Abstract
The activation of a variety of cell surface receptors results in a biphasic increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration due to the release or mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores and to the entry of Ca2+ from the extracellular space. It is well established that phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis is responsible for the changes in Ca2+ homeostasis. Stimulation of Ca2(+)-mobilizing receptors also results in the phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of the minor plasma membrane phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, with the concomitant formation of inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate [1,4,5)IP3) and diacylglycerol. Analogous to the adenylyl cyclase signaling system, receptor-mediated stimulation of phospholipase C also appears to be mediated by one or more intermediary guanine nucleotide-dependent regulatory proteins. There is strong evidence that (1,4,5)IP3 stimulates Ca2+ release from intracellular stores. The Ca2(+)-releasing actions of (1,4,5)IP3 are terminated by its metabolism through two distinct pathways. (1,4,5)IP3 is dephosphorylated by a 5-phosphatase to inositol (1,4) bisphosphate; alternatively, (1,4,5)IP3 can be phosphorylated to inositol (1,3,4,5) tetrakisphosphate by a 3-kinase. Whereas the mechanism of Ca2+ mobilization is understood, the precise mechanisms involved in Ca2+ entry are not known. A recent proposal that (1,4,5)IP3 secondarily elicits Ca2+ entry by emptying an intracellular Ca2+ pool will be considered. This review summarizes our current understanding of the mechanisms by which inositol phosphates regulate cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Nature of the receptor-regulated calcium pool in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:557–565. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. The metabolism of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate to inositol 1,3-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9444–9447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., García A., Posadas C., García-Sáinz J. A. Differential effect of pertussis toxin on the affinity state for agonists of renal alpha 1- and alpha 2- adrenoceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8076–8079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Bross T. E., Irvine R. F., Majerus P. W. The metabolism of tris- and tetraphosphates of inositol by 5-phosphomonoesterase and 3-kinase enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2146–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Wilson D. B., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of the inositol cyclic phosphate products of phosphoinositide cleavage by phospholipase C. Metabolism in cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):122–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfert D. M., Hill S., Pershadsingh H. A., Sherman W. R., McDonald J. M. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes Ca2+ from isolated adipocyte endoplasmic reticulum but not from plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):37–44. doi: 10.1042/bj2360037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate concentration relative to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in pancreatic minilobules on stimulation with carbamylcholine in the absence of lithium. Possible role as a second messenger in long- but not short-term responses. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13892–13895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Refai M. F., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Evidence for two alpha-adrenergic binding sites in liver plasma membranes. Studies with [3H]epinephrine and [3H]dihydroergocryptine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4375–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Martin M. W., Hughes A. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive, high affinity binding of carbachol to muscarinic cholinergic receptors of 1321N1 astrocytoma cells is insensitive to pertussis toxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Uhing R. J., Exton J. H. Solubilization of the vasopressin receptor from rat liver plasma membranes. Evidence for a receptor X GTP-binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16871–16877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Guanine nucleotides stimulate production of inositol trisphosphate in rat cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):799–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2320799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Geynet P., Hanoune J. Hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptors show agonist-specific regulation by guanine nucleotides. Loss of nucleotide effect after adrenalectomy. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11577–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. Enzyme secretion and the incorporation of P32 into phospholipides of pancreas slices. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):967–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Potentiation by thrombin of the secretion of serotonin from permeabilized platelets equilibrated with Ca2+ buffers. Relationship to protein phosphorylation and diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):351–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2220351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Receptor-induced diacylglycerol formation in permeabilized platelets; possible role for a GTP-binding protein. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):605–629. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Berrie C. P., Morris A. J., Downes C. P. Inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate is not a product of muscarinic receptor-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2430211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Berridge M. J. Inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates in GH4 cells. J Exp Biol. 1985 Nov;119:395–401. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Interaction of the stimulatory and inhibitory regulatory proteins of the adenylyl cyclase system with the catalytic component of cyc-S49 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13178–13185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Bansal V. S., Majerus P. W. Pathway for inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and 1,4-bisphosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol phosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization from Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Inositol(1,3,4,5)tetrakisphosphate-induced activation of sea urchin eggs requires the presence of inositol trisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Gardner P. Ion channels activated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in plasma membrane of human T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):301–304. doi: 10.1038/326301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
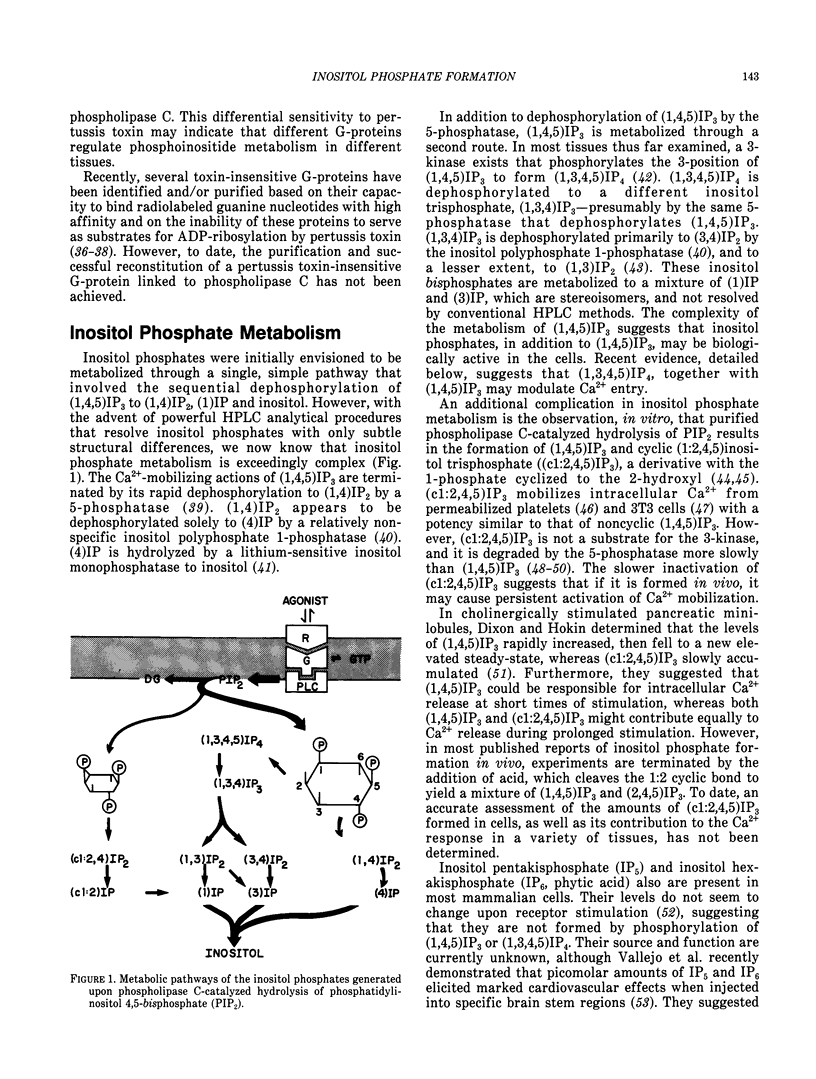
- Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A., Martin T. F. Direct stimulation by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in GH3 cell membranes by a guanine nucleotide-modulated mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Prpic V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Effect of islet-activating pertussis toxin on the binding characteristics of Ca2+-mobilizing hormones and on agonist activation of phosphorylase in hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;29(2):196–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Martin M. W., Harden T. K., Brown J. H. Pertussis toxin does not inhibit muscarinic-receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis or calcium mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):933–937. doi: 10.1042/bj2270933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17362–17369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Calcium, phospholipid turnover and transmembrane signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 5;302(1108):101–112. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1983.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandol S. J., Schoeffield M. S., Fimmel C. J., Muallem S. The agonist-sensitive calcium pool in the pancreatic acinar cell. Activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ influx mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16963–16968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B., Lew P. D. Ca2+ homeostasis in permeabilized human neutrophils. Characterization of Ca2+-sequestering pools and the action of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13777–13782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Poggioli J., Weiss S. J. Receptor regulation of calcium release and calcium permeability in parotid gland cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):37–45. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragan C. I., Watling K. J., Gee N. S., Aspley S., Jackson R. G., Reid G. G., Baker R., Billington D. C., Barnaby R. J., Leeson P. D. The dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4-bisphosphate to inositol in liver and brain involves two distinct Li+-sensitive enzymes and proceeds via inositol 4-phosphate. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):143–148. doi: 10.1042/bj2490143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Parry J. B., Tang E. K., Irvine R. F., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Metabolism of D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate by rat liver, including the synthesis of a novel isomer of myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):139–147. doi: 10.1042/bj2460139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack B. E., Bell J. E., Benos D. J. Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate injection mimics fertilization potentials in sea urchin eggs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C340–C344. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smigel M. D. Purification of the catalyst of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1976–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snavely M. D., Insel P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes in the rat renal cortex. Differential regulation of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors by guanyl nucleotides and Na. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):532–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Carter N., Chahwala S. B., Morris A. J., Whetton A. D., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate is present in both mammalian and avian cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2490271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Bayerdörffer E., Haase W., Irvine R. F., Schulz I. Effect of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate on isolated subcellular fractions of rat pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):241–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. A guanine nucleotide-dependent regulatory protein couples substance P receptors to phospholipase C in rat parotid gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Putney J. W., Jr Size of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive calcium pool in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):435–438. doi: 10.1042/bj2320435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W., Gill D. L. Influence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and guanine nucleotides on intracellular calcium release within the N1E-115 neuronal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3184–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Jiang H., Prpic V., Exton J. H. Regulation of a liver plasma membrane phosphoinositide phosphodiesterase by guanine nucleotides and calcium. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80394-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Jackson T., Lightman S., Hanley M. R. Occurrence and extracellular actions of inositol pentakis- and hexakisphosphate in mammalian brain. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):656–658. doi: 10.1038/330656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Evans T., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K., Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Identification and purification from bovine brain of a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein distinct from Gs, Gi and Go. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):431–439. doi: 10.1042/bj2460431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Bross T. E., Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides by purified sheep seminal vesicle phospholipase C enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11718–11724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Bross T. E., Sherman W. R., Berger R. A., Majerus P. W. Inositol cyclic phosphates are produced by cleavage of phosphatidylphosphoinositols (polyphosphoinositides) with purified sheep seminal vesicle phospholipase C enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4013–4017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W., Sherman W. R., Tyler A. N., Rubin L. J., Brown J. E. Isolation and characterization of the inositol cyclic phosphate products of polyphosphoinositide cleavage by phospholipase C. Physiological effects in permeabilized platelets and Limulus photoreceptor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13496–13501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


