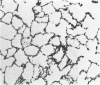
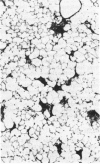
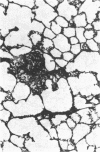
Abstract
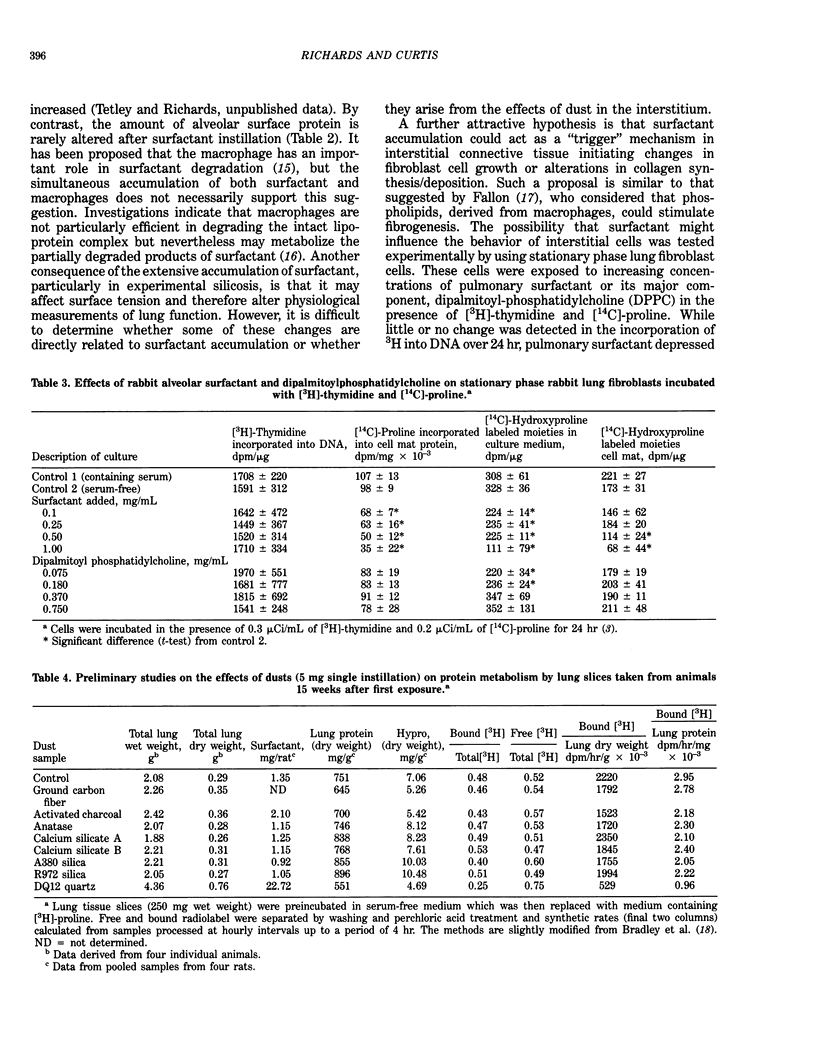
The sequence of cellular and biochemical events in response to the deposition of dust particles in lung tissue is described. Primary reactions at the lung surface include changes in the free cell population, the alveolar surface protein and in the quantity of pulmonary surfactant, a lipoprotein-rich material secreted by Type II cells. The relationship between these changes and lung fibrogenesis is discussed. It is suggested that such primary changes are protective mechanisms which may assist in the prevention of fibrogenesis rather than lead to an increase in collagen formation and deposition. If these primary defenses are overcome, then the interstitial fibroblastlike cell may have a prominent role in fibrogenesis. Therefore detailed observations of the interaction between lung fibroblasts and mineral dusts in vitro are described. As fibrogenesis may be arrested in vivo, or possibly reversed, and does not always progress to fibrosis, final consideration is given to the step from fibrogenesis to fibrosis. It is suggested that this step may involve other tissue proteins apart from collagen and that the irreversible nature of fibrosis can be explained by the formation of strong intermolecular crosslinks between different proteins. The types of crosslinks that may be involved are discussed. Emphasis is placed on the role of calcium-dependent transglutaminases in fibrosis, as these enzymes have hitherto received little attention.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams M. E. Isolation and quantitative estimation of pulmonary surface-active lipoprotein. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Mar;21(2):718–720. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.2.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absher M., Sylwester D. Effects of silica on human lung fibroblasts: survival data analysis of time-lapse cinematography data. Environ Res. 1981 Dec;26(2):438–452. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(81)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali I. U., Hynes R. O. Role of disulfide bonds in the attachment and function of large, external, transformation-sensitive glycoprotein at the cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 16;510(1):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Peach C. M. Isolation and structural identification of a labile intermolecular crosslink in collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):812–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. Y., Hook G. E. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: analysis of airway and alveolar proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):979–990. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignon J., Jaurand M. C., Pinchon M. C., Sapin C., Warnet J. M. Immunoelectron microscopic and immunochemical demonstrations of serum proteins in the alveolar lining material of the rat lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Feb;113(2):109–120. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley K. H., McConnell S. D., Crystal R. G. Lung collagen composition and synthesis. Characterization and changes with age. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2674–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Hill L. H., Adkins B., Jr, O'Connor R. W. Chrysotile asbestos inhalation in rats: deposition pattern and reaction of alveolar epithelium and pulmonary macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):670–679. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Hill L. H. Interstitial accumulation of inhaled chrysotile asbestos fibers and consequent formation of microcalcifications. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):107–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell R., Anderson M. The induction of fibrogenesis by silica-treated alveolar macrophages. Environ Res. 1973 Dec;6(4):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(73)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I. Comparative studies on tissue transglutaminase and factor XIII. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:240–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. B. Potential adverse effects of lung macrophages and neutrophils. Fed Proc. 1979 Nov;38(12):2644–2647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G., Ray A. K., Buckelew A. R., Jr Pulmonary surfactant: distribution of lipids, proteins and surface activity in ultracentrifugation of rabbit pulmonary washing and derived fractions. Lipids. 1977 Nov;12(11):879–888. doi: 10.1007/BF02533306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Okada T. A. Electron microscopy of human fibroblasts in tissue culture during logarithmic and confluent stages of growth. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Lorand L. Fibrin-stabilizing factor (factor XIII). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:177–191. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C., Ackerman J., Butterfield A., Williams S. Asbestos induces selective release of lysosomal enzymes from mononuclear phagocytes. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):423–425. doi: 10.1038/251423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai R., Hext P., Richards R. The prevention of asbestos-induced hemolysis. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1931–1938. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai R., Richards R. J. Effects of chrysotile on a lysosomal enzyme preparation and on the hydrolytic enzyme activity of cultured alveolar macrophages. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Sep;51:125–130. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8351125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai R., Richards R. J. The adsorption of biological macromolecules by mineral dusts. Environ Res. 1978 Jul;16(1-3):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(78)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai R., Tetley T. D., Curtis C. G., Powell G. M., Richards R. J. Studies on the fate of pulmonary surfactant in the lung. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj1760455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: a key cell for wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;54:183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop P. M., Blumenfeld O. O., Seifter S. Structure and metabolism of connective 801 tissue proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:617–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G., Richards R. J. Preliminary studies on the isolation, separation and identification of pulmonary-lavage proteins from the rabbit [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Dec;7(6):1285–1287. doi: 10.1042/bst0071285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding H. W., Rogers G. E. The occurrence of the -( -glutamyl)lysine cross-link in the medulla of hair and quill. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. J. The unusual links and cross-links of collagen. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:109–190. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harington J. S., Ritchie M., King P. C., Miller K. The in-vitro effects of silica-treated hamster macrophages on collagen production by hamster fibroblasts. J Pathol. 1973 Jan;109(1):21–37. doi: 10.1002/path.1711090104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. L., Desai R., Hext P., Tetley T., Richards R. Characterization of pulmonary surfactant from ox, rabbit, rat and sheep. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):707–714. doi: 10.1042/bj1510707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschek W. M., Witschi H. Pulmonary fibrosis--a possible mechanism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;51(3):475–487. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L., Tuttle W. A. Early damage indicators in the lung. II. Time sequence of protein accumulation and lipid loss in the airways of beagle dogs with beta irradiation of the lung. Radiat Res. 1978 Oct;76(1):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Fletcher K., Wyatt I. Changes in the composition of lung lipids and the "turnover" of dipalmitoyl lecithin in experimental alveolar lipo-proteinosis induced by inhaled quartz. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Aug;55(4):384–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Styles J. A. Activity of a macrophage factor in collagen formation by silica. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):521–522. doi: 10.1038/214521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G. The fibrogenic action of silica. Br Med Bull. 1969 Sep;25(3):282–287. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hext P. M., Hunt J., Dodgson K. S., Richards R. J. The effects of long-term exposure of lung fibroblast strains to chrysotile asbestos. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Apr;58(2):160–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hext P. M., Richards R. J. Biochemical effects of asbestiform minerals on lung fibroblast cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Jun;57(3):281–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. Extensive disulfide bonding at the mammalian cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2855–2859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. M., Edwards J. H., Wagner J. C. Absorption of serum proteins by inorganic dusts. Br J Ind Med. 1972 Jul;29(3):287–292. doi: 10.1136/oem.29.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Mosher D. F., Vaheri A. Dimeric character of fibronectin, a major cell surface-associated glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand J. B., Pilkington T. R., Lorand L. Inhibitors of fibrin cross-linking: relevance for thrombolysis. Nature. 1966 Jun 18;210(5042):1273–1274. doi: 10.1038/2101273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D., Gray A. Titration of the acceptor cross-linking sites in fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:155–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L. Fibrinoligase: the fibrin-stabilizing factor system of blood plasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:6–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic G., Gallop P. M., Tanzer M. L. The nature of crosslinking in collagens from mineralized tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):644–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockros L. F., Roberts W. W., Lorand L. Viscoelastic properties of ligation-inhibited fibrin clots. Biophys Chem. 1974 Aug;2(2):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6614–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGELSCHMIDT G., RIVERS D., KING E. J., TREVELLA W. DUST AND COLLAGEN CONTENT OF LUNGS OF COAL-WORKERS WITH PROGRESSIVE MASSIVE FIBROSIS. Br J Ind Med. 1963 Jul;20:181–191. doi: 10.1136/oem.20.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naimark A. Cellular dynamics and lipid metabolism in the lung. Fed Proc. 1973 Sep;32(9):1967–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewoehner D. E., Hoidal J. R. Lung fibrosis and emphysema: divergent responses to a common injury? Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):359–360. doi: 10.1126/science.7089570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman D., Duckert F. Proceedings: Factor XIII, fibrin and collagen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Nov 15;34(2):551–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J., Peyton M. P., Finlayson J. S. Epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl) lysine cross-links: determination in fibrin from normal and factor XIII-deficient individuals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:98–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Cobb L. M., Hardy C. J., Rose F. A., Tetley T. D. Effects in the rat of inhaling PVC dust at the nuisance dust level (10 mg/m3). Arch Environ Health. 1981 Jan-Feb;36(1):14–19. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1981.10667600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Hext P. M., Blundell G., Henderson W. J., Volcani B. E. Ultrastructural changes in lung fibroblast cultures exposed to chrysotile asbestos. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Jun;55(3):275–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Hunt J. Reaction of mineral dusts with primary lung fibroblast cultures. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Sep;51:61–65. doi: 10.1289/ehp.835161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Jacoby F. Light microscope studies on the effects of chrysotile asbestos and fiber glass on the morphology and reticulin formation of cultured lung fibroblasts. Environ Res. 1976 Feb;11(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(76)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Wusteman F. S., Dodgson K. S. The direct effects of dusts on lung fibroblasts grown in vitro. Life Sci I. 1971 Oct 15;10(20):1149–1159. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. J., Wusteman F. S. The effects of silica dust and alveolar macrophages on lung fibroblasts grown in vitro. Life Sci. 1974 Jan 16;14(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. W., Lorand L., Mockros L. F. Viscoelastic properties of fibrin clots. Biorheology. 1973 Mar;10(1):29–42. doi: 10.3233/bir-1973-10105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpelli E. M., Wolfson D. R., Colacicco G. Protein and lipid-protein fractions of lung washings: immunological characterization. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Jun;34(6):750–753. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.6.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Hayes J. A., Korthy A. L., Lewis G. P. Centrilobular emphysema experimentally induced by cadmium chloride aerosol. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):40–48. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria A., Soria C., Boulard C. Fibrin stabilizing factor (F XIII) and collagen polymerization. Experientia. 1975 Nov 15;31(11):1355–1357. doi: 10.1007/BF01945824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven F. S., Coy G. R., Jackson D. S. Evidence for intra-chain masked carboxyl groups in polymeric collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 22;271(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y. Interaction of asbestos with alveolar cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 Dec;9:241–252. doi: 10.1289/ehp.749241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J., ELSDEN D. F., PARTRIDGE S. M. PARTIAL STRUCTURE OF TWO MAJOR DEGRADATION PRODUCTS FROM THE CROSS-LINKAGES IN ELASTIN. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:651–652. doi: 10.1038/200651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Mechanic G. Isolation of lysinonorleucine from collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90775-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetley T. D., Hext P. M., Richards R. J., McDermott M. Chrysotile-induced asbestosis: changes in the free cell population, pulmonary surfactant and whole lung tissue of rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Oct;57(5):505–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetley T. D., Richards R. J., Harwood J. L. Changes in pulmonary surfactant and phosphatidylcholine metabolism in rats exposed to chrysotile asbestos dust. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):323–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1660323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Wusteman F. S., Edwards J. H., Hill R. J. The composition of massive lesions in coal miners. Thorax. 1975 Aug;30(4):382–388. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.4.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Ashman H. G., Notides A. C., Pabalan S. S., Lorand L. Transamidase reactions involved in the enzymic coagulation of semen: isolation of -glutamyl- -lysine dipeptide from clotted secretion protein of guinea pig seminal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2322–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]