Abstract
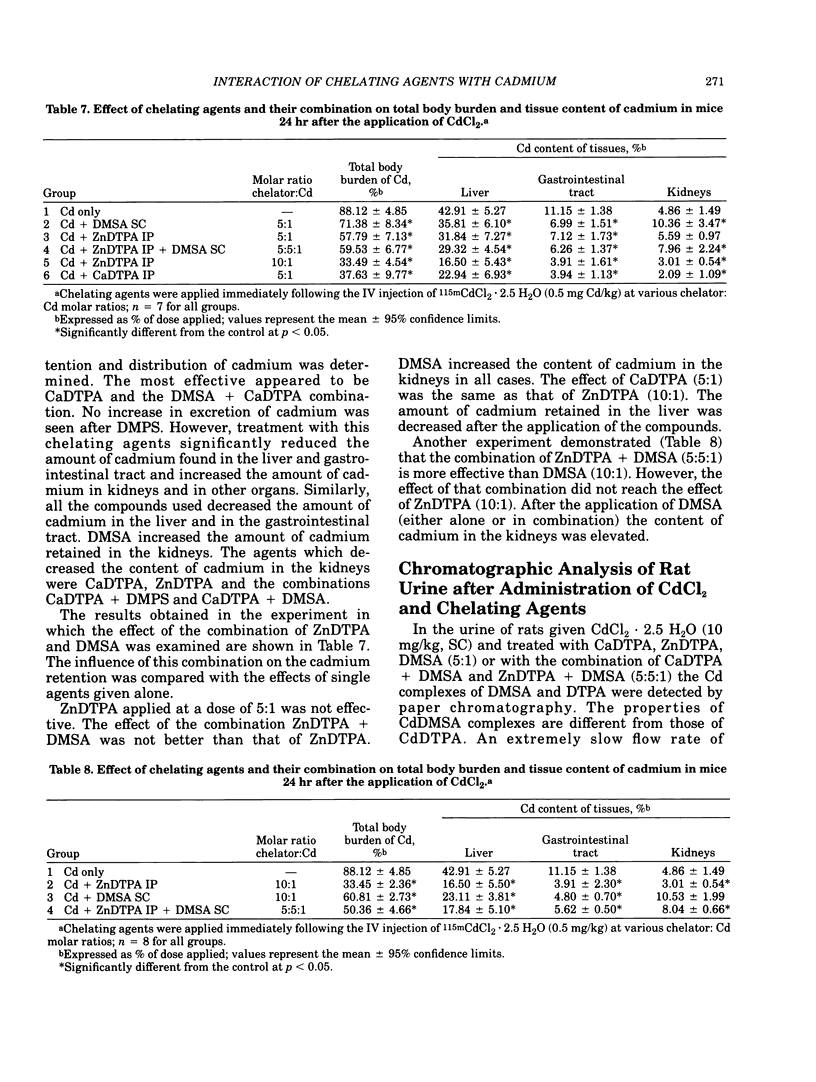
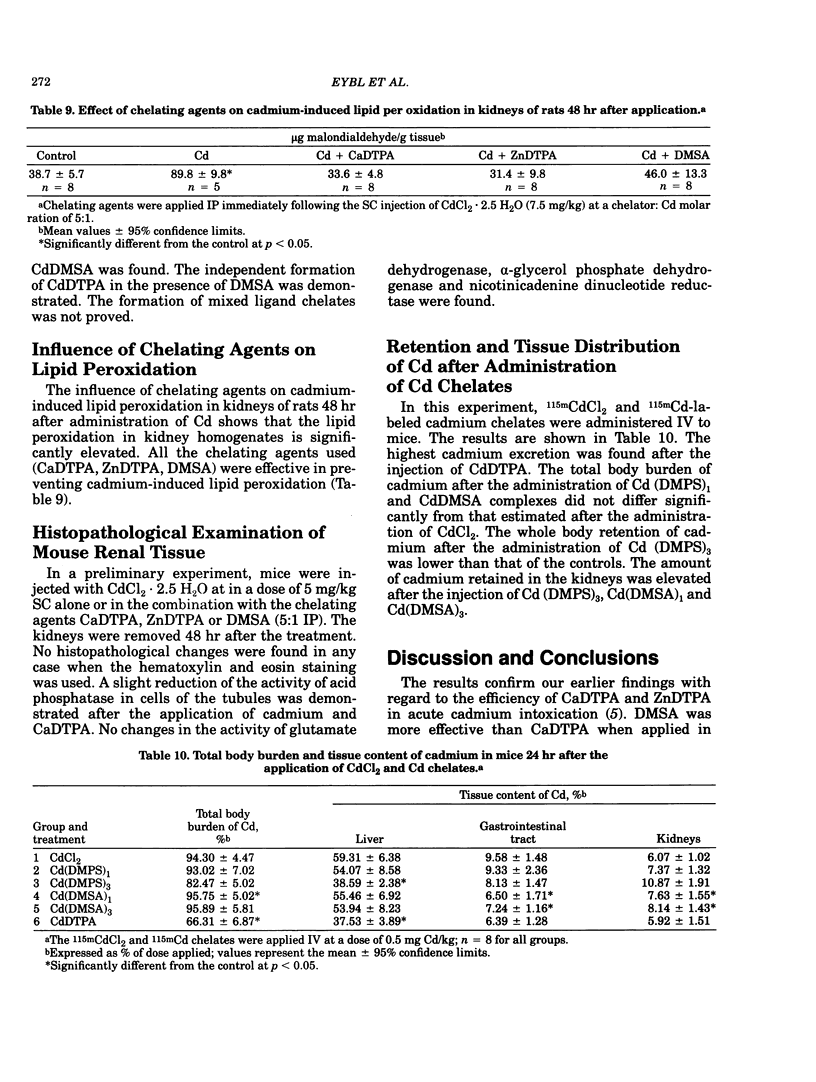
The influence of several chelating agents (CaDTPA, ZnDTPA, CaEDTA, ZnEDTA, DMSA, D-penicillamine and DMPS, DMP and DDC) on the acute toxicity of CdCl2 and on the whole body retention and tissue distribution of cadmium after the IV application of 115mCdCl2 was compared in mice. The chelating agents were applied immediately after the application of cadmium. CaDTPA, ZnDTPA and DMSA appeared to be the most effective antidotes. However, DMSA increased the amount of cadmium retained in kidneys. The treatment of cadmium-poisoned mice with the combination of DMSA (IP) and ZnDTPA (SC) (all the compounds were injected in equimolar dose) decreased the toxicity of cadmium more than treatment with one chelating agents (given in a 2:1 dose). However, by studying the effect of these chelating agents and their combination of the retention and distribution of Cd in mice, it was demonstrated that the combined application of the antidotes showed little or no improvement over the results obtained with the most effective of the individual components. In the urine of rats injected with CdCl2 and treated with the chelating agents (CaDTPA, ZnDTPA, DMSA), the presence of cadmium complexes was demonstrated. The formation of mixed ligand chelates in vivo was not proved. Experiments in mice given a single injection of 115mCd-labeled Cd complexes of DMPS, DMSA and DTPA showed a high retention of cadmium in the organisms after the IV application of CdDMPS and CdDMSA complexes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantilena L. R., Jr, Klaassen C. D. Comparison of the effectiveness of several chelators after single administration on the toxicity, excretion, and distribution of cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 May;58(3):452–460. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eybl V., Sýkora J. Die Schutzwirkung von Chelatbildnern bei der akuten Kadmiumchloridvergiftung. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1966;16(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eybl V., Sýkora J., Mertl F. Einfluss der Ca- und Zn-Komplexe von Aminopolykarbonsäuren auf Ausscheidung und Verteilung des Kadmiums. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1973;30(4):515–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eybl V., Sýkora J., Mertl F. Einfluss der Chelatbildner auf die Ausscheidung des Cadmiums bei Cadmiumvergiftung. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1965 Nov 4;252(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eybl V., Sýkora J., Mertl F. Toxizität und Stoffwechsel der Kadmiumkomplexe der Aminopolykarbonsäuren. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1966;16(2):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eybl V., Sýkora J., Mertl F. Wirkung von CaADTA und CaDTPA bei der Kadmiumvergiftung. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1966;17(2):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. M., Weaver A. D., Weller W. L. The relative effectiveness of some chelating agents as antidotes in acute cadmium poisoning. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;22(3):581–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. G., Basinger M. A., Jones M. M., Gibbs S. J. A comparison of diethyldithiocarbamate and EDTA as antidotes for acute cadmium intoxication. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;38(2):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas-Bohne F. Chelate treatment in acute cadmium poisoning. Experientia. 1980 Aug 15;36(8):1001–1002. doi: 10.1007/BF01953846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderman F. W., Sr Chelation therapy in nickel poisoning. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1981 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBUR K. M., BERNHEIM F., SHAPIRO O. W. The thiobarbituric acid reagent as a test for the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by various agents. Arch Biochem. 1949 Dec;24(2):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


