Abstract
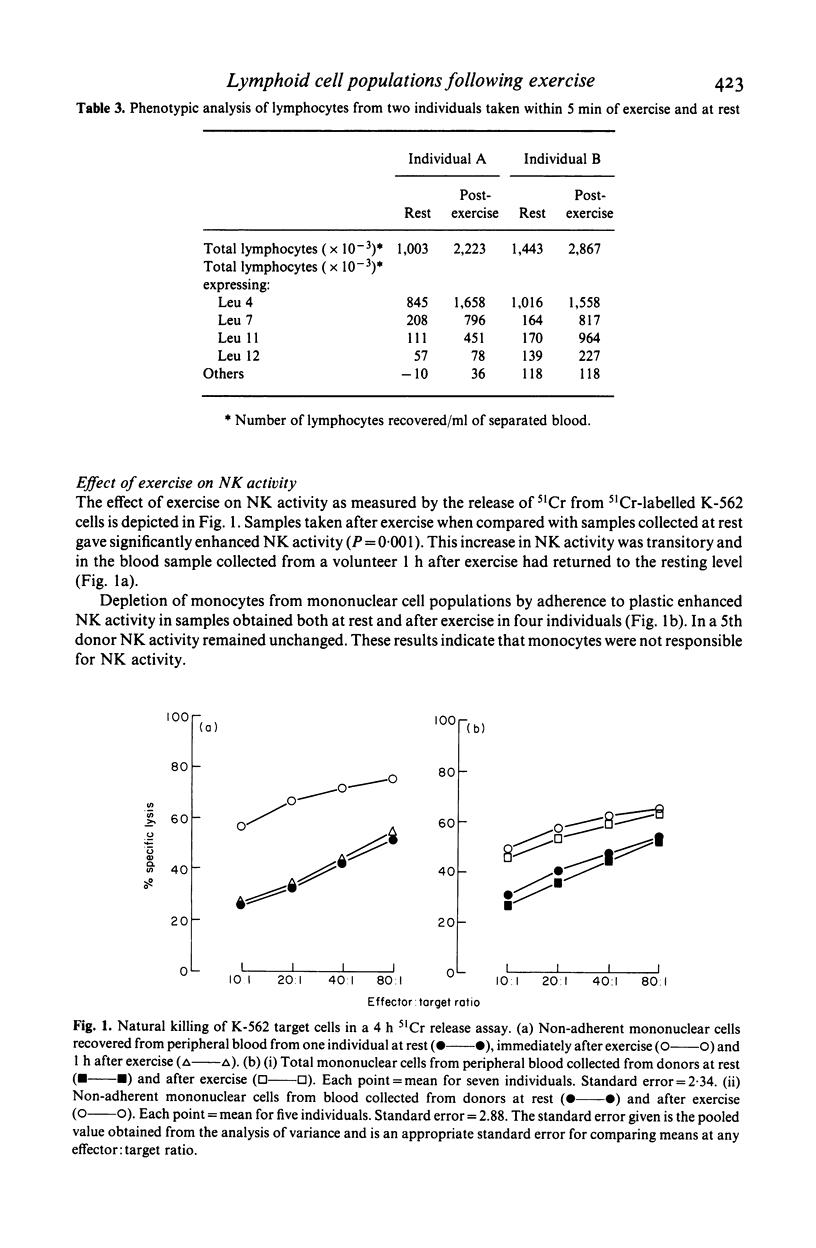
Marked lymphocytosis occurs after exercise. In a study of healthy volunteers this was dominated by one population lacking T cell and B cell determinants and another expressing the Leu 2a phenotype (cytotoxic/suppressor). Lymphocytes from two individuals were characterised further and a near five-fold increase in cells expressing antigens associated with natural killer (NK) cells (Leu 7 and Leu 11) was noted. In addition, these emergent lymphocytes, unlike most T cells, lacked acid alpha-naphthyl esterase activity. In functional studies, exercise led to significantly greater NK activity but, in spite of altering the distribution of lymphocyte subpopulations, there was no detectable change in the proliferative response to the T cell mitogen, concanavalin A, over a wide range of cell concentration, mitogen dose and time. The numbers of low density macrophages and dendritic cells increased concomitantly with the increase in total lymphocytes. We conclude that exercise increases the proportion of circulating NK cells and cells expressing the Leu 2a phenotype.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage R. J., Linch D. C., Worman C. P., Cawley J. C. The morphology and cytochemistry of human T-cell subpopulations defined by monoclonal antibodies and Fc receptors. Br J Haematol. 1982 Aug;51(4):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon T. H., de Vere-Tyndall A., Tyrrell D. A., Denman A. M., Ansell B. M. Interferon system in patients with systemic juvenile chronic arthritis: in vivo and in vitro studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergroth V., Konttinen Y. T., Reitamo S. A method for the identification of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes by sequential immunogold and esterase double staining. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jun;31(6):837–839. doi: 10.1177/31.6.6188784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. K., Munro A. J. Human anti-tetanus antibody response in vitro: autologous and allogeneic T cells provide help by different routes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Oct;46(1):171–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrant J., Clark J. C., Lee H., Knight S. C., O'Brien J. Conditions for measuring DNA synthesis in PHA stimulated human lymphocytes in 20 microliters hanging drops with various cell concentrations and periods of culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(4):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedfors E., Holm G., Ivansen M., Wahren J. Physiological variation of blood lymphocyte reactivity: T-cell subsets, immunoglobulin production, and mixed-lymphocyte reactivity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedfors E., Holm G., Ohnell B. Variations of blood lymphocytes during work studied by cell surface markers, DNA synthesis and cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):328–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Allison A. C., Ward P., Kight N. Identification of human mononuclear leucocyte populations by esterase staining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Balfour B. M., O'Brien J., Buttifant L., Sumerska T., Clarke J. Role of veiled cells in lymphocyte activation. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1057–1060. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., O'Brien J. A., Farrant J. Injury to human granulocytes at low temperatures. Cryobiology. 1980 Jun;17(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(80)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulenkampff J., Janossy G., Greaves M. F. Acid esterase in human lymphoid cells and leukaemic blasts: a marker for T lymphocytes. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbour P. A., Grayzel A. I., Miller A. E. Endogenous and interferon-augmented natural killer cell activity of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Studies of patients with multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):11–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North M. E., Brenner M. K. Induction of immunoglobulin and antigen-dependent antibody synthesis in human lymphocytes, using supernatants from mitogen-stimulated cultures. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):157–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J., Knight S., Quick N. A., Moore E. H., Platt A. S. A simple technique for harvesting lymphocytes cultured in Terasaki plates. J Immunol Methods. 1979;27(3):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. A human NK and K cell subset shares with cytotoxic T cells expression of the antigen recognized by antibody OKT8. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajvanshi V., Peter H. H., Avenarius H. J. Spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity (SCMC) associated with lymphocytes negative for acid alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase (ANAE) activity. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1979 Mar;155(4):330–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M., Evans J., Smith M. A. Physiological variation in circulating B cell:T cell ratio in man. Nature. 1974 Feb 8;247(5440):387–389. doi: 10.1038/247387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Britvan L., Dorey F. Activation of human NKCC by moderate exercise: increased frequency of NK cells with enhanced capability of effector--target lytic interactions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):352–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


