Abstract
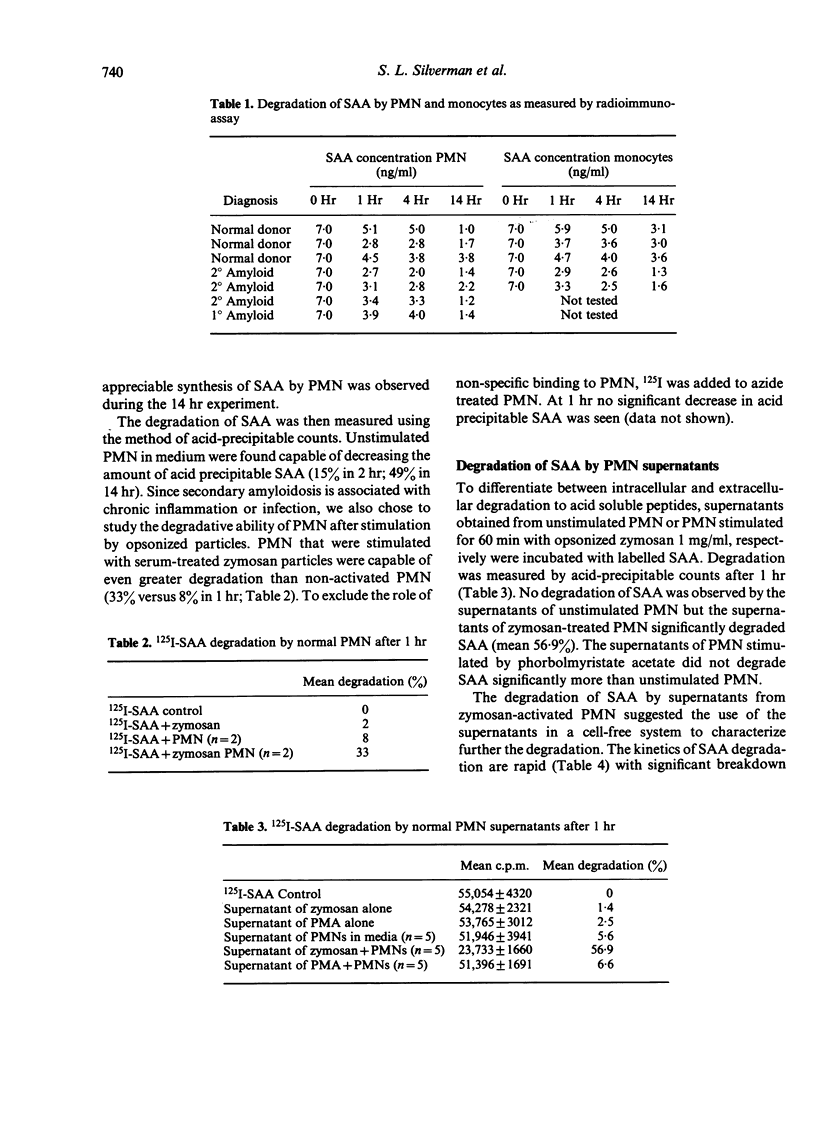
To determine the role of inflammation in amyloidogenesis, we have studied the degradation of human serum amyloid A (SAA) protein by purified preparations of human blood polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) and monocytes. When both PMN and monocytes were incubated in SAA-containing medium, the concentration of SAA as measured by a competitive anti-AA radioimmunoassay decreased over time. The rate of decrease of SAA was similar for both monocytes and PMN and there were no differences between four patients with amyloidosis and three normal controls. Resting PMN from normal volunteers were able to degrade SAA to smaller acid-soluble peptides within 16 hr while zymosan-activated PMN produced significant degradation within 1 hr (31%–50%). The supernatants from zymosan-treated PMN also caused marked SAA degradation within 1 hr.
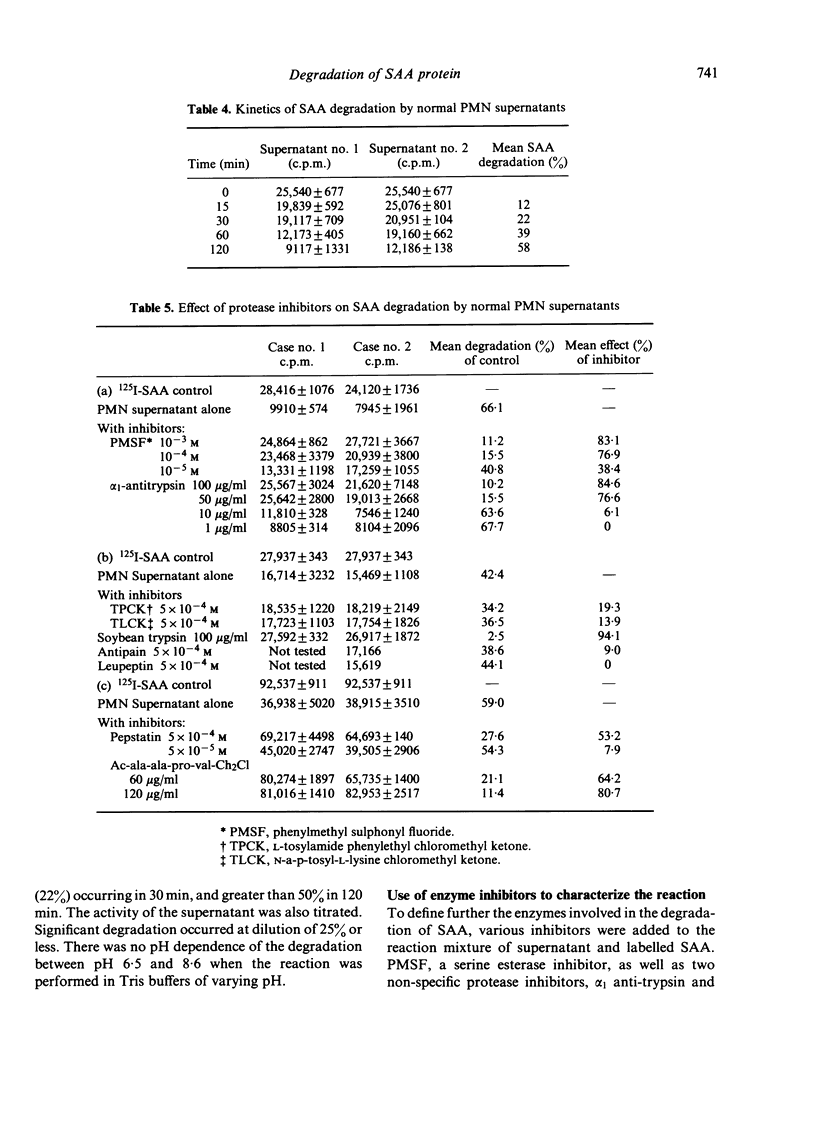
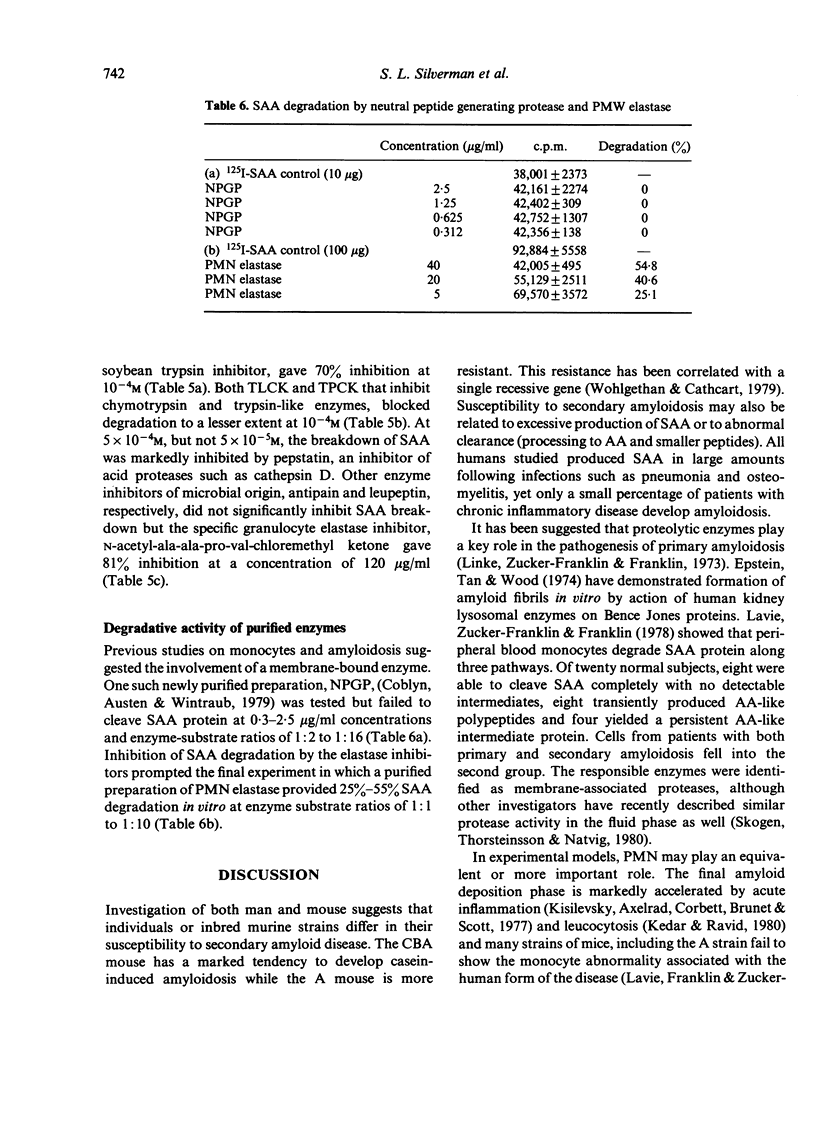
The following enzyme inhibitors were able to prevent degradation of SAA by PMN supernatants; phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride, a serine esterase inhibitor; α1 anti-trypsin and soybean trypsin inhibitor; and acetyl-ala-ala-pro-val-chloromethyl ketone, an elastase inhibitor. The ability of a neutral lysosomal enzyme to degrade SAA was further confirmed by showing that purified PMN elastase significantly degraded 125I-SAA.
We conclude that PMN contain one or more lysosomal enzymes capable of degrading SAA, an apoprotein of HDL3 serum lipoproteins. Alteration in SAA proteolysis by activated PMN may contribute to the deposition of amyloid fibrils in the tissues of patients with chronic inflammatory disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausserman L. L., Herbert P. N., McAdam K. P. Heterogeneity of human serum amyloid A proteins. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Kleiner E. Synthesis and secretion of serum amyloid protein A (SAA) by hepatocytes in mice treated with casein. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):495–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Scheinberg M. A., Shirahama T., Cathcart E. S., Skinner M. Kinetics of serum amyloid protein A in casein-induced murine amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):412–417. doi: 10.1172/JCI108654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coblyn J. S., Austen K. F., Wintroub B. U. Purification and characterization of a human neutrophil neutral protease. The neutral peptide-generating protease. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):998–1005. doi: 10.1172/JCI109400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V., Tan M., Wood I. S. Formation of "amyloid" fibrils in vitro by action of human kidney lysosomal enzymes on Bence Jones proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedar I., Ravid M. The role of polymorphonuclear leucocytes and T lymphocytes in experimental murine amyloidosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;10(1):63–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R., Axelrad M., Corbett W., Brunet S., Scott F. The role of inflammatory cells in the pathogenesis of amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1977 Dec;37(6):544–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Degradation of serum amyloid A protein by surface-associated enzymes of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1020–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Elastase-type proteases on the surface of human blood monocytes: possible role in amyloid formation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke R. P., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. D. Morphologic, chemical, and immunologic studies of amyloid-like fibrils formed from Bence Jones Proteins by proteolysis. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):10–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C., Gupton B. F., Harley A. D., Nishino N., Whitley R. J. Specificity of porcine pancreatic elastase, human leukocyte elastase and cathepsin G. Inhibition with peptide chloromethyl ketones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 23;485(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Sullivan L. Serum amyloid A: evidence for its origin in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1181–1186. doi: 10.1172/JCI109237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger M. J., McAdam K. P., Kaplan M. M., Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Monokine-induced synthesis of serum amyloid A protein by hepatocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):498–500. doi: 10.1038/285498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Dukor P., Zurier R. B. Effect of cyclic AMP on release of lysosomal enzymes from phagocytes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):131–135. doi: 10.1038/newbio231131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgethan J. R., Cathcart E. S. Amyloid resistance in A/J mice is determined by a single gene. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):453–454. doi: 10.1038/278453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Bralove D. A., Gallin J. I. The differential mobilization of human neutrophil granules. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate and ionophore A23187. Am J Pathol. 1977 May;87(2):273–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


