Abstract
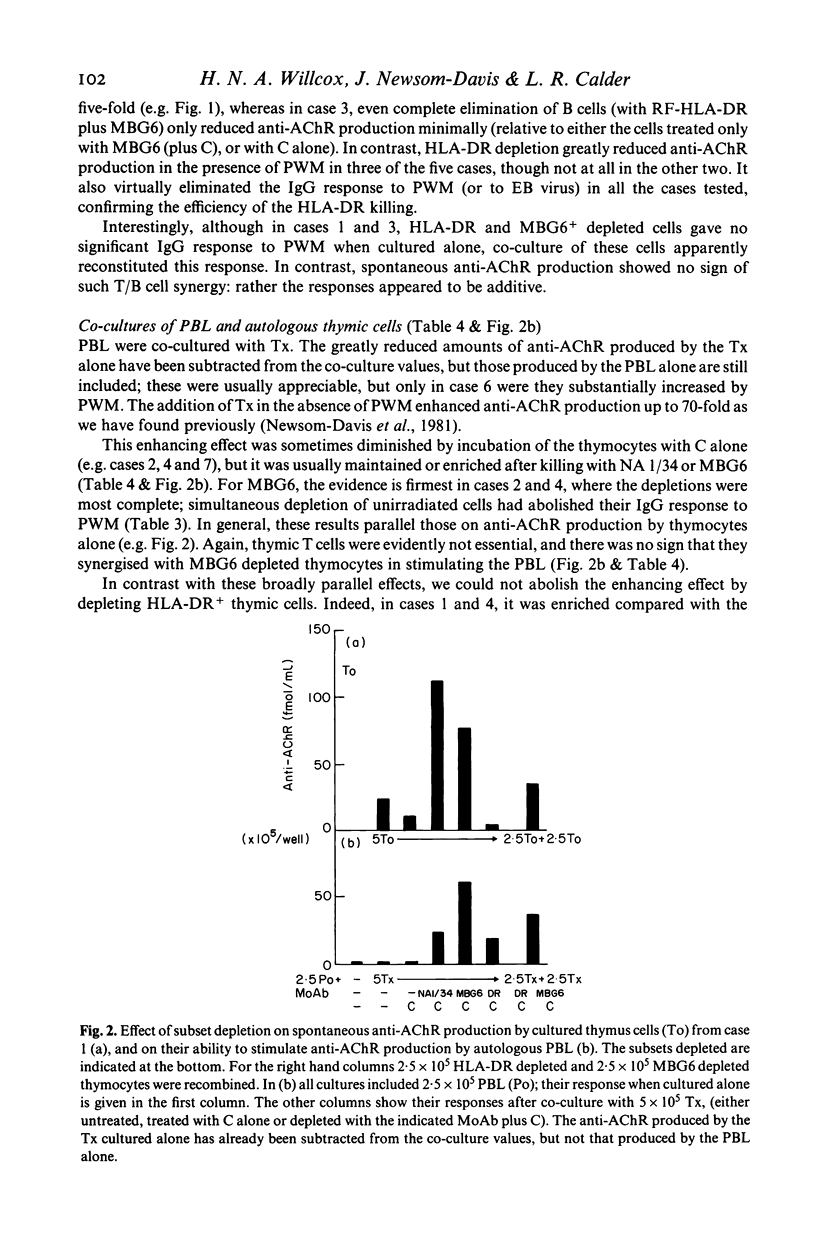
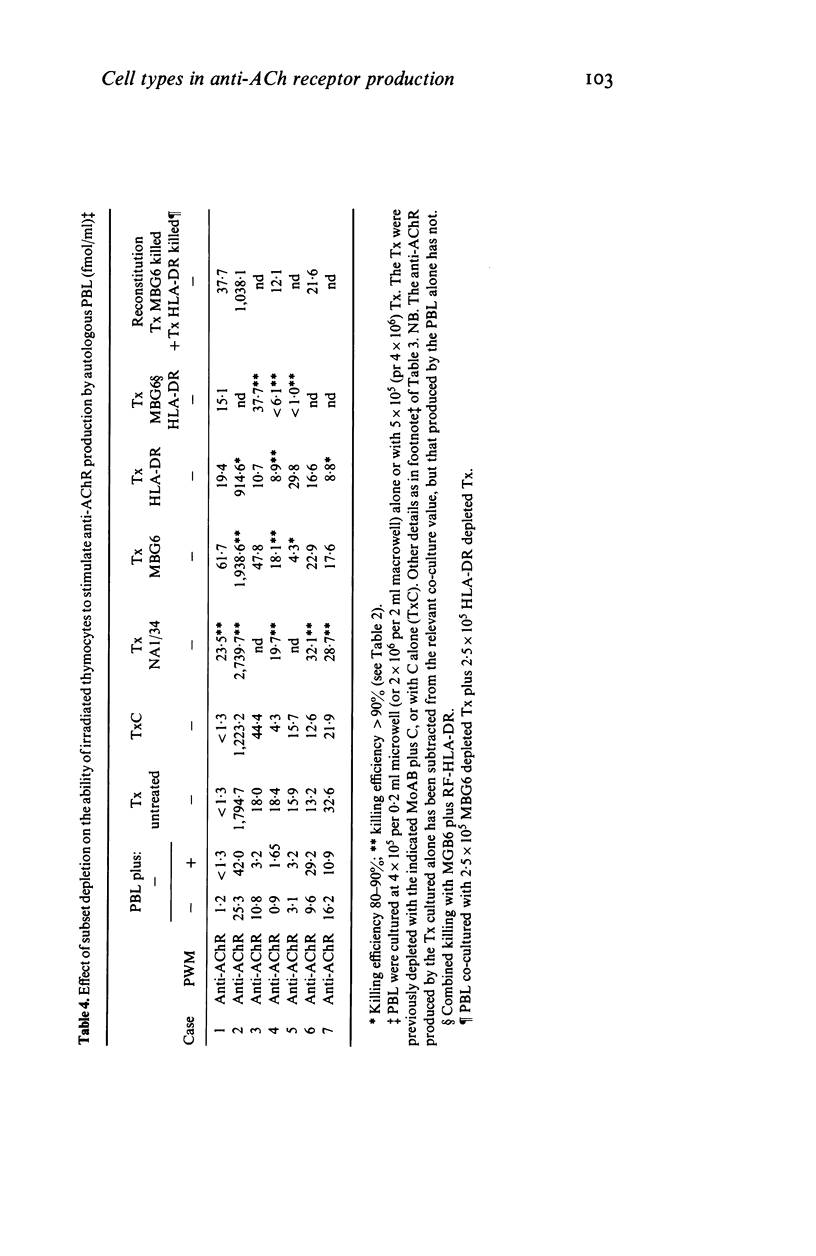
In most young myasthenia gravis patients, the thymic medulla contains germinal centres. Thymocytes from these cases spontaneously synthesize anti-acetylcholine receptor autoantibody (anti-AChR) in culture; after irradiation they may also selectively stimulate anti-AChR antibody production by autologous blood lymphocytes. By depleting cortical or mature thymic T cells by complement killing, we now show that neither of these responses depends on thymic T cells, unlike the total IgG response to pokeweed mitogen which is T cell-dependent and shows T/B cell synergy. The results suggest that much of the spontaneous anti-AChR production is by autonomous thymic plasma cells, which may be HLA-DR-. The ability to stimulate autologous blood lymphocytes does not require viable HLA-DR+ thymic cells but appears to depend on rare antigen presenting cells from the germinal centres. In preliminary experiments, blood T cells were apparently also necessary.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
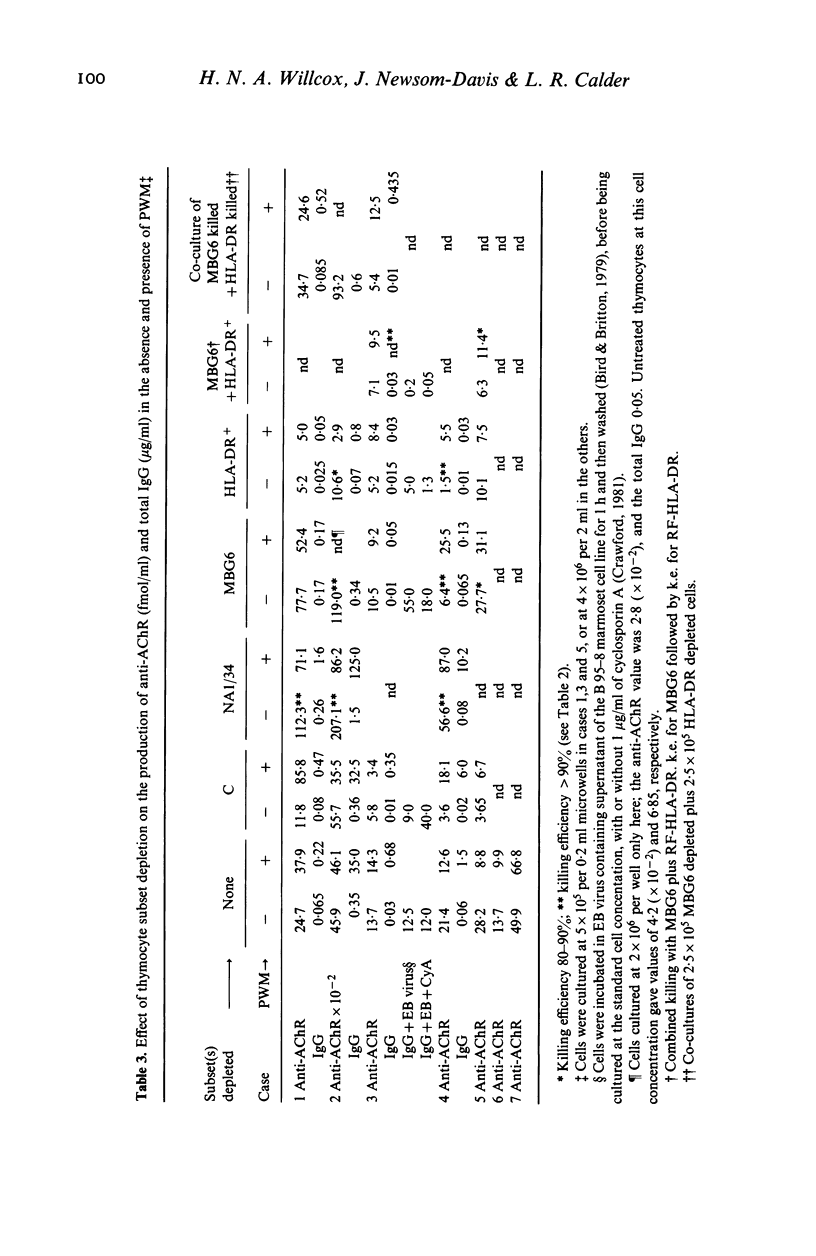
- Bastin J. M., Granger S., Tidman N., Janossy G., McMichael A. J. Recognition of a human T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen by an IgM monoclonal antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):597–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. G., Britton S. A new approach to the study of human B lymphocyte function using an indirect plaque assay and a direct B cell activator. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:41–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodger M. P., Izaguirre C. A., Blacklock H. A., Hoffbrand A. V. Surface antigenic determinants on human pluripotent and unipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):1006–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Morphologic and immunopathologic findings in myasthenia gravis and in congenital myasthenic syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Jul;43(7):577–589. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.7.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Stein H., Mason D. Y., Ziegler A. Human dendritic reticulum cells of lymphoid follicles: their antigenic profile and their identification as multinucleated giant cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1983;42(2):161–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Grennan D. Isolation and properties of spleen follicular dendritic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;149:823–827. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-9066-4_113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Myasthenic immunoglobulin accelerates acetylcholine receptor degradation. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.850793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Humphrey J. H. The generation of memory cells. I. The role of C3 in the generation of B memory cells. Immunology. 1977 Jul;33(1):31–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Pilch J. R., Galfré G., Mason D. Y., Fabre J. W., Milstein C. A human thymocyte antigen defined by a hybrid myeloma monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Willcox N., Calder L. Thymus cells in myasthenia gravis selectively enhance production of anti-acetylcholine-receptor antibody by autologous blood lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 26;305(22):1313–1318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111263052203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira H., Ishizaka K. Reaginic antibody formation in the mouse. XI. Participation of long-lived antibody-forming cells in persistent antibody formation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Feb;58(1):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
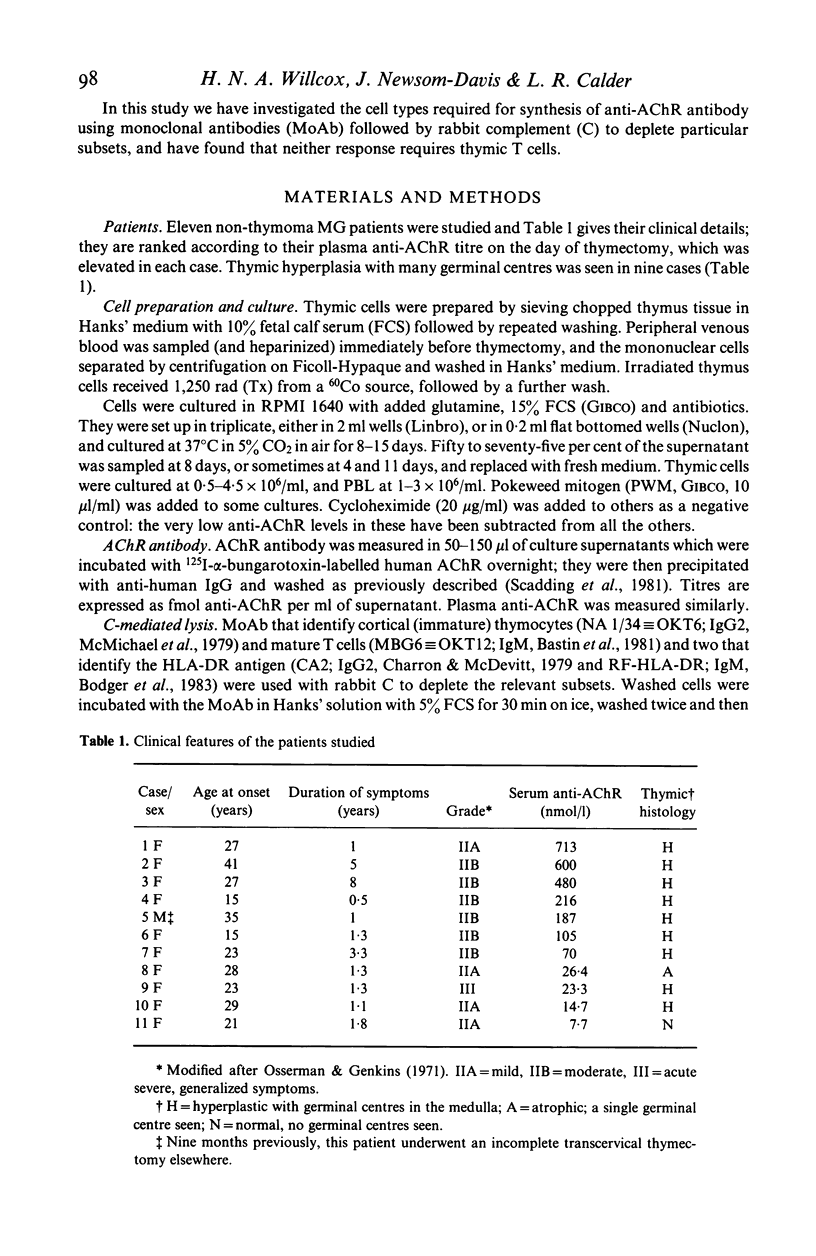
- Osserman K. E., Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a twenty-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971 Nov-Dec;38(6):497–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding G. K., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J., Henry K. Acetylcholine receptor antibody synthesis by thymic lymphocytes: correlation with thymic histology. Neurology. 1981 Aug;31(8):935–943. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.8.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Willcox H. N., Newsom-Davis J. Immunohistological studies of the thymus in myasthenia gravis. Correlation with clinical state and thymocyte culture responses. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Dec;3(4):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
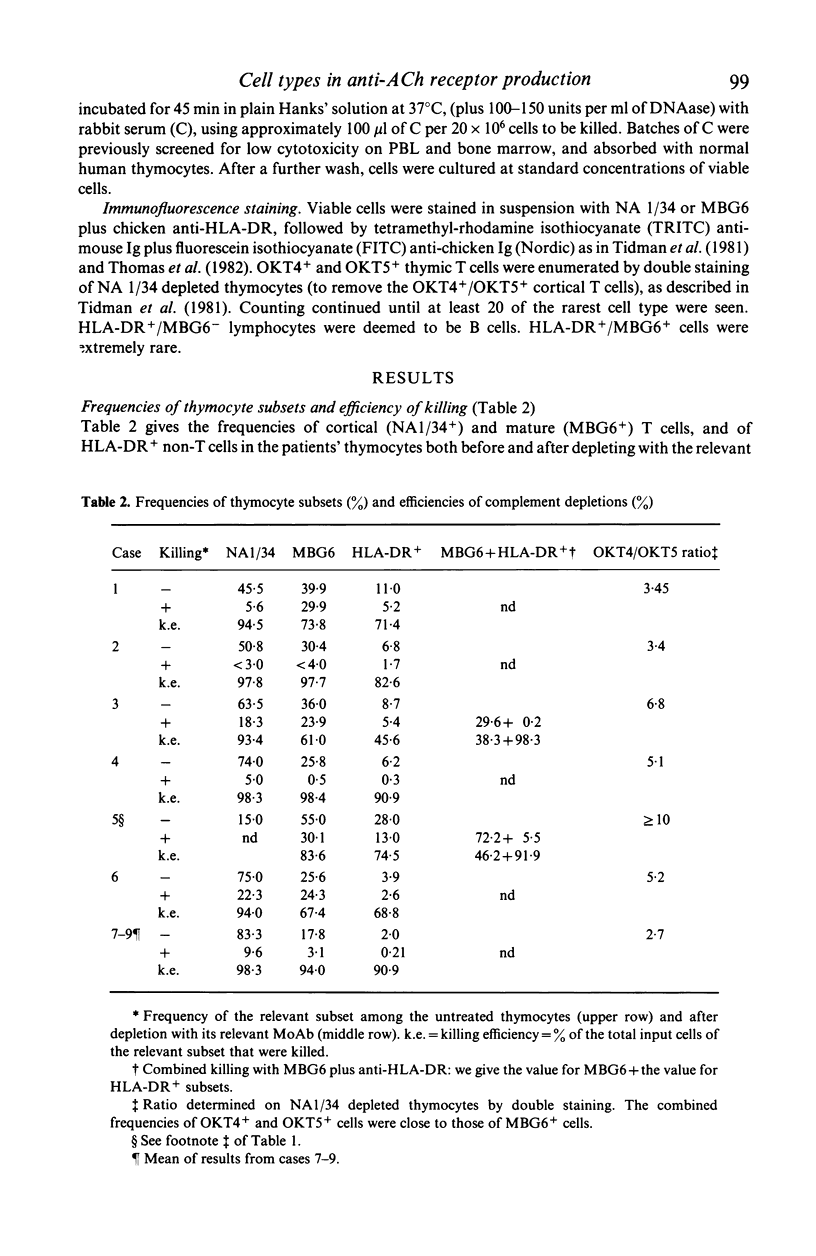
- Tidman N., Janossy G., Bodger M., Granger S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Delineation of human thymocyte differentiation pathways utilizing double-staining techniques with monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Sep;45(3):457–467. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox H. N., Newsom-Davis J., Calder L. R. Greatly increased autoantibody production in myasthenia gravis by thymocyte suspensions prepared with proteolytic enzymes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):378–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


