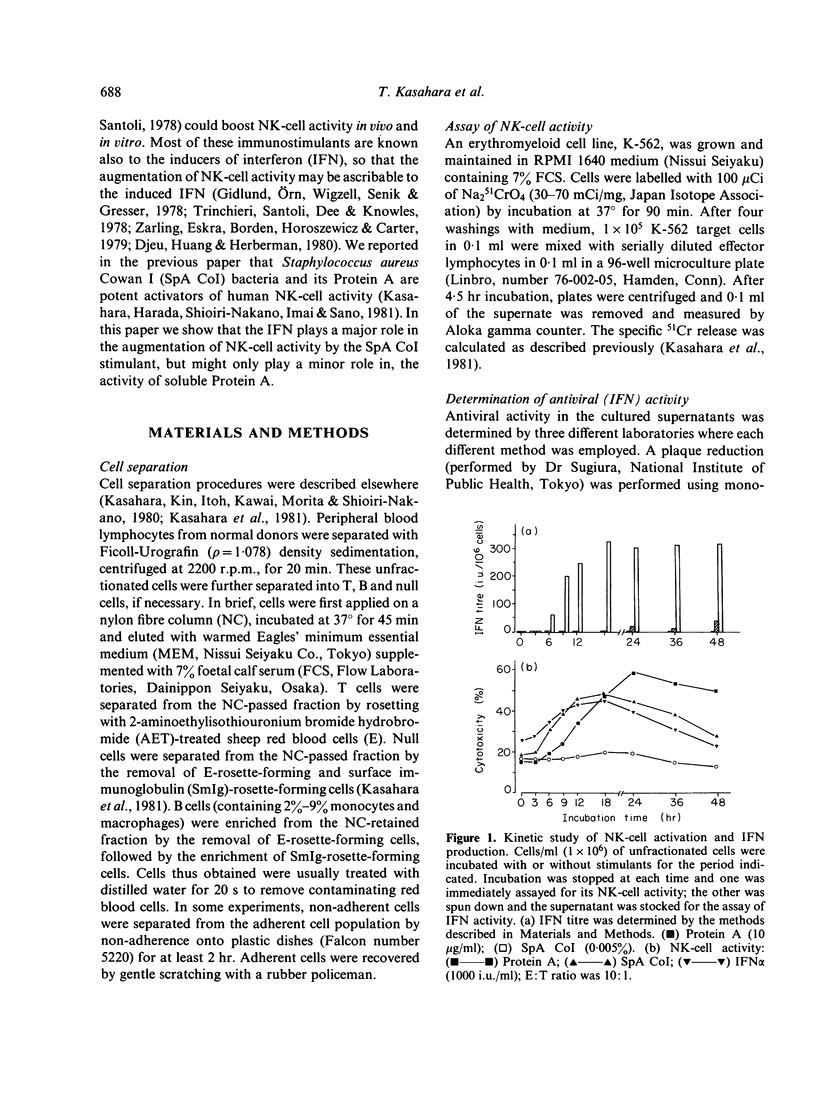
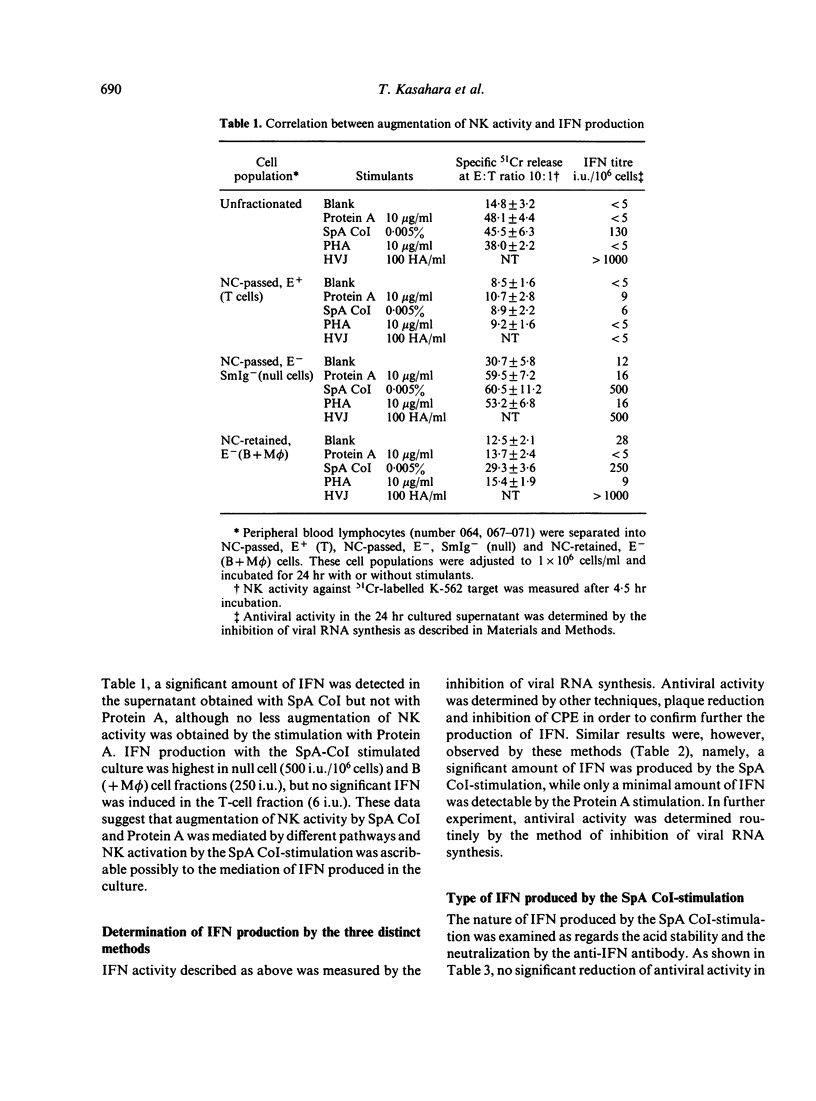
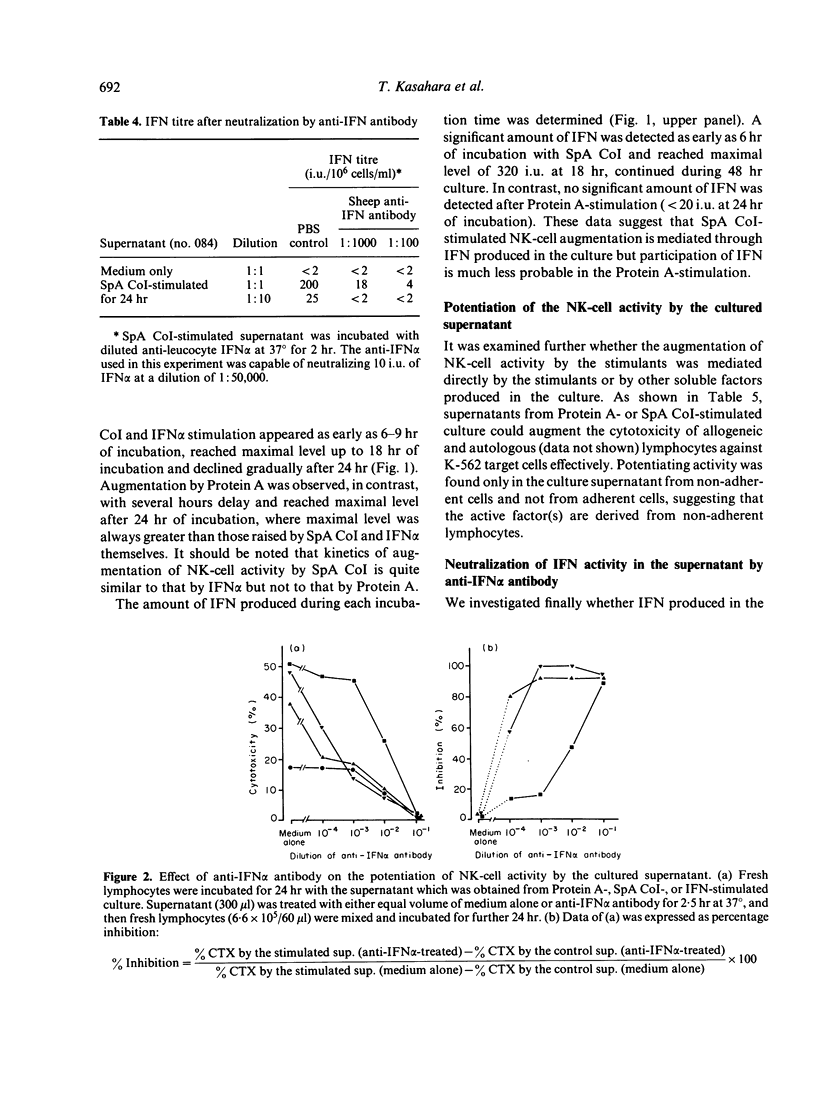
In the previous paper we reported that human natural killer (NK) cell activity was augmented greatly by preincubation with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I bacteria (SpA CoI) or its Protein A. We examined here whether the augmentation with these stimulants is ascribable to the direct activation of NK cells or mediated by some soluble factors produced by the stimulants. It was found that a significant amount of interferon (IFN) was produced by the SpA CoI-stimulation but not by the Protein A-stimulation, although the latter usually induced augmentation of NK-cell activity not less than SpA CoI-stimulation. IFN produced by SpA CoI was considered to belong to alpha-type IFN, because it was stable at pH 2.0 and could be neutralized effectively by anti-IFN alpha antibody. Kinetics of NK-cell activation by SpA CoI (but not by Protein A) were very similar to those by IFN alpha. Furthermore, augmentation of NK-cell activity with SpA CoI-stimulated supernatant was inhibited almost completely by diluted anti-IFN alpha antibody, whereas augmentation with Protein A-stimulated supernatant could not be abolished by the same treatment. It was, therefore, suggested that augmentation of NK-cell activity with SpA CoI might be ascribable in most part to the IFN induced, whereas Protein A can stimulated NK or T cells directly or soluble factors other than IFN might work as well.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins J. L., Patek P. Q., Cohn M. Tumorigenicity and lysis by natural killers. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):89–106. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Role of macrophages in the augementation of mouse natural killer cell activity by poly I:C and interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Huang K. Y., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer activity and induction of interferon by tumor cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):781–789. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Staal S., Djeu J. Y. Augmentation of natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic target cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):216–229. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Donahoe R. M., Gordon F. B., Dressler H. R. Enhancement of phagocytosis by interferon-containing preparations. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):581–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.581-588.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Relative ability of mitogens to stimulate production of interferon by lymphoid cells and to induce suppression of the in vitro immune response. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jan;154(1):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Harada H., Shioiri-Nakano K., Imai M., Sano T. Potentiation of natural killer activity of human lymphocytes by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and its protein A. Immunology. 1981 Feb;42(2):175–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Kin K., Itoh Y., Kawai T., Morita M., Shioiri-Nakano K. Cellular cooperation in lymphocyte activation. IV. Requirement of cell-to-cell interaction for the activation of human T and B lymphocytes by protein A. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jan;49(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlan R. I., Ceredig R., White D. O. Comparison of natural killer cells induced by Kunjin virus and Corynebacterium parvum with those occurring naturally in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):832–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.832-836.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratliff T. L., McCool R. E., Catalona W. J. Interferon induction and augmentation of natural-killer activity by Staphylococcus protein A. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 1;57(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold H., Kraft D., Scheiner O., Meindl P., Bodo G. Enhancement of NK, but not K cell activity by different interferons. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(2):152–161. doi: 10.1159/000232507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIURA A., KILBOURNE E. D. GENETIC STUDIES OF INFLUENZA VIRUSES. II. PLAQUE FORMATION BY INFLUENZA VIRUSES IN A CLONE OF A VARIANT HUMAN HETEROPLOID CELL LINE. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:478–488. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiya M., Kano S., Oshimi K., Gonda N., Takaku F. Stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulations by protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;61(4):394–406. doi: 10.1159/000232467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Reactivity of lymphocytes from normal persons on cultured tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2898–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Dee R. R., Knowles B. B. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Identification of the anti-viral activity as interferon and characterization of the human effector lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1299–1313. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Falcoff R., Catinot L., Falcoff E. Affinity chromatographic analysis of murine interferons induced by viruses and by T and B cell stimulants. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Apr-Jun;128C(3):699–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. II. Characterization of natural killer cells in peritoneal exudates. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Eskra L., Borden E. C., Horoszewicz J., Carter W. A. Activation of human natural killer cells cytotoxic for human leukemia cells by purified interferon. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ley M., van Damme J., Claeys H., Weening H., Heine J. W., Billiau A., Vermylen C., de Somer P. Interferon induced in human leukocytes by mitogens: production, partial purification and characterization. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Nov;10(11):877–883. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


