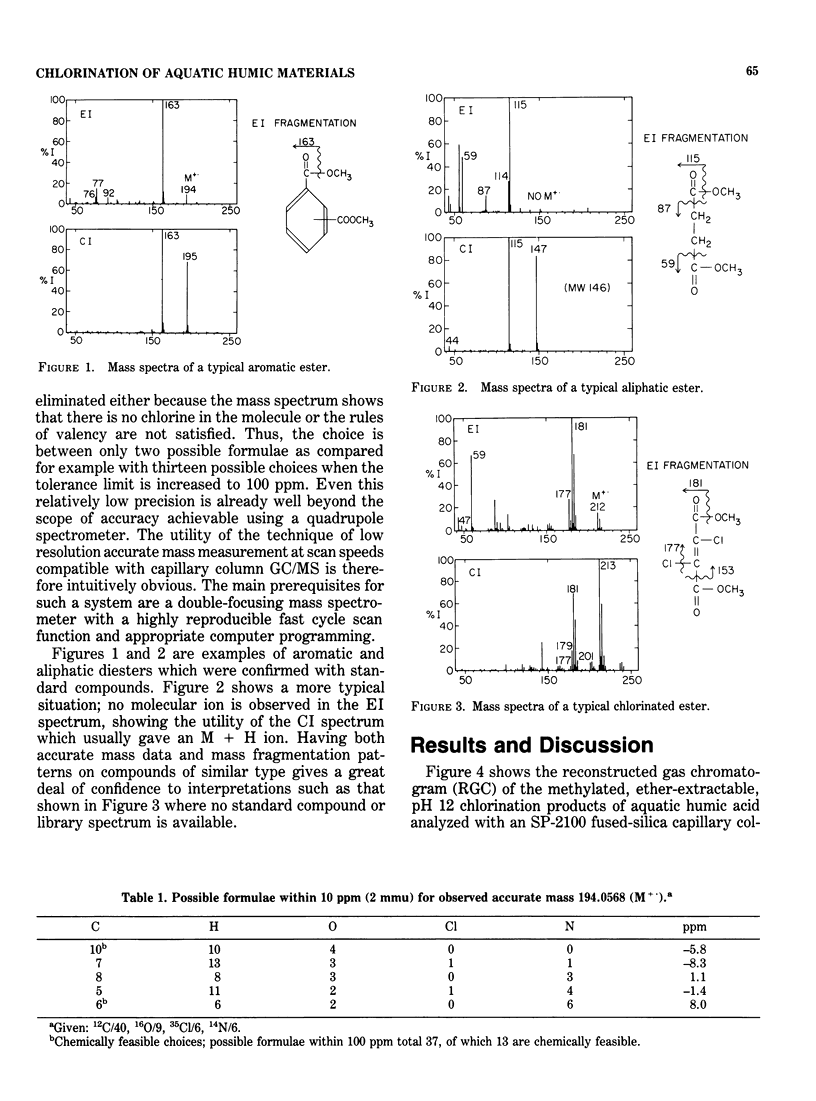
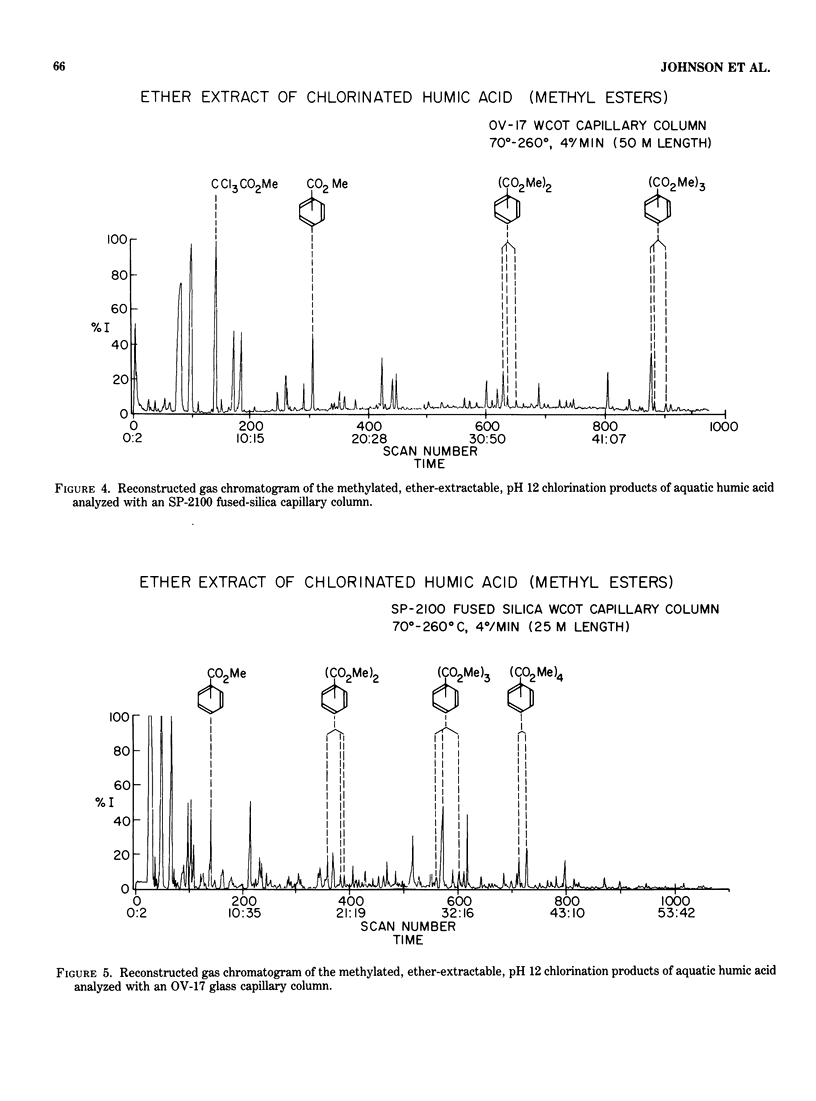
Abstract
A major concern of the chlorination of aquatic humic materials is the ubiquitous production of trihalomethanes. A large number of other chlorinated organic compounds, however, have been shown to be formed by chlorine's reaction with humic substances. In this study, humic material was concentrated from a coastal North Carolina lake and chlorinated at a chlorine to carbon mole ratio of 1.5 at pH 12. A high pH was necessary for complete dissolution of the humic material and for production of adequate quantities of oxidation and chlorination products for extraction, separation and mass spectrometric identification. After concentration in ether, samples were methylated, separated with a 50-m OV-17 glass capillary column or a 25 m SP-2100 fused-silica column and identified. A Hewlett-Packard 5710A gas chromatograph interfaced to a VG Micromass 7070F double-focusing mass spectrometer was used. Low resolution, accurate mass measurements were made with a combined EI-Cl source. The ability to do low resolution, accurate mass measurements made possible a rapid scan function necessary for capillary column gas chromatography. Accurate mass measurements allowed increased confidence in the identification of compounds, most of which are not available as standards. The products identified in these studies were chlorinated aliphatic straight-chain acids dominated by di- and trichloroacetic acid and the chlorinated dicarboxylic acids: succinic, fumaric and maleic acids. Chlorinated and unchlorinated aliphatic mono- and dicarboxylic acids and unchlorinated polycarboxylic aromatic acids comprise the remaining bulk of the compounds identified.
Full text
PDF