Abstract
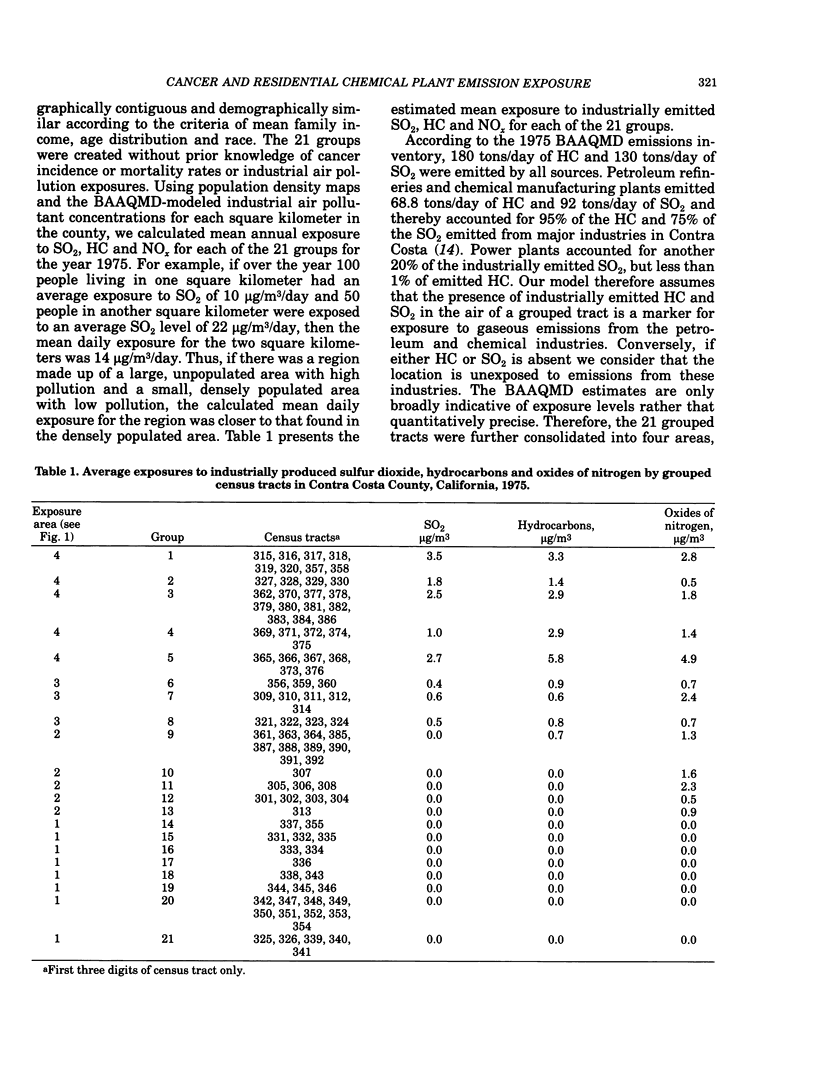
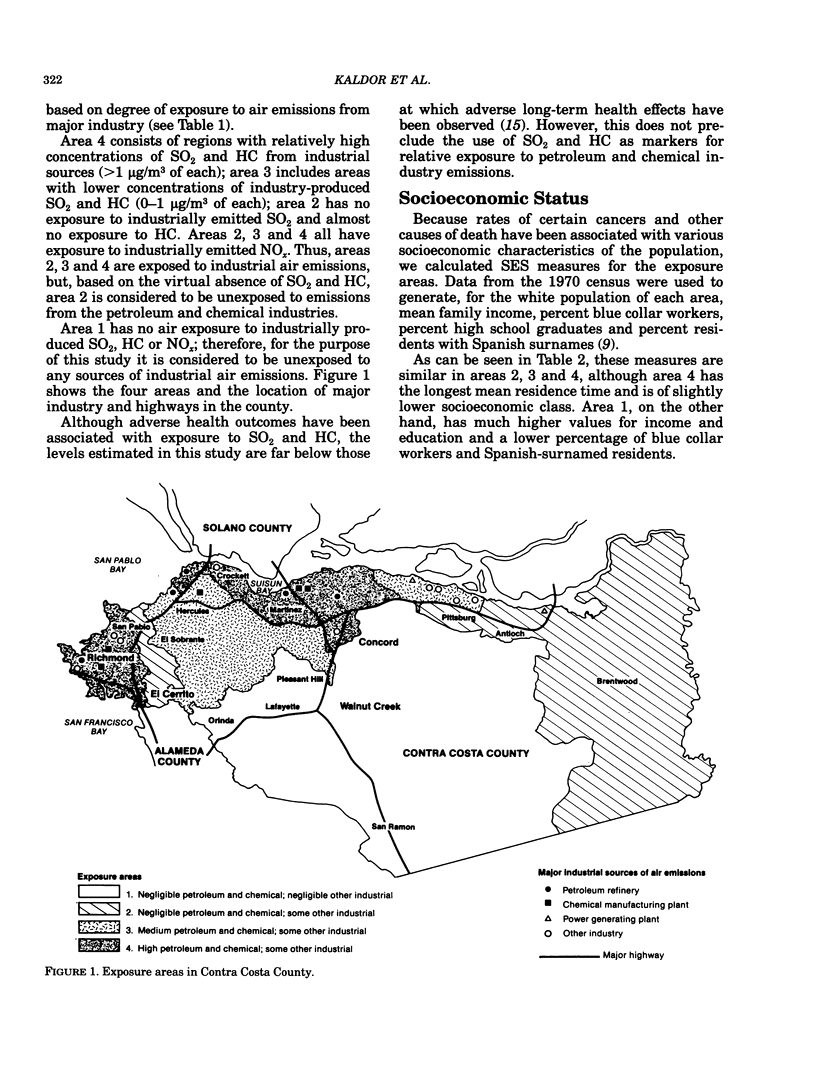
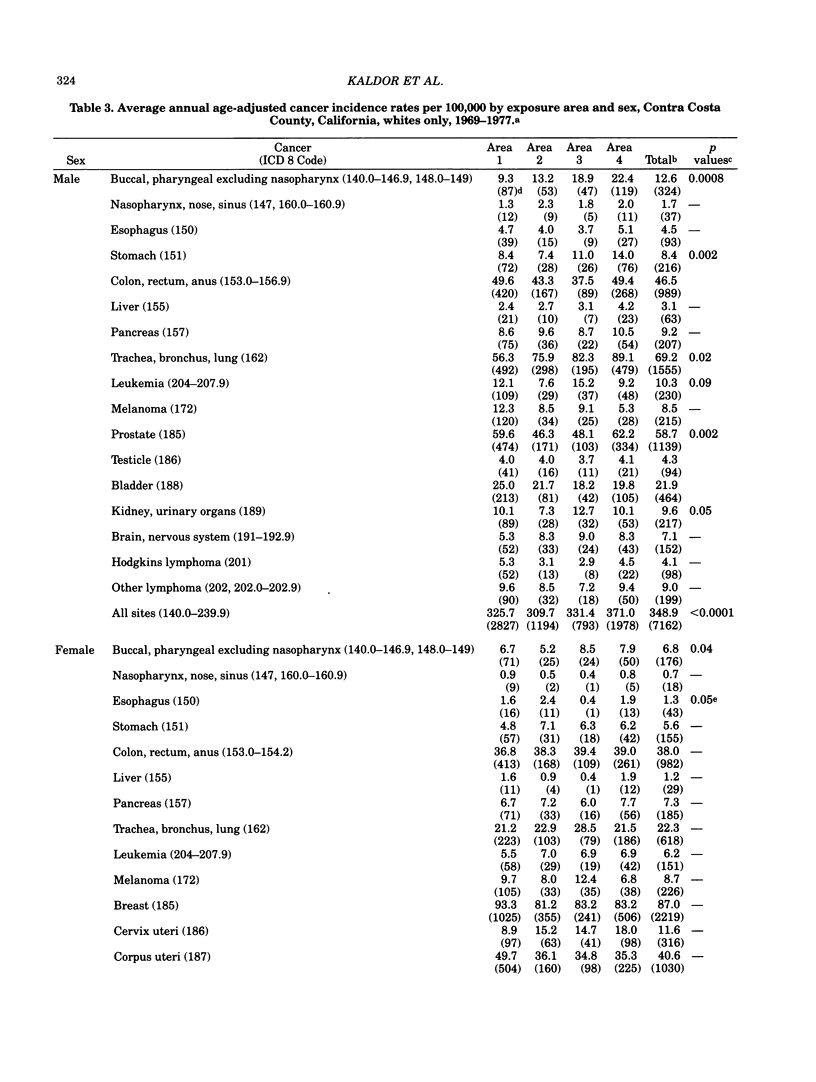
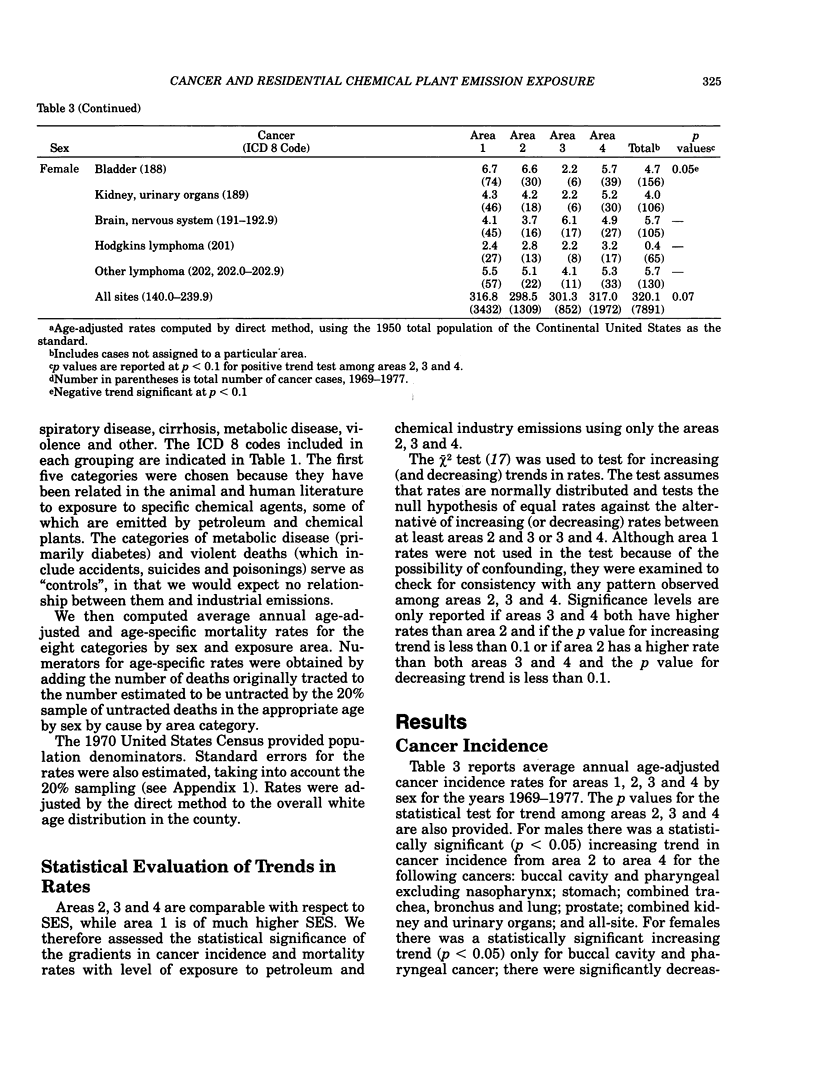
An ecologic study design was used to investigate the relationship between exposure to air emissions produced by the petroleum and chemical industries, and average annual cancer incidence and major cause mortality rates among whites in Contra Costa County, California. Estimates for the exposure to major industrial sources of sulfur dioxide, hydrocarbons and oxides of nitrogen were used to subdivide the county by level of exposure to petroleum refinery and chemical plant emissions. Cancer incidence and major cause mortality rates were then calculated for whites in each of the exposure areas. In both males and females, residential exposure to petroleum and chemical air emissions was associated with an increased incidence of cancer of the buccal cavity and pharynx. In males, age-adjusted incidence rates for cancers of the stomach, lung, prostate and kidney and urinary organs were also associated with petroleum and chemical plant air emission exposures. In both sexes, we found a strong positive association between degree of residential exposure and death rates from cardiovascular disease and cancer, and a less strong positive association between exposure and death rates from cerebrovascular disease. There was also a positive association in men for deaths from cirrhosis of the liver. Although these observed associations occurred across areas of similar socioeconomic and broad occupational class, confounding variables and the "ecologic fallacy" must be considered as possible explanations. In particular, the stronger findings in men suggest an occupational explanation of the cancer incidence trends, and the effect observed in cirrhosis mortality suggests that lifestyle variables such as alcohol consumption were not adequately controlled for. While the public health implications of our findings remain unclear, the evidence presented is sufficient to warrant follow-up studies based on individual data in which possible biases can be more readily controlled.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blot W. J., Brinton L. A., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Stone B. J. Cancer mortality in U.S. counties with petroleum industries. Science. 1977 Oct 7;198(4312):51–53. doi: 10.1126/science.897679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Geographic patterns of lung cancer: industrial correlations. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Jun;103(6):539–550. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S. Lung cancer and the petroleum industry in Louisiana. J Occup Med. 1980 Jun;22(6):384–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Shear C. L., Seale D. B. Lung cancer mortality and residential proximity to industry. Environ Health Perspect. 1982 Nov;45:157–164. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8245157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanis N. M., Stavraky K. M., Fowler J. L. Cancer mortality in oil refinery workers. J Occup Med. 1979 Mar;21(3):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearey C. D., Ury H., Siegelaub A., Ho M. K., Salomon H., Cella R. L. Lack of association between cancer incidence and residence near petrochemical industry in the San Francisco Bay area. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jun;64(6):1295–1299. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.6.1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. E., Gordon R. J., Menck H., Soohoo J., Martin S. P., Pike M. C. Lung cancer and air pollution in southcentral Los Angeles County. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Jun;101(6):477–488. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Cancer mortality in U.S. counties with chemical industries. Environ Res. 1975 Apr;9(2):196–207. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(75)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesselman J. J. Assessing effects of confounding variables. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Jul;108(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. L., Decoufle P., Moure-Eraso R. Mortality among workers employed in petroleum refining and petrochemical plants. J Occup Med. 1980 Feb;22(2):97–103. doi: 10.1097/00043764-198002000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


