Abstract
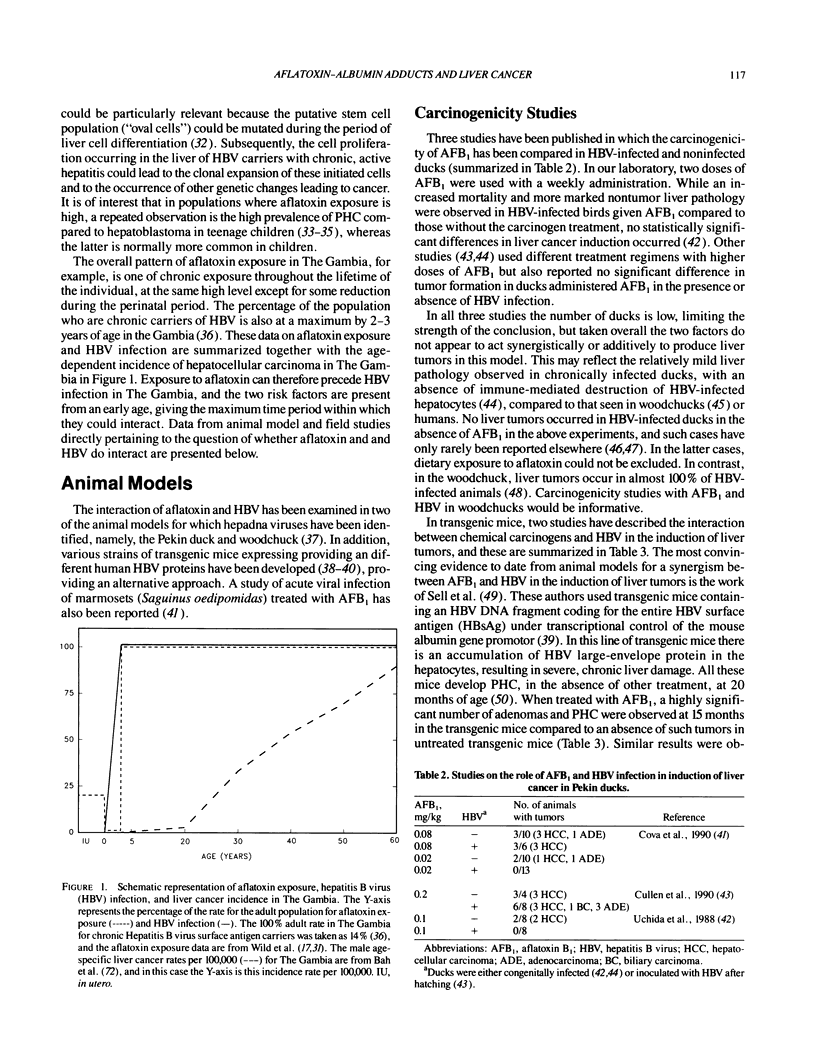
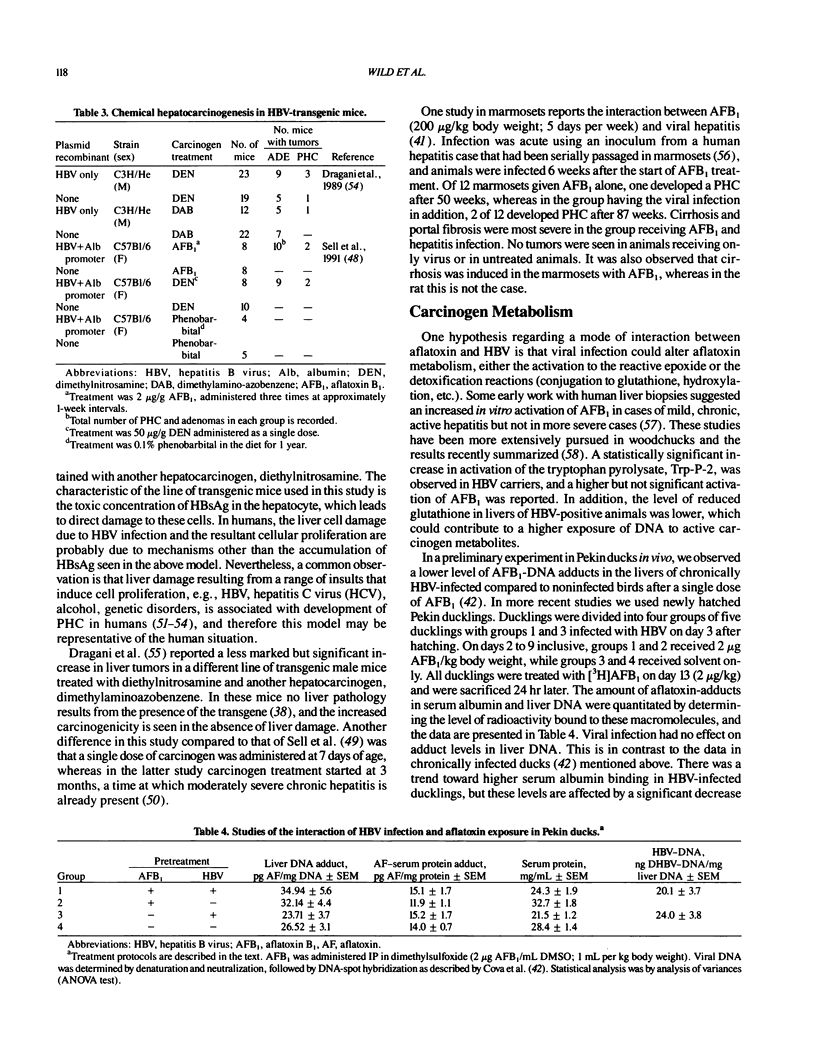
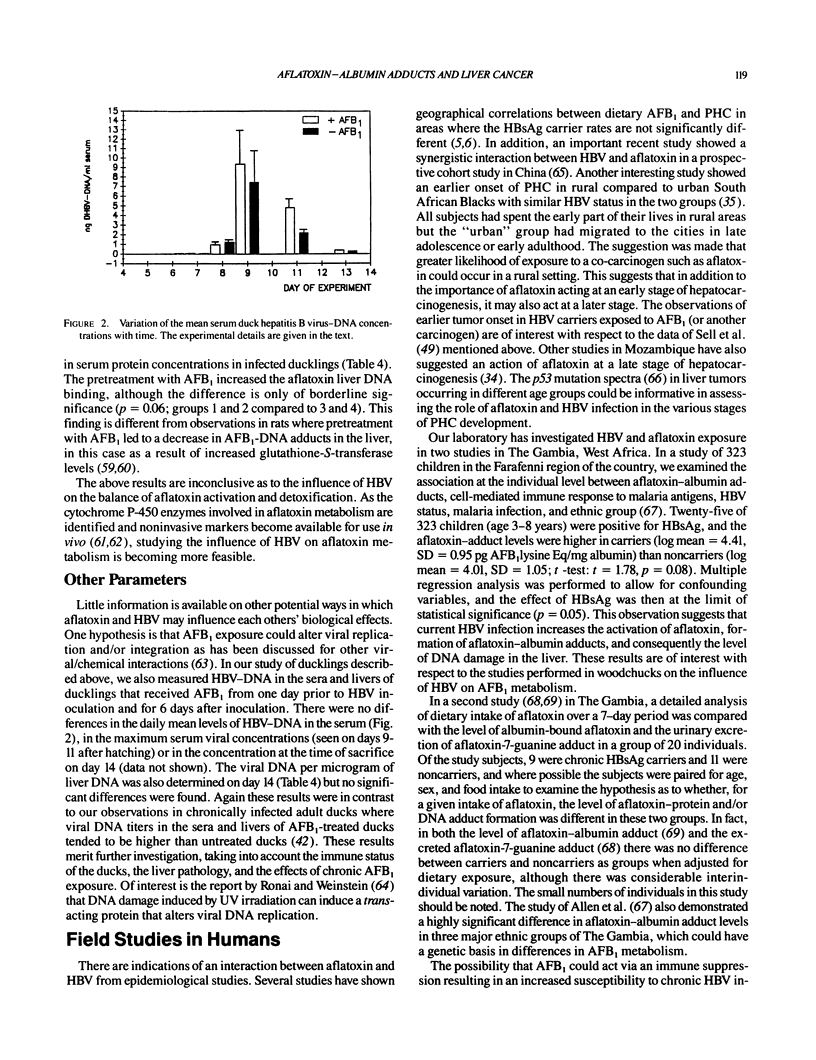
Aflatoxin exposure and hepatitis B virus infection have been implicated as major risk factors for primary hepatocellular carcinoma (PHC) in high-incidence regions of the world. Investigations using the assay of aflatoxin bound to peripheral blood albumin have shown that exposure can occur throughout the life span of the individual, including during the perinatal period, in high-incidence areas such as The Gambia, Senegal, Kenya, and The People's Republic of China. The possibility of measuring aflatoxin exposure at the individual level permits an investigation of the putative mechanisms of interaction of this carcinogen with HBV in the etiopathogenesis of PHC. Animal models, e.g., Pekin duck and HBV-transgenic mice, have also been used to study these questions, and the available data are reviewed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babinet C., Farza H., Morello D., Hadchouel M., Pourcel C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1160–1163. doi: 10.1126/science.3865370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Kew M., Wands J., Ozturk M. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):429–431. doi: 10.1038/350429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. D., DeLoia J. A., elAwady M. K., Gearhart J. D. Tissue preferential expression of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen gene in two lines of HBV transgenic mice. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.649-654.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron H. M., Warwick G. P. Primary cancer of the liver in Kenyan children. Br J Cancer. 1977 Dec;36(6):793–803. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell T. C., Chen J. S., Liu C. B., Li J. Y., Parpia B. Nonassociation of aflatoxin with primary liver cancer in a cross-sectional ecological survey in the People's Republic of China. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6882–6893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Pinkert C. A., Milich D. R., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1157–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.3865369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen J. M., Marion P. L., Sherman G. J., Hong X., Newbold J. E. Hepatic neoplasms in aflatoxin B1-treated, congenital duck hepatitis B virus-infected, and virus-free pekin ducks. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):4072–4080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen J. M., Ruebner B. H., Hsieh L. S., Hyde D. M., Hsieh D. P. Carcinogenicity of dietary aflatoxin M1 in male Fischer rats compared to aflatoxin B1. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 1;47(7):1913–1917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Flora S., Bennicelli C., Camoirano A., Izzotti A., Hietanen E., Bartsch H., Picciotto A., Millman I. Metabolic activation of food hepatocarcinogens in hepatitis B virus-infected humans and animals. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;347:167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Flora S., Romano M., Basso C., Serra D., Astengo M., Picciotto A. Metabolic activation of hepatocarcinogens in chronic hepatitis B. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov;144(3):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(85)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinhardt F., Holmes A. W., Capps R. B., Popper H. Studies on the transmission of human viral hepatitis to marmoset monkeys. I. Transmission of disease, serial passages, and description of liver lesions. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):673–688. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragani T. A., Manenti G., Farza H., Della Porta G., Tiollais P., Pourcel C. Transgenic mice containing hepatitis B virus sequences are more susceptible to carcinogen-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jun;11(6):953–956. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsford H. A., Sell S., Chisari F. V. Hepatocarcinogenesis due to chronic liver cell injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3400–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan L. S., Skipper P. L., Peng X. C., Groopman J. D., Chen J. S., Wogan G. N., Tannenbaum S. R. Serum albumin adducts in the molecular epidemiology of aflatoxin carcinogenesis: correlation with aflatoxin B1 intake and urinary excretion of aflatoxin M1. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jul;9(7):1323–1325. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.7.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. D., Hall A. J., Whittle H., Hudson G. J., Wogan G. N., Montesano R., Wild C. P. Molecular dosimetry of aflatoxin-N7-guanine in human urine obtained in The Gambia, West Africa. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Mar-Apr;1(3):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Shimada T. Oxidation of toxic and carcinogenic chemicals by human cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol. 1991 Jul-Aug;4(4):391–407. doi: 10.1021/tx00022a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. C., Garner R. C. Immunological and HPLC detection of aflatoxin adducts in human tissues after an acute poisoning incident in S.E. Asia. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Apr;12(4):741–743. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward N. K., Walker G. J., Graham W., Cooksley E. Hepatocellular carcinoma mutation. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):764–764. doi: 10.1038/352764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh L. L., Hsu S. W., Chen D. S., Santella R. M. Immunological detection of aflatoxin B1-DNA adducts formed in vivo. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6328–6331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Metcalf R. A., Sun T., Welsh J. A., Wang N. J., Harris C. C. Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):427–428. doi: 10.1038/350427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imwidthaya S., Anukarahanonta T., Komolpis P. Bacterial, fungal and aflatoxin contamination of cereals and cereal products in Bangkok. J Med Assoc Thai. 1987 Jul;70(7):390–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M. C., Rossouw E., Hodkinson J., Paterson A., Dusheiko G. M., Whitcutt J. M. Hepatitis B virus status of southern African Blacks with hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison between rural and urban patients. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., Garro A., Leo M. A., Mak K. M., Worner T. Alcohol and cancer. Hepatology. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):1005–1019. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limmer J., Fleig W. E., Leupold D., Bittner R., Ditschuneit H., Beger H. G. Hepatocellular carcinoma in type I glycogen storage disease. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):531–537. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Liu C., Svoboda D. J. Long term effects of aflatoxin B1 and viral hepatitis on marmoset liver. A preliminary report. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):267–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loury D. N., Hsieh D. P. Effects of chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin M1 on the in vivo covalent binding of aflatoxin B1 to hepatic macromolecules. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1984;13(4-6):575–587. doi: 10.1080/15287398409530522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutwick L. I. Relation between aflatoxin, hepatitis-B virus, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1979 Apr 7;1(8119):755–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Knight S. S., Ho B. K., Guo Y. Y., Robinson W. S., Popper H. Liver disease associated with duck hepatitis B virus infection of domestic ducks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):898–902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Taylor J. M. Experimental systems for the study of hepadnavirus and hepatitis delta virus infections. Hepatology. 1989 Apr;9(4):635–645. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal G. E., Metcalfe S. A., Legg R. F., Judah D. H., Green J. A. Mechanism of the resistance to cytotoxicity which precedes aflatoxin B1 hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(5):457–461. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.5.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Fischer R., Sonnenberg A., Stremmel W., Trampisch H. J., Strohmeyer G. Survival and causes of death in cirrhotic and in noncirrhotic patients with primary hemochromatosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 14;313(20):1256–1262. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511143132004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olubuyide I. O., Makarananda K., Judah D. J., Neal G. E. Investigation of the assay of AFB1-albumin adducts using proteolysis products in ELISA. Int J Cancer. 1991 May 30;48(3):468–472. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk M. p53 mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma after aflatoxin exposure. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1356–1359. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92236-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers F., Bosch X., Kaldor J., Linsell A., Pluijmen M. Aflatoxin exposure, hepatitis B virus infection and liver cancer in Swaziland. Int J Cancer. 1987 May 15;39(5):545–553. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Roth L., Purcell R. H., Tennant B. C., Gerin J. L. Hepatocarcinogenicity of the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):866–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Shih J. W., Gerin J. L., Wong D. C., Hoyer B. H., London W. T., Sly D. L., Purcell R. H. Woodchuck hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation of histologic with virologic observations. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):91–98. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronai Z. A., Weinstein I. B. Identification of a UV-induced trans-acting protein that stimulates polyomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1057–1060. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1057-1060.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. K., Yuan J. M., Yu M. C., Wogan G. N., Qian G. S., Tu J. T., Groopman J. D., Gao Y. T., Henderson B. E. Urinary aflatoxin biomarkers and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1992 Apr 18;339(8799):943–946. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91528-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbioni G., Ambs S., Wogan G. N., Groopman J. D. The aflatoxin-lysine adduct quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography from human serum albumin samples. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Nov;11(11):2063–2066. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.11.2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Hunt J. M., Dunsford H. A., Chisari F. V. Synergy between hepatitis B virus expression and chemical hepatocarcinogens in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 15;51(4):1278–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Is there a liver stem cell? Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3811–3815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Hirohata T., Koga S., Sugimachi K., Kanematsu T., Ohryohji F., Nawata H., Ishibashi H., Maeda Y., Kiyokawa H. Hepatitis C and hepatitis B in the etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Japanese population. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):2842–2847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Suzuki K., Esumi M., Arii M., Shikata T. Influence of aflatoxin B1 intoxication on duck livers with duck hepatitis B virus infection. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1559–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vall Mayans M., Hall A. J., Inskip H. M., Chotard J., Lindsay S. W., Coromina E., Mendy M., Alonso P. L., Whittle H. Risk factors for transmission of hepatitis B virus to Gambian children. Lancet. 1990 Nov 3;336(8723):1107–1109. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92580-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rensburg S. J., Cook-Mozaffari P., Van Schalkwyk D. J., Van der Watt J. J., Vincent T. J., Purchase I. F. Hepatocellular carcinoma and dietary aflatoxin in Mozambique and Transkei. Br J Cancer. 1985 May;51(5):713–726. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B. Synergistic interactions between chemical carcinogens, tumor promoters, and viruses and their relevance to human liver cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 1989;14(2):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Hudson G. J., Sabbioni G., Chapot B., Hall A. J., Wogan G. N., Whittle H., Montesano R., Groopman J. D. Dietary intake of aflatoxins and the level of albumin-bound aflatoxin in peripheral blood in The Gambia, West Africa. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Mar-Apr;1(3):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Jiang Y. Z., Allen S. J., Jansen L. A., Hall A. J., Montesano R. Aflatoxin-albumin adducts in human sera from different regions of the world. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2271–2274. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Jiang Y. Z., Sabbioni G., Chapot B., Montesano R. Evaluation of methods for quantitation of aflatoxin-albumin adducts and their application to human exposure assessment. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Montesano R. Correspondence re: T. Colin Campbell et al., Nonassociation of aflatoxin with primary liver cancer in a cross-sectional ecological survey in the People's Republic of China. Cancer Res., 50:6882-6893, 1990. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3825–3827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Pionneau F. A., Montesano R., Mutiro C. F., Chetsanga C. J. Aflatoxin detected in human breast milk by immunoassay. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):328–333. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. P., Rasheed F. N., Jawla M. F., Hall A. J., Jansen L. A., Montesano R. In-utero exposure to aflatoxin in west Africa. Lancet. 1991 Jun 29;337(8757):1602–1602. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93295-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson A. P., Denning D. W., Morgan M. R. Analysis of UK sera for aflatoxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Hum Toxicol. 1988 Jul;7(4):353–356. doi: 10.1177/096032718800700410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C. R. Metabolic factors in cancer susceptibility. Cancer Surv. 1990;9(3):437–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh F. S., Yu M. C., Mo C. C., Luo S., Tong M. J., Henderson B. E. Hepatitis B virus, aflatoxins, and hepatocellular carcinoma in southern Guangxi, China. Cancer Res. 1989 May 1;49(9):2506–2509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Zhou Y. Z., Imazeki F., Okuda K. Duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and serum of Chinese ducks: integration of viral DNA in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5180–5184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarba A., Wild C. P., Hall A. J., Montesano R., Hudson G. J., Groopman J. D. Aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk from The Gambia, west Africa, quantified by combined monoclonal antibody immunoaffinity chromatography and HPLC. Carcinogenesis. 1992 May;13(5):891–894. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.5.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


