Abstract
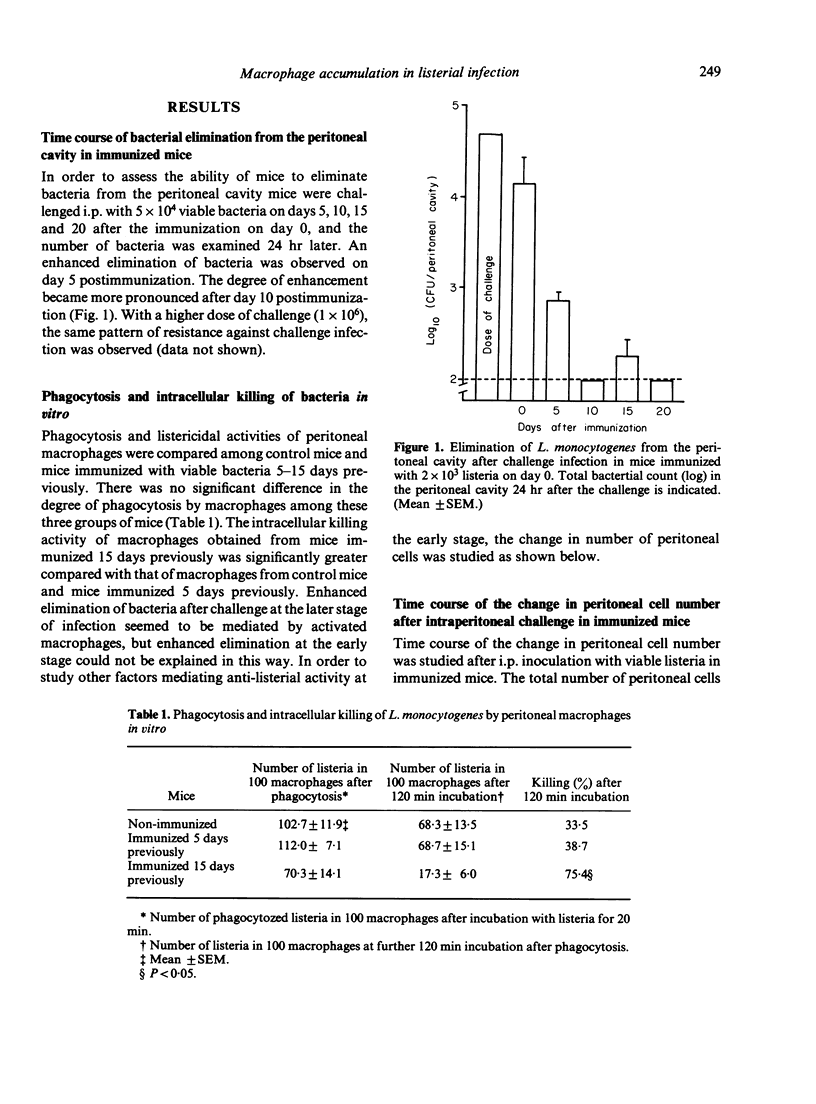
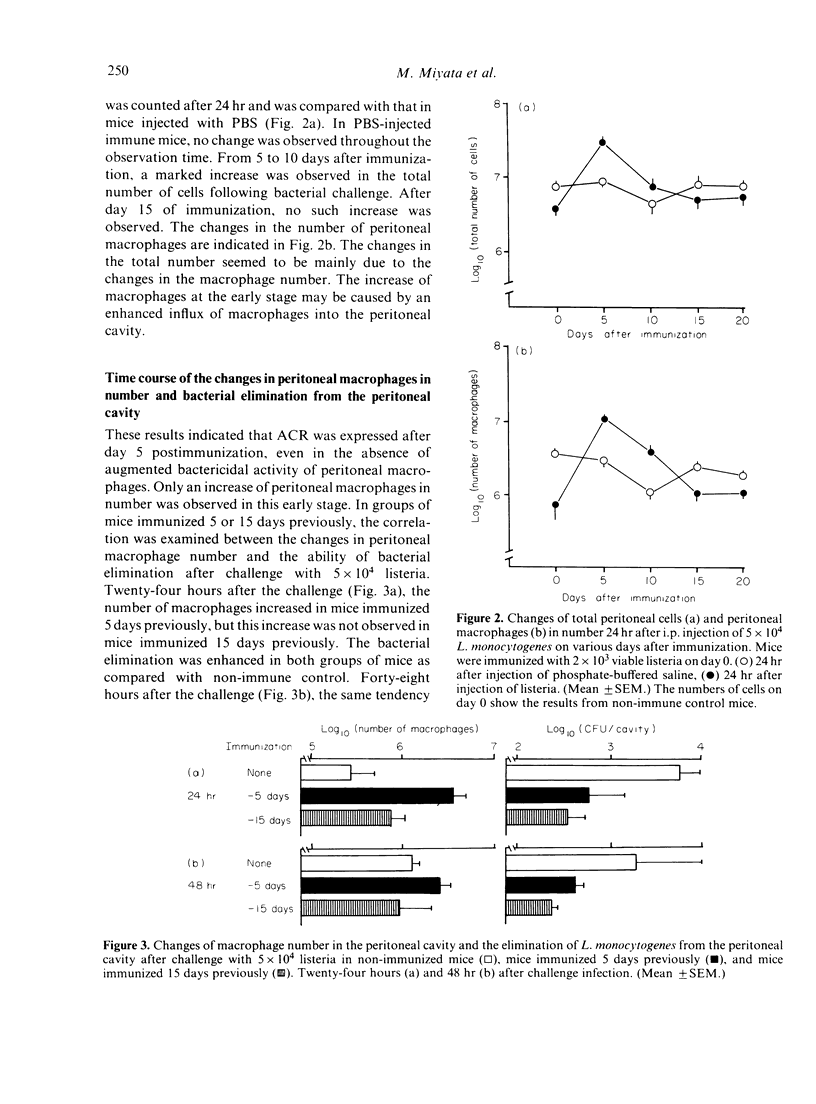
Mice were immunized with 1 X 10(3) viable Listeria monocytogenes, and the mechanism of the acquired resistance against challenge infection with 5 X 10(4) L. monocytogenes was studied by the use of the peritoneal cavity of mice as the site of challenge. An enhanced elimination of bacteria from the peritoneal cavity became detectable on day 5 after immunization, and lasted thereafter. Before day 10 postimmunization, a marked accumulation of macrophages was observed after the challenge but the in vitro listericidal activity of macrophages was not so enhanced. After day 15 postimmunization, peritoneal macrophages did not increase in number after the challenge but the in vitro listericidal activity of macrophages was the stronger. Accumulation of non-activated macrophages seemed to contribute mainly to the expression of acquired resistance against challenge in the early stage of immunization. So-called activated macrophages appeared to be generated only in the later stage of immunization. Thus it was suggested that there may be at least two steps in the expression of acquired listerial resistance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. A. Immunocompetent cells in resistance to bacterial infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):284–313. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.284-313.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Bockemühl J. Listeria monocytogenes infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.437-439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Hof H. Cell-mediated resistance to infection with Listeria monocytogenes in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):382–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.382-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. Effects of Dextran Sulfate 500 on Cell-Mediated Resistance to Infection with Listeria monocytogenes in Mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1105–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1105-1109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Nomoto K., Akeda H., Takeya K. Enhanced elimination of Listeria monocytogenes at the site of delayed footpad reaction. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.1-4.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Takeya K., Nomoto K., Shimotori S. Three phases of phagocyte contribution to resistance against Listeria monocytogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 May;106(1):165–171. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Remold H. G., David J. R. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):275–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Genetic linkage of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes with macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):402–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Shimotori S., Taniguchi T., Nomoto K. Cellular mechanisms in the protection against infection by Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jun;100(2):373–379. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsukawa K., Mitsuyama M., Takeya K., Nomoto K. Differing contribution of polymorphonuclear cells and macrophages to protection of mice against Listeria monocytogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Nov;115(1):161–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-1-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. The production by antigen-stimulated lymphocytes of a leukotactic factor distinct from migration inhibitory factor. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis: effects of bacteria and viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Mar-Apr;2(2):293–318. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


