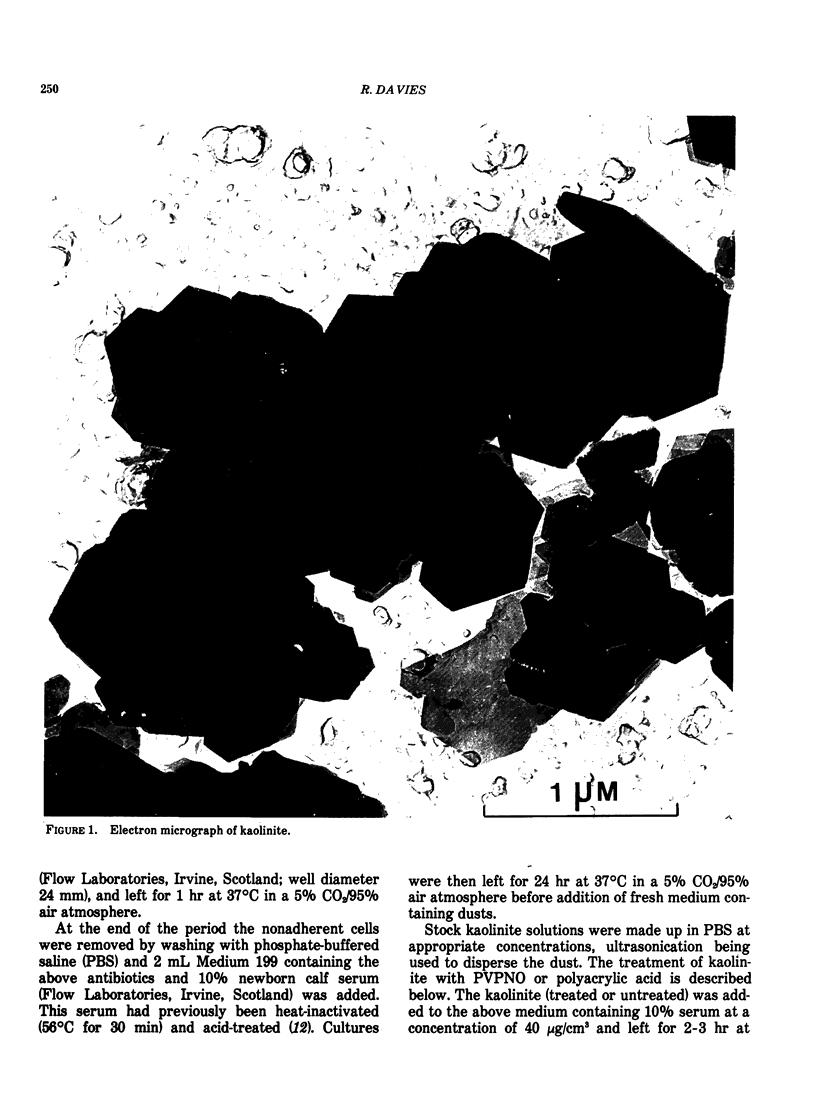
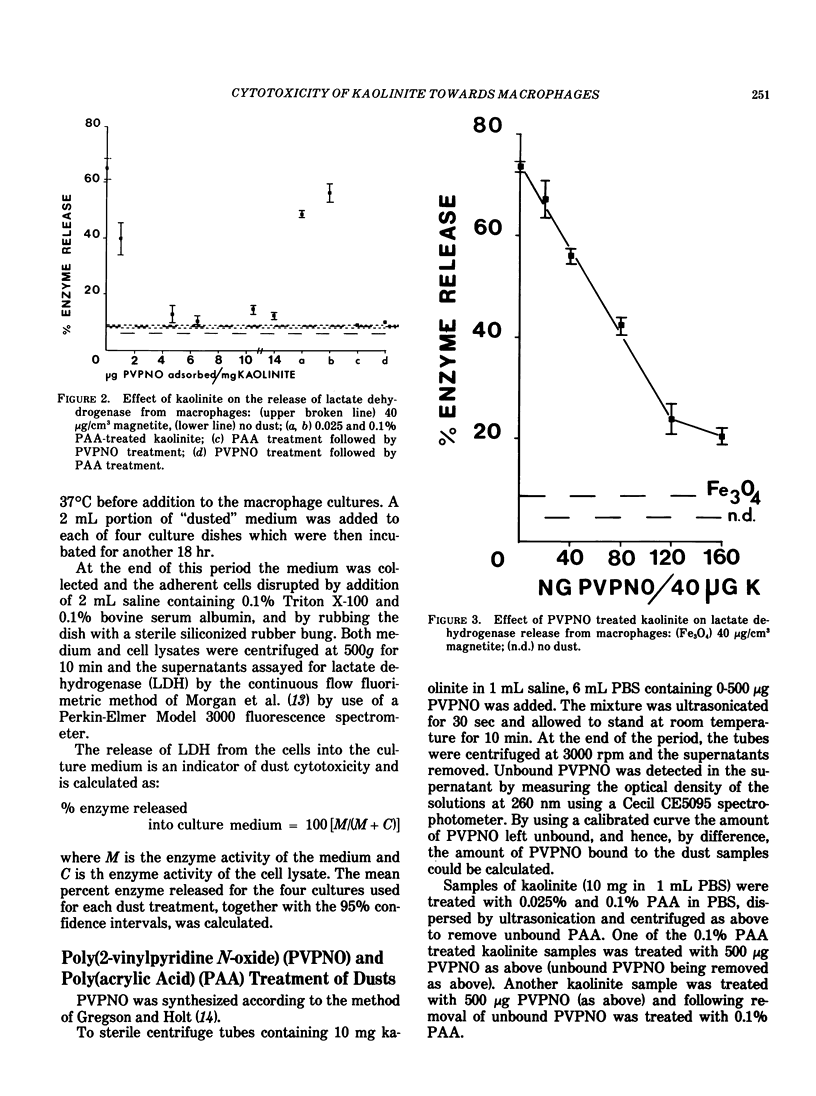
Abstract
The cytotoxicity of a high purity Cornish kaolinite toward mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro was examined. The material was cytotoxic towards these cells, the activity could be decreased substantially by pretreating the dust with poly(2-vinylpyridine N-oxide). Pretreatment of the dusts with poly(acrylic acid) had a small effect on cytotoxicity, but combinations of the polymer treatments virtually abolished the material's biological activity towards macrophages. These studies indicated that the cytotoxicity of kaolinite is not due to its flakelike morphology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATTYGALLE D., HARRISON C. V., KING E. J., MOHANTY G. P. Infective pneumoconiosis. I. The influence of dead tubercle bacilli (BCG) on the dust lesions produced by anthracite, coal-mine dust, and kaolin in the lungs of rats and guinea-pigs. Br J Ind Med. 1954 Oct;11(4):245–259. doi: 10.1136/oem.11.4.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M. The fibrogenic effects of mineral dusts injected into the pleural cavity of mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Apr;53(2):190–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. F., Lindsay H., Beck E. G. Some derivatives of polyvinylpyridine 1-oxides and their effect on the cytotoxicity of quartz in macrophage cultures. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;38(1):192–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Leffingwell C. M., Bulman C. A. Effects of kaolinite on amino acid transport and incorporation into protein by rabbit pulmonary alveolar macrophages. Arch Environ Health. 1980 Jul-Aug;35(4):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., NAGELSCHMIDT G. Study of the toxicity of dust with use of the in vitro dehydrogenase technique. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1959 Nov;20:383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. M., Vint S., Rideout J. M. Continuous flow fluorimetric assay of lysosomal enzymes. Med Lab Sci. 1978 Oct;35(4):335–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEERS G. PREVALENCE OF PNEUMOCONIOSIS IN CORNISH KAOLIN WORKERS. Br J Ind Med. 1964 Jul;21:218–225. doi: 10.1136/oem.21.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]