Abstract
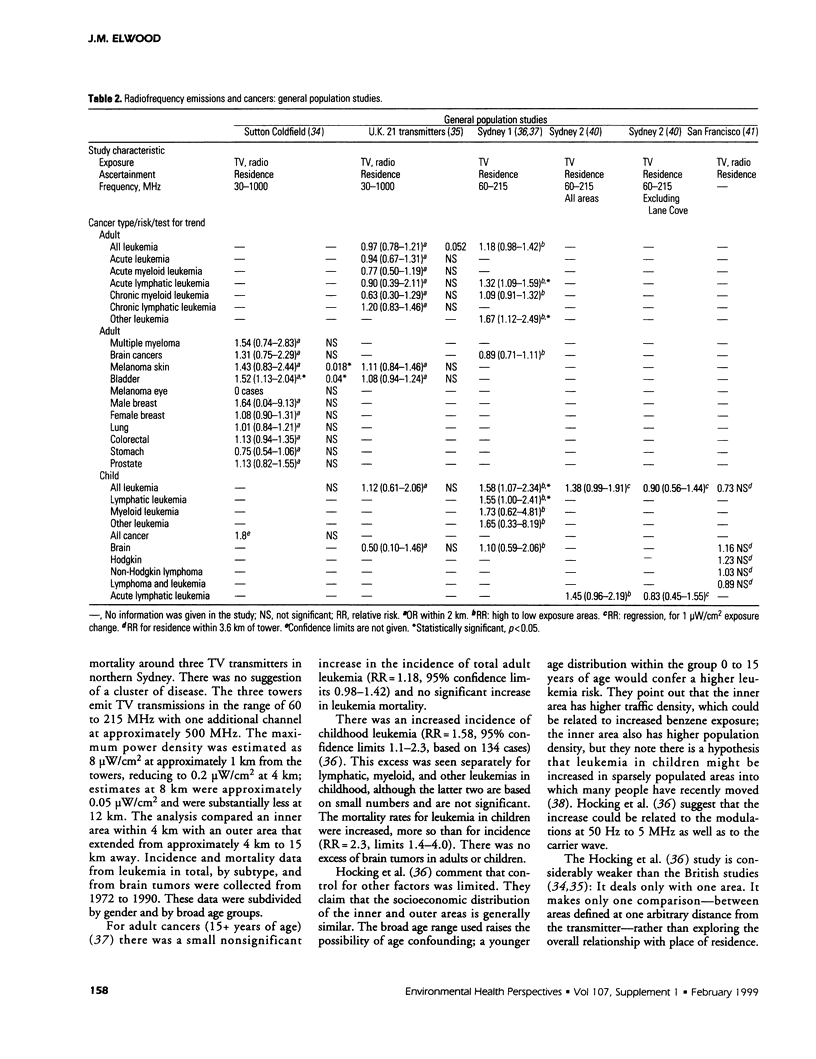
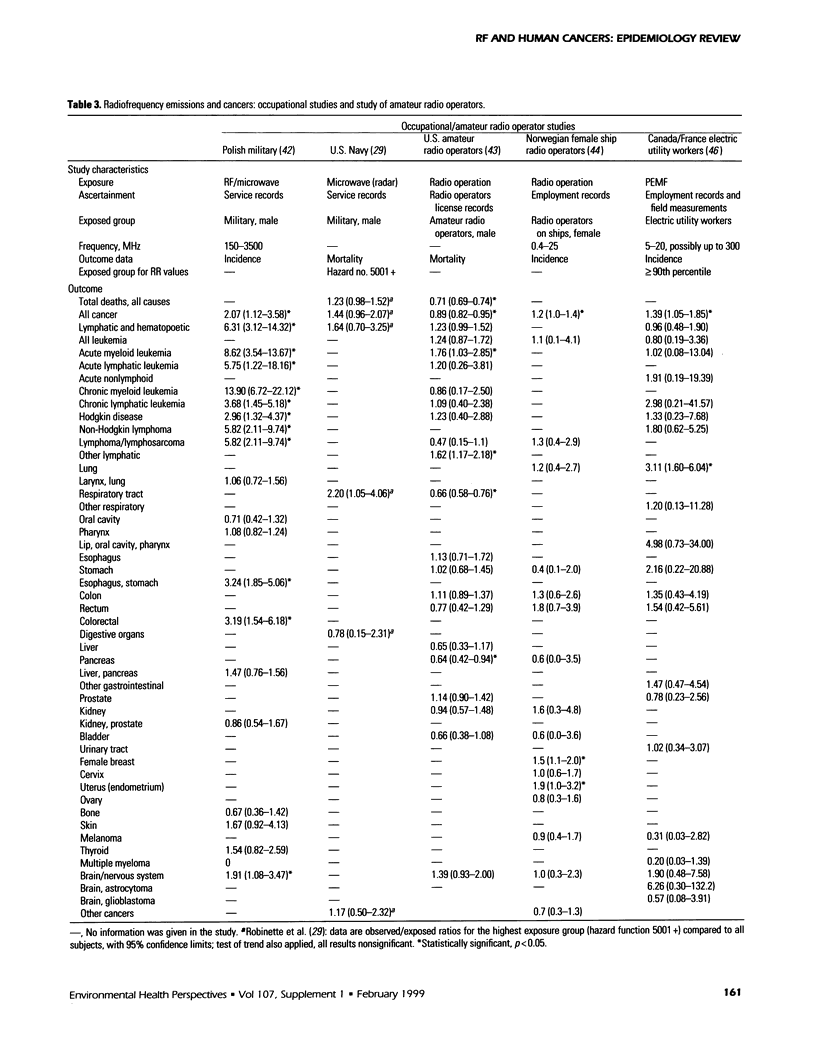
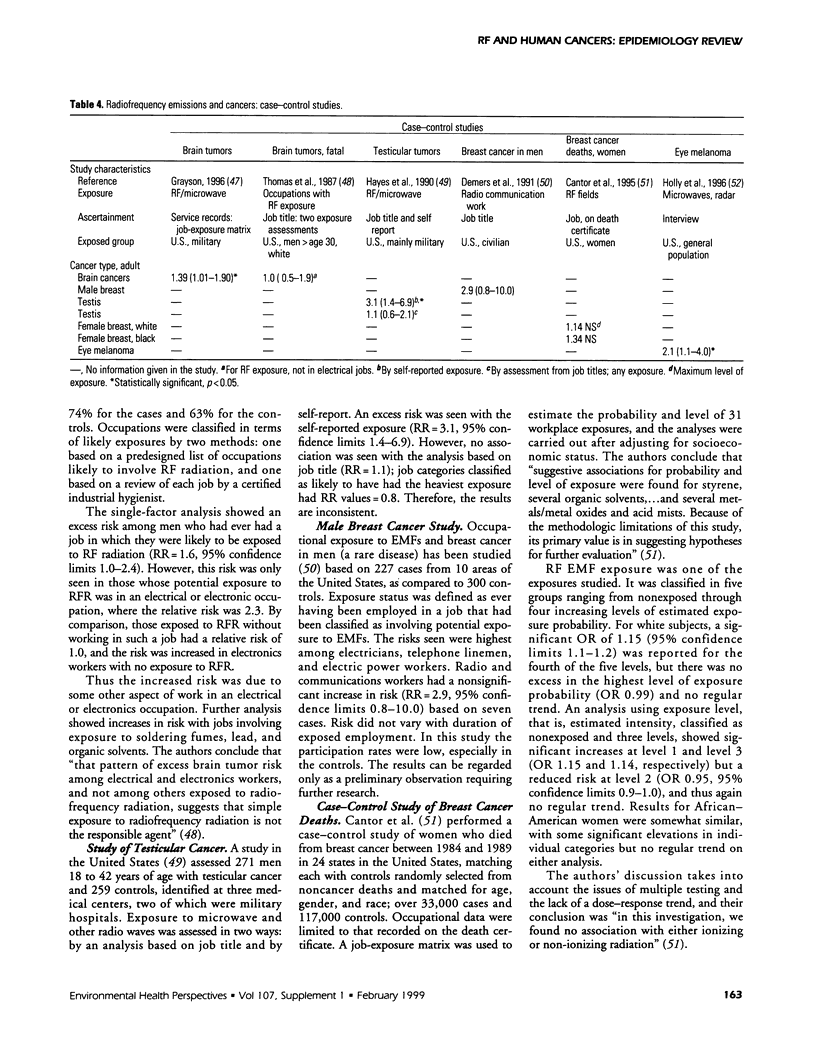
This paper reviews studies that have assessed associations between likely exposure to radiofrequency (RF) transmissions and various types of human cancer. These studies include three cluster investigations and five studies relating to general populations; all of these studies consider place of residence at the time of cancer diagnosis in regard to proximity to radio or television transmitters. There are also five relevant occupational cohort studies and several case-control studies of particular types of cancer. These studies assessed a large number of possible associations. Several positive associations suggesting an increased risk of some types of cancer in those who may have had greater exposure to RF emissions have been reported. However, the results are inconsistent: there is no type of cancer that has been consistently associated with RF exposures. The epidemiologic evidence falls short of the strength and consistency of evidence that is required to come to a reasonable conclusion that RF emissions are a likely cause of one or more types of human cancer. The evidence is weak in regard to its inconsistency, the design of the studies, the lack of detail on actual exposures, and the limitations of the studies in their ability to deal with other likely relevant factors. In some studies there may be biases in the data used
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert E. N., Slaby F., Roche J., Loftus J. Effect of amplitude-modulated 147 MHz radiofrequency radiation on calcium ion efflux from avian brain tissue. Radiat Res. 1987 Jan;109(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong B., Thériault G., Guénel P., Deadman J., Goldberg M., Héroux P. Association between exposure to pulsed electromagnetic fields and cancer in electric utility workers in Quebec, Canada, and France. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Nov 1;140(9):805–820. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRON C. I., BARAFF A. A. Medical considerations of exposure to microwaves (radar). J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Nov 1;168(9):1194–1199. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.03000090024006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcer-Kubiczek E. K., Harrison G. H. Neoplastic transformation of C3H/10T1/2 cells following exposure to 120-Hz modulated 2.45-GHz microwaves and phorbol ester tumor promoter. Radiat Res. 1991 Apr;126(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bawin S. M., Kaczmarek L. K., Adey W. R. Effects of modulated VHF fields on the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;247:74–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb35984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall C., Delzell E., Cole P., Brill I. Brain tumors among electronics industry workers. Epidemiology. 1996 Mar;7(2):125–130. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199603000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Kartun K., Pieper S., Adey W. R. Increased ornithine decarboxylase activity in cultured cells exposed to low energy modulated microwave fields and phorbol ester tumor promoters. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4222–4226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Lundak R. L., Fletcher R. M., Adey W. R. Alterations in protein kinase activity following exposure of cultured human lymphocytes to modulated microwave fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 1984;5(3):341–351. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor K. P., Stewart P. A., Brinton L. A., Dosemeci M. Occupational exposures and female breast cancer mortality in the United States. J Occup Environ Med. 1995 Mar;37(3):336–348. doi: 10.1097/00043764-199503000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Guy A. W., Kunz L. L., Johnson R. B., Crowley J. J., Krupp J. H. Long-term, low-level microwave irradiation of rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 1992;13(6):469–496. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250130605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Mostofi F. K. Cluster of testicular cancer in police officers exposed to hand-held radar. Am J Ind Med. 1993 Aug;24(2):231–233. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700240209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Guire L., Theriault G., Iturra H., Provencher S., Cyr D., Case B. W. Increased incidence of malignant melanoma of the skin in workers in a telecommunications industry. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Dec;45(12):824–828. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.12.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers P. A., Thomas D. B., Rosenblatt K. A., Jimenez L. M., McTiernan A., Stalsberg H., Stemhagen A., Thompson W. D., Curnen M. G., Satariano W. Occupational exposure to electromagnetic fields and breast cancer in men. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Aug 15;134(4):340–347. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjević Z., Kolak A., Stojković M., Ranković N., Ristić P. A study of the health status of radar workers. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1979 Apr;50(4):396–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolk H., Elliott P., Shaddick G., Walls P., Thakrar B. Cancer incidence near radio and television transmitters in Great Britain. II. All high power transmitters. Am J Epidemiol. 1997 Jan 1;145(1):10–17. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolk H., Shaddick G., Walls P., Grundy C., Thakrar B., Kleinschmidt I., Elliott P. Cancer incidence near radio and television transmitters in Great Britain. I. Sutton Coldfield transmitter. Am J Epidemiol. 1997 Jan 1;145(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaj-Vrhovac V., Fucić A., Horvat D. The correlation between the frequency of micronuclei and specific chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes exposed to microwave radiation in vitro. Mutat Res. 1992 Mar;281(3):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(92)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson O. M., McRobert T. L., Campbell L. J., Hocking B. A., Gordon I. A chromosomal study of workers with long-term exposure to radio-frequency radiation. Med J Aust. 1991 Sep 2;155(5):289–292. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1991.tb142282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith JR. Epidemiologic Evidence of Radiofrequency Radiation (Microwave) Effects on Health in Military, Broadcasting, and Occupational Studies. Int J Occup Environ Health. 1995 Jan;1(1):47–57. doi: 10.1179/oeh.1995.1.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson J. K. Radiation exposure, socioeconomic status, and brain tumor risk in the US Air Force: a nested case-control study. Am J Epidemiol. 1996 Mar 1;143(5):480–486. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Speculations on the cause of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 1988 Feb;2(2):120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. B. THE ENVIRONMENT AND DISEASE: ASSOCIATION OR CAUSATION? Proc R Soc Med. 1965 May;58:295–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. B., Brown L. M., Pottern L. M., Gomez M., Kardaun J. W., Hoover R. N., O'Connell K. J., Sutzman R. E., Javadpour N. Occupation and risk for testicular cancer: a case-control study. Int J Epidemiol. 1990 Dec;19(4):825–831. doi: 10.1093/ije/19.4.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking B., Gordon I. R., Grain H. L., Hatfield G. E. Cancer incidence and mortality and proximity to TV towers. Med J Aust. 1996 Dec 2;165(11-12):601–605. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb138661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking B., Gordon I., Hatfield G., Grain H. Re: "Cancer incidence near radio and television transmitters in Great Britain. I. Sutton Coldfield transmitter. II. All high power transmitters". Am J Epidemiol. 1998 Jan 1;147(1):90–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holly E. A., Aston D. A., Ahn D. K., Smith A. H. Intraocular melanoma linked to occupations and chemical exposures. Epidemiology. 1996 Jan;7(1):55–61. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199601000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvåle G., Heuch I., Nilssen S. Reproductive factors and cancers of the breast and genital organs--are the different cancer sites similarly affected? Cancer Detect Prev. 1991;15(5):369–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai H., Singh N. P. Acute low-intensity microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 1995;16(3):207–210. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250160309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai H., Singh N. P. Single- and double-strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1996 Apr;69(4):513–521. doi: 10.1080/095530096145814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litovitz T. A., Krause D., Penafiel M., Elson E. C., Mullins J. M. The role of coherence time in the effect of microwaves on ornithine decarboxylase activity. Bioelectromagnetics. 1993;14(5):395–403. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin J. H., Linet M. S., Boice J. D., Jr, Buckley J., Conrath S. M., Hatch E. E., Kleinerman R. A., Tarone R. E., Wacholder S., Robison L. L. Case-control study of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and residential radon exposure. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998 Feb 18;90(4):294–300. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.4.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyle D. B., Schechter P., Adey W. R., Lundak R. L. Suppression of T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity following exposure to sinusoidally amplitude-modulated fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 1983;4(3):281–292. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskarinec G., Cooper J., Swygert L. Investigation of increased incidence in childhood leukemia near radio towers in Hawaii: preliminary observations. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1994;13(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie D. R., Yin Y., Morrell S. Childhood incidence of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and exposure to broadcast radiation in Sydney--a second look. Aust N Z J Public Health. 1998;22(3 Suppl):360–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-842x.1998.tb01392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milham S., Jr Increased mortality in amateur radio operators due to lymphatic and hematopoietic malignancies. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Jan;127(1):50–54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern H. Uses of ecologic analysis in epidemiologic research. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1336–1344. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repacholi M. H., Basten A., Gebski V., Noonan D., Finnie J., Harris A. W. Lymphomas in E mu-Pim1 transgenic mice exposed to pulsed 900 MHZ electromagnetic fields. Radiat Res. 1997 May;147(5):631–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repacholi M. H. Low-level exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields: health effects and research needs. Bioelectromagnetics. 1998;19(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinette C. D., Silverman C., Jablon S. Effects upon health of occupational exposure to microwave radiation (radar). Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Jul;112(1):39–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J. A sobering start for the cluster busters' conference. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jul;132(1 Suppl):S6–13. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J., Chou C. K., Morgan R., Balzano Q., Guy A. W., Funch D. P., Preston-Martin S., Mandel J., Steffens R., Carlo G. Assessment of cellular telephone and other radio frequency exposure for epidemiologic research. Epidemiology. 1996 May;7(3):291–298. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199605000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santini R., Hosni M., Deschaux P., Pacheco H. B16 melanoma development in black mice exposed to low-level microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 1988;9(1):105–107. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250090110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Ali S., Behari J. Effect of low power microwave on the mouse genome: a direct DNA analysis. Mutat Res. 1994 Jan;320(1-2):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvin S., Schulman J., Merrill D. W. Distance and risk measures for the analysis of spatial data: a study of childhood cancers. Soc Sci Med. 1992 Apr;34(7):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(92)90364-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmigielski S., Szudzinski A., Pietraszek A., Bielec M., Janiak M., Wrembel J. K. Accelerated development of spontaneous and benzopyrene-induced skin cancer in mice exposed to 2450-MHz microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 1982;3(2):179–191. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. L., Stolley P. D., Stemhagen A., Fontham E. T., Bleecker M. L., Stewart P. A., Hoover R. N. Brain tumor mortality risk among men with electrical and electronics jobs: a case-control study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Aug;79(2):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynes T., Hannevik M., Andersen A., Vistnes A. I., Haldorsen T. Incidence of breast cancer in Norwegian female radio and telegraph operators. Cancer Causes Control. 1996 Mar;7(2):197–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00051295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnqvist S., Knave B., Ahlbom A., Persson T. Incidence of leukaemia and brain tumours in some "electrical occupations". Br J Ind Med. 1991 Sep;48(9):597–603. doi: 10.1136/oem.48.9.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vågerö D., Ahlbom A., Olin R., Sahlsten S. Cancer morbidity among workers in the telecommunications industry. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Mar;42(3):191–195. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M. Comment on "Acute low-intensity microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain cells" by Henry Lai and Narendra P. Singh. Bioelectromagnetics. 1996;17(2):165–166. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-186X(1996)17:2<165::AID-BEM12>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


