Abstract
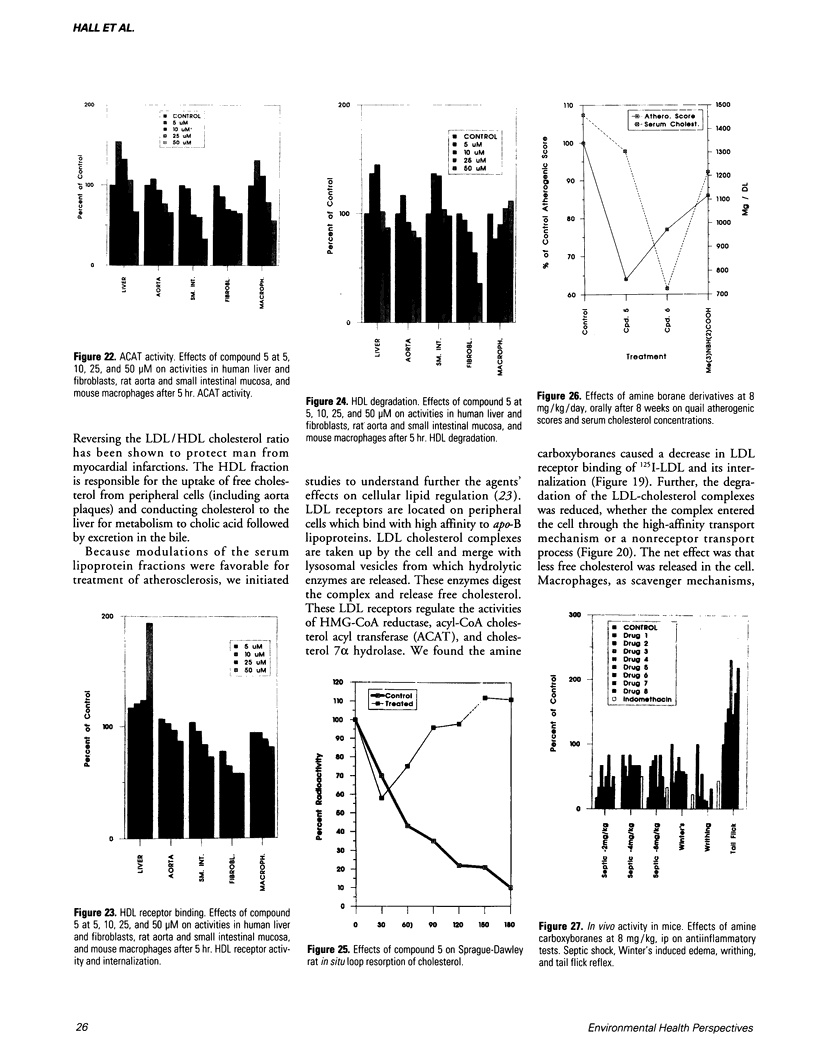
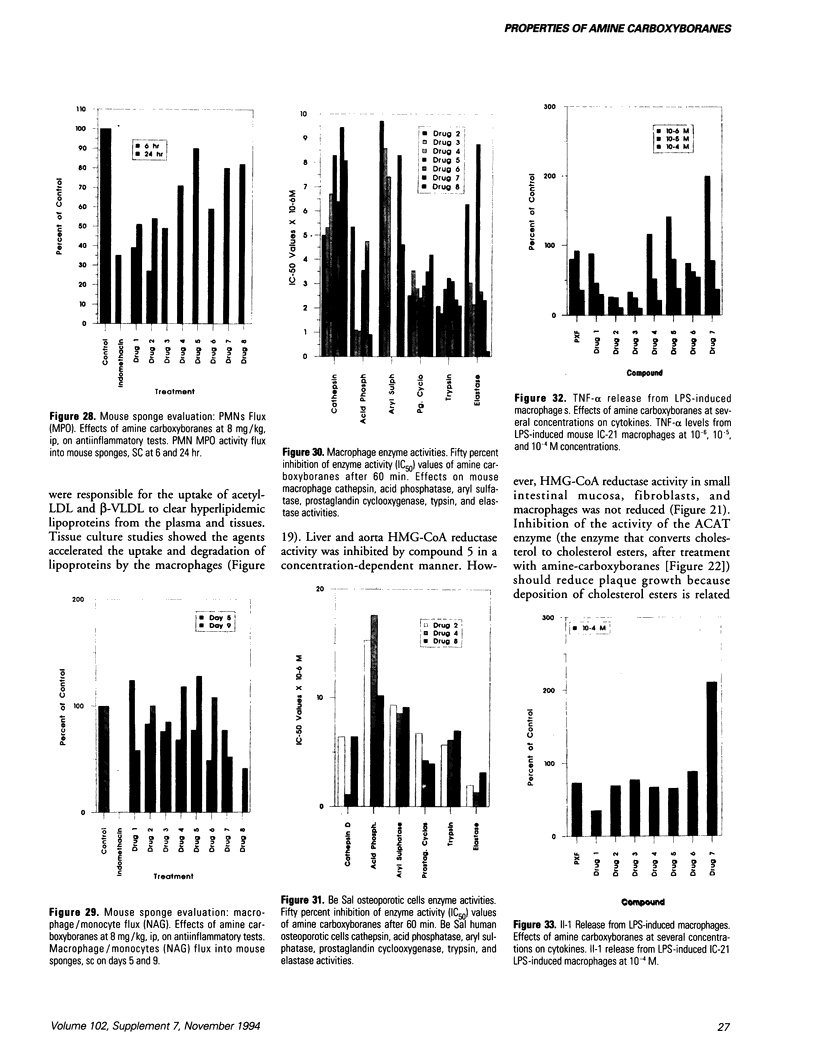
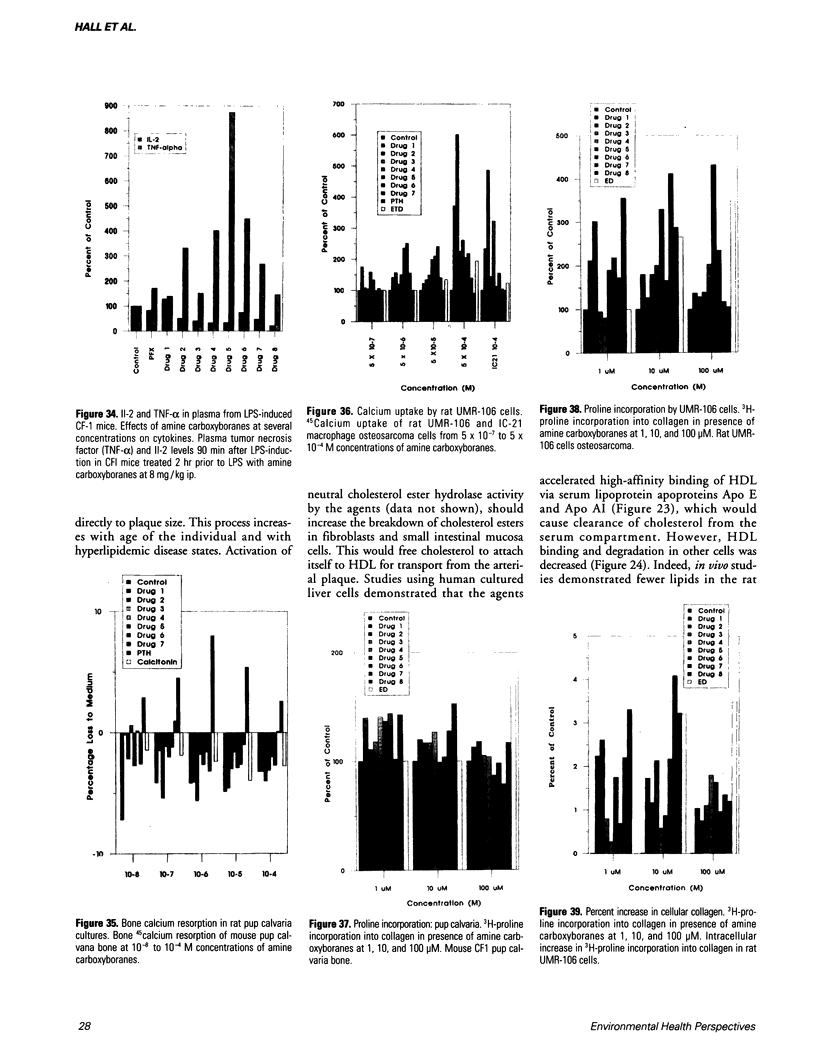
The amine-carboxyborane derivatives were shown to be effective antineoplastic/cytotoxic agents with selective activity against single-cell and solid tumors derived from murine and human leukemias, lymphomas, sarcomas, and carcinomas. The agents inhibited DNA and RNA synthesis in preference to protein synthesis in L1210 lymphoid leukemia cells. Inosine-monophosphate dehydrogenase apparently is a target site of the compounds; similar effects on phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate amido transferase, orotidine-monophosphate decarboxylase, and both nucleoside and nucleotide kinases were observed. Deoxyribonucleotide pool levels were reduced in the cells; DNA strand scission was observed with the agents. In rodents, the amine carboxyboranes were potent hypolipidemic agents, lowering both serum cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations, in addition to lowering cholesterol content of very low-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and elevating high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentrations. De novo regulatory enzymes involved in lipid synthesis were also inhibited (e.g., hypocholesterolemic 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-Coenzyme A reductase, acyl-Coenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase, and sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase). Concurrently, the agents modulated LDL and HDL receptor binding, internalization, and degradation, so that less cholesterol was delivered to the plaques and more broken down from esters and conducted to the liver for biliary excretion. Tissue lipids in the aorta wall of the rat were reduced and fewer atherosclerotic morphologic lesions were present in quail aortas after treatment with the agents. Cholesterol resorption from the rat intestine was reduced in the presence of drug. Genetic hyperlipidemic mice demonstrated the same types of reduction after treatment with the agents. The agents would effectively lower lipids in tissue based on the inhibition of regulatory enzymes in pigs. These findings should help improve domestic meat supplies from fowl and pigs. The amine-carboxyboranes were effective anti-inflammatory agents against septic shock, induced edema, pleurisy, and chronic arthritis at 2.5 to 8 mg/kg. Lysosomal and proteolytic enzyme activities were also inhibited. More significantly, the agents were dual inhibitors of prostaglandin cyclooxygenase and 5'-lipoxygenase activities. These compounds also affected cytokine release and white cell migration. Subsequent studies showed that the amine-carboxyboranes were potent anti-osteoporotic agents reducing calcium resorption as well as increasing calcium and proline incorporation into mouse pup calvaria and rat UMR-106 collagen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey P. J. Sponge implants as models. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:327–334. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M. K., Maiti P. K., Roy S., Mittakanti M., Morse K. W., Hall I. H. Relationship of hypolipidemic and antineoplastic activities of tricyclohexyl- and triphenylphosphine boranes, carboxyboranes, cyanoboranes, and related derivatives. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 1992 May;325(5):267–272. doi: 10.1002/ardp.19923250504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilon G., Raisz L. G. Comparison of the effects of stimulators and inhibitors of resorption on the release of lysosomal enzymes and radioactive calcium from fetal bone in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):1969–1975. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. L., Belliotti T. R., Boctor A. M., Connor D. T., Kostlan C. R., Nies D. E., Ortwine D. F., Schrier D. J., Sircar J. C. Styrylpyrazoles, styrylisoxazoles, and styrylisothiazoles. Novel 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1991 Feb;34(2):518–525. doi: 10.1021/jm00106a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Brotherton R. J., Docks E. L., Griffin T. S., Sood A., Spielvogel B. F. Hypolipidemic activity of some hydropolyborate salts in rodents. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(8):1007–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Das M. K., Harchelroad F., Jr, Wisian-Neilson P., McPhail A. T., Spielvogel B. F. Antihyperlipidemic activity of amine cyanoboranes, amine carboxyboranes, and related compounds. J Pharm Sci. 1981 Mar;70(3):339–341. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600700333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Gilbert C. J., McPhail A. T., Morse K. W., Hassett K., Spielvogel B. F. Antineoplastic activity of a series of boron analogues of alpha-amino acids. J Pharm Sci. 1985 Jul;74(7):755–758. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600740712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Griffin T. S., Docks E. L., Brotherton R. J., Futch G. Hypolipidemic activity of N,N-dimethyl-n-octadecylamine borane in rodents. J Pharm Sci. 1986 Jul;75(7):706–710. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600750719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Hall E. S., Chi L. K., Shaw B. R., Sood A., Spielvogel B. F. Antineoplastic activity of boron-containing thymidine nucleosides in Tmolt3 leukemic cells. Anticancer Res. 1992 Jul-Aug;12(4):1091–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Hall E. S., Wong O. T. The anti-neoplastic activity of 2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione and N-butyl-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in human and murine tumor cells. Anticancer Drugs. 1992 Feb;3(1):55–62. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199202000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Izydore R., Hall E. S., Miller M. C., 3rd, Daniels D. L., Debnath M. L., Woodard T. The antineoplastic and cytotoxicity of benzohydroxamic acids and related derivatives in murine and human tumor cells. Anticancer Drugs. 1992 Jun;3(3):273–280. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199206000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Lee K. H., Starnes C. O., Muraoka O., Sumida Y., Waddell T. G. Antihyperlipidemic activity of sesquiterpene lactones and related compounds. J Pharm Sci. 1980 Jun;69(6):694–697. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600690622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Simlot R., Oswald C. B., Murthy A. R., elSourady H., Chapman J. M., Jr The anti-inflammatory activity of 5H-dibenz[c,e]azepine-5,7(6H)dione, 6,7-dihydro-5H-dibenz[c,e]azepine, N-benzoylbenzamide and 1H-benz[d,e]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)dione derivatives in rodents. Acta Pharm Nord. 1990;2(6):387–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Spielvogel B. F., Griffin T. S., Docks E. L., Brotherton R. J. The effects of boron hypolipidemic agents on LDL and HDL receptor binding and related enzyme activities of rat hepatocytes, aorta cells and human fibroblasts. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;65(3):297–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Spielvogel B. F., Sood A., Ahmed F., Jafri S. Hypolipidemic activity of trimethylamine-carbomethoxyborane and related derivatives in rodents. J Pharm Sci. 1987 May;76(5):359–365. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. H., Spielvogel B. F., Sood A. The antineoplastic activity of trimethylamine carboxyboranes and related esters and amides in murine and human tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 1990 Dec;1(2):133–141. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199012000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko I., Hazama-Shimada Y., Endo A. Inhibitory effects on lipid metabolism in cultured cells of ML-236B, a potent inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. G., Swingle K. F. 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-(2'-thenoyl)phenol(R-830): a novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent with antioxidant properties. Agents Actions. 1982 Dec;12(5-6):674–683. doi: 10.1007/BF01965078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A., Sood C. K., Spielvogel B. F., Hall I. H., Wong O. T., Mittakanti M., Morse K. Synthesis and hypolipidemic activity of amine-carboxyboranes, and their amides and esters in rodents. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 1991 Jul;324(7):423–432. doi: 10.1002/ardp.19913240705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A., Sood C. K., Spielvogel B. F., Hall I. H., Wong O. T. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory activities of amine-boranes and esters of boron analogues of choline and thiocholine. J Pharm Sci. 1992 May;81(5):458–462. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600810514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A., Spielvogel B. F., Shaw B. R., Carlton L. D., Burnham B. S., Hall E. S., Hall I. H. The synthesis and antineoplastic activity of 2'-deoxy-nucleoside-cyanoboranes in murine and human culture cells. Anticancer Res. 1992 Mar-Apr;12(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood C. K., Sood A., Spielvogel B. F., Yousef J. A., Burnham B., Hall I. H. Synthesis and antineoplastic activity of some cyano-, carboxy-, carbomethoxy-, and carbamoylborane adducts of heterocyclic amines. J Pharm Sci. 1991 Dec;80(12):1133–1140. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600801209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielvogel B. F., Sood A., Morse K. W., Wong O. T., Hall I. H. The cytotoxicity of amine-cyanoboranes, amine-cyanoalkylboranes and aminomethyl-phosphonate cyanoborane adducts against the growth of murine and human tissue culture cells. Pharmazie. 1991 Aug;46(8):592–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P. H., Krieger N. S. Comparison of fetal rat limb bones and neonatal mouse calvaria: effects of parathyroid hormone and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Calcif Tissue Int. 1983;35(2):172–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02405027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


