Abstract
A migration inhibition assay, using lymph node lymphocytes, has been used as an in vitro assay for cell-mediated immunity (CMI) to ovalbumin in the mesenteric lymph nodes of mice fed ovalbumin. Migration inhibition developed only if an ovalbumin feed was preceded by cyclophosphamide administration; sensitization developed within 24 hr of a single ovalbumin feed, persisted for 14 days and could be recalled on secondary oral challenge with ovalbumin. The intestinal CMI occurred in the absence of detectable systemic immunity and was found only in mice given cyclophosphamide before oral immunization. These results confirm earlier reports on induction of CMI to ovalbumin in the intestinal mucosa, and support the hypothesis that abrogation of a gut-associated suppressor system is necessary to allow induction of intestinal CMI to a dietary protein.
Full text
PDF

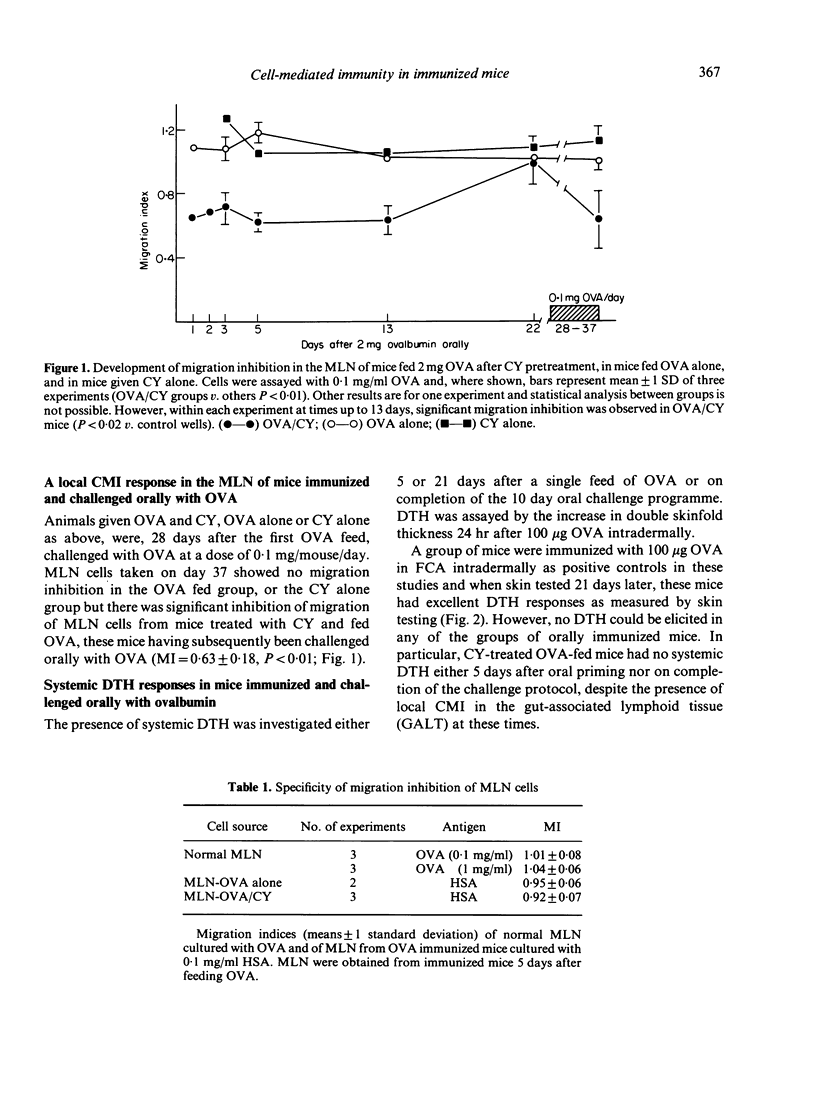
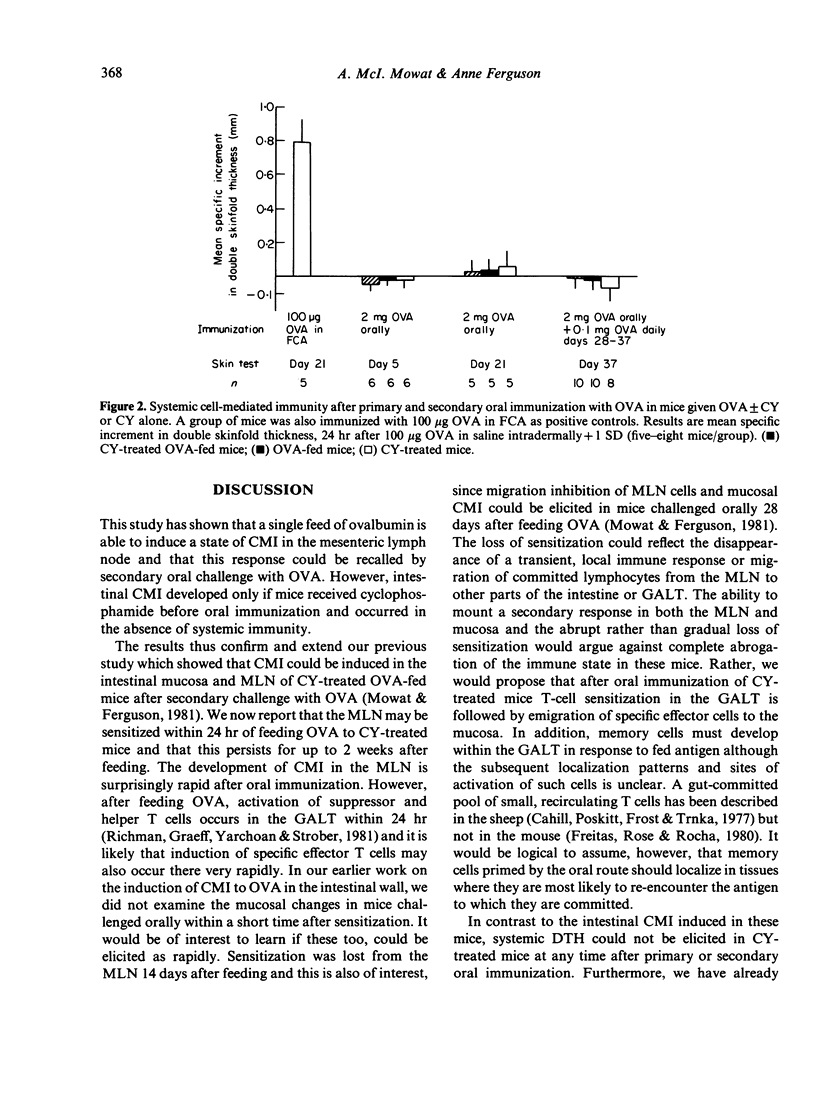


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cahill R. N., Poskitt D. C., Frost D. C., Trnka Z. Two distinct pools of recirculating T lymphocytes: migratory characteristics of nodal and intestinal T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):420–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Systemic tolerance and secretory immunity after oral immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1459–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolezel J., Bienenstock J. A and non- A immune response after oral and parenteral immunization of the hamster. Cell Immunol. 1971 Oct;2(5):458–468. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick G. T., Bohl E. H. Local and systemic cell-mediated immunity against transmissible gastroenteritis, an intestinal viral infection of swine. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1000–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rose M., Rocha B. Random recirculation of small T lymphocytes from thoracic duct lymph in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1980 Nov;56(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadol N., Waldman R. H., Clem L. W. Inhibition of macrophage migration by normal guinea pig intestinal secretions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Apr;151(4):654–658. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. S., Kraft S. C., Peterson R. D., Rothberg R. M. Relative absence of circulating antigen-reactive cells during oral immunization. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):757–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Waldman R. H. Cell-mediated immunity shown by lymphocytes from the respiratory tract. Science. 1970 Aug 14;169(3946):696–697. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3946.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley J., Newby T. J., Bourne F. J. The cell-mediated immune response of the pig to orally administered antigen. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):225–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Hanson D. G. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. IV. Evidence for tolerance and specific active suppression of cell-mediated immune responses to ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2344–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity in the small intestinal mucosa. V. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to a dietary antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):574–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Strobel S., Drummond H. E., Ferguson A. Immunological responses to fed protein antigens in mice. I. Reversal of oral tolerance to ovalbumin by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):105–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Yarchoan R., Strober W. Simultaneous induction of antigen-specific IgA helper T cells and IgG suppressor T cells in the murine Peyer's patch after protein feeding. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2079–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Parrott D. M., Bruce R. G. Migration of lymphoblasts to the small intestine. II. Divergent migration of mesenteric and peripheral immunoblasts to sites of inflammation in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1976 Nov;27(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


