Abstract
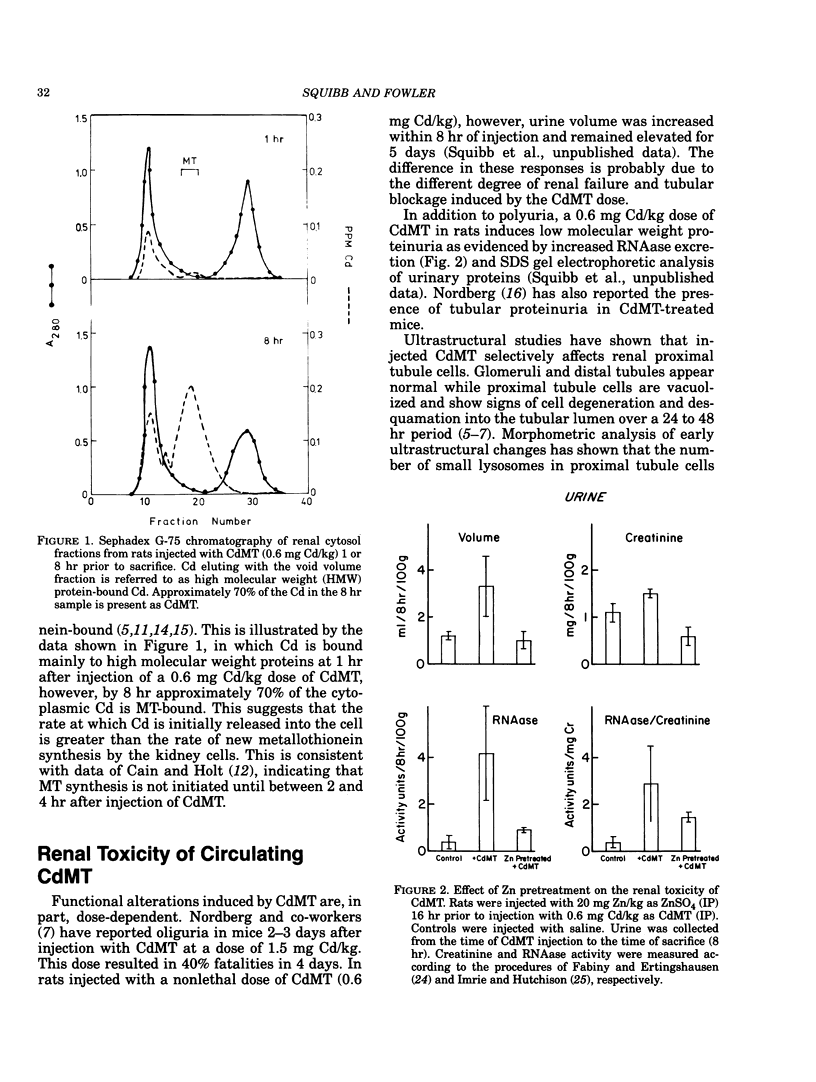
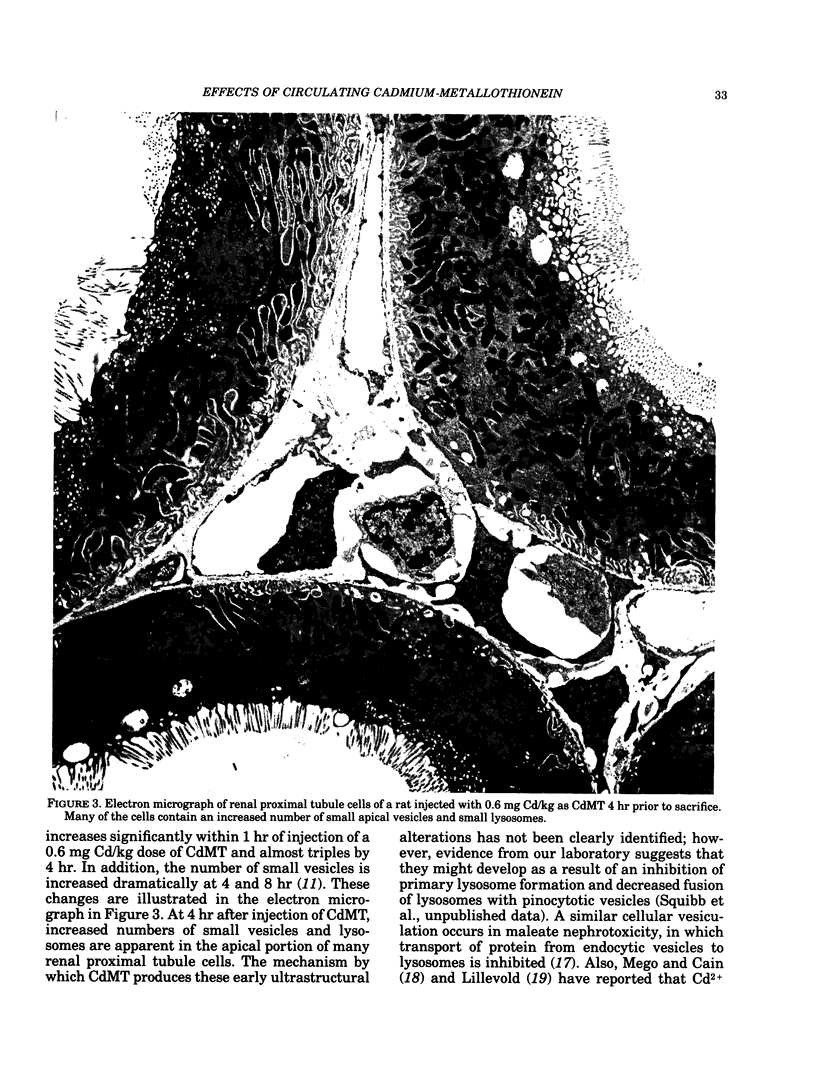
The mechanism of cadmium-metallothionein (CdMT)-mediated nephrotoxicity is being studied in rats using an acute dose regimen. Results of metabolism studies have shown that injected CdMT is rapidly degraded by the kidney with the release of Cd2+ into the cell cytoplasm. Ultrastructural studies indicate that an increase in the number of small lysosomes is the first measurable effect of CdMT in the kidney at 1 hr. This is followed by an increase in the number of small vesicles at 4 hr. It is proposed that these effects are the result of decreased primary lysosome formation and an inhibition of the fusion of pinocytotic vesicles with cell lysosomes by Cd. Functional alterations measured 8 hr after CdMT injection include an increase in urine volume and increased excretion of the low molecular weight protein, RNAase. Prior induction of renal MT by Zn pretreatment prevents the induction of polyuria and low molecular weight proteinuria by CdMT. These data provide further evidence that CdMT nephrotoxicity occurs as a result of Cd2+ toxicity within the cell.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremner I., Hoekstra W. G., Davies N. T., Young B. W. Metabolism of 35S-labelled copper-, zinc-and cadmium-thionein in the rat. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Dec;23(3):355–367. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan S. E., Hidalgo H. A. Nuclear 115cadmium: uptake and disappearance correlated with cadmium-binding protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):858–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain K., Holt D. E. Studies of cadmium-thionein induced nephropathy: time course of cadmium-thionein uptake and degradation. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Feb;43(2):223–237. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Vander Mallie R. J., Garvey J. S. A radioimmunoassay for human metallothionein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;55(1):94–102. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherian M. G., Goyer R. A., Delaquerriere-Richardson L. Cadmium-metallothionein-induced nephropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;38(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherian M. G., Goyer R. A. Methallothioneins and their role in the metabolism and toxicity of metals. Life Sci. 1978 Jul 3;23(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherian M. G., Shaikh Z. A. Metabolism of intravenously injected cadmium-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):863–869. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E. I., Maunsbach A. B. Proteinuria induced by sodium maleate in rats: effects on ultrastructure and protein handling in renal proximal tubule. Kidney Int. 1980 Jun;17(6):771–787. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiny D. L., Ertingshausen G. Automated reaction-rate method for determination of serum creatinine with the CentrifiChem. Clin Chem. 1971 Aug;17(8):696–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes E. C. Renal tubular transport of cadmium-metallothionein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;45(2):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo H. A., Koppa V., Bryan S. E. Effect of cadmium on RNA-polymerase and protein sythesis in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imrie R. C., Hutchison W. C. Changes in the activity of rat adrenal ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor after administration of corticotrophin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 6;108(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillevold P. E. Effect of cadmium acetate on the uptake and degradation of formaldehyde-treated 125I-labelled human serum albumin in rat liver non-parenchymal cells in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Nov 15;29(22):3103–3105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mego J. L., Cain J. A. An effect of cadmium and heterolysosome formation and function in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jun 15;24(11-12):1227–1232. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg G. F., Goyer R., Nordberg M. Comparative toxicity of cadmium-metallothionein and cadmium chloride on mouse kidney. Arch Pathol. 1975 Apr;99(4):192–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg G. F. Renal effects of mercury- and cadmium-metallothionein. Experientia Suppl. 1979;34:347–350. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6493-0_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh Z. A. Metallothionein as a storage protein for cadmium: its toxicological implications. Dev Toxicol Environ Sci. 1982;9:69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Pritchard J. B., Fowler B. A. Renal metabolism and toxicity of metallothionein. Dev Toxicol Environ Sci. 1982;9:181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Ridlington J. W., Carmichael N. G., Fowler B. A. Early cellular effects of circulating cadmium-thionein on kidney proximal tubules. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Feb;28:287–296. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7928287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. T., Yamamura M. Rat kidney metallothionein induced by injection of Cd-thionein: Changes of chromatographic properties with time and their relation to copper content and kidney dysfunction. Toxicol Lett. 1980 Feb;5(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(80)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M., Etienne A. T. Studies on the toxicity and metabolism of cadmium-thionein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 1;26(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. Functions of hepatic and renal metallothioneins in the control of the metabolism of cadmium and certain other bivalent cations. Experientia Suppl. 1979;34:313–320. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6493-0_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]