Abstract
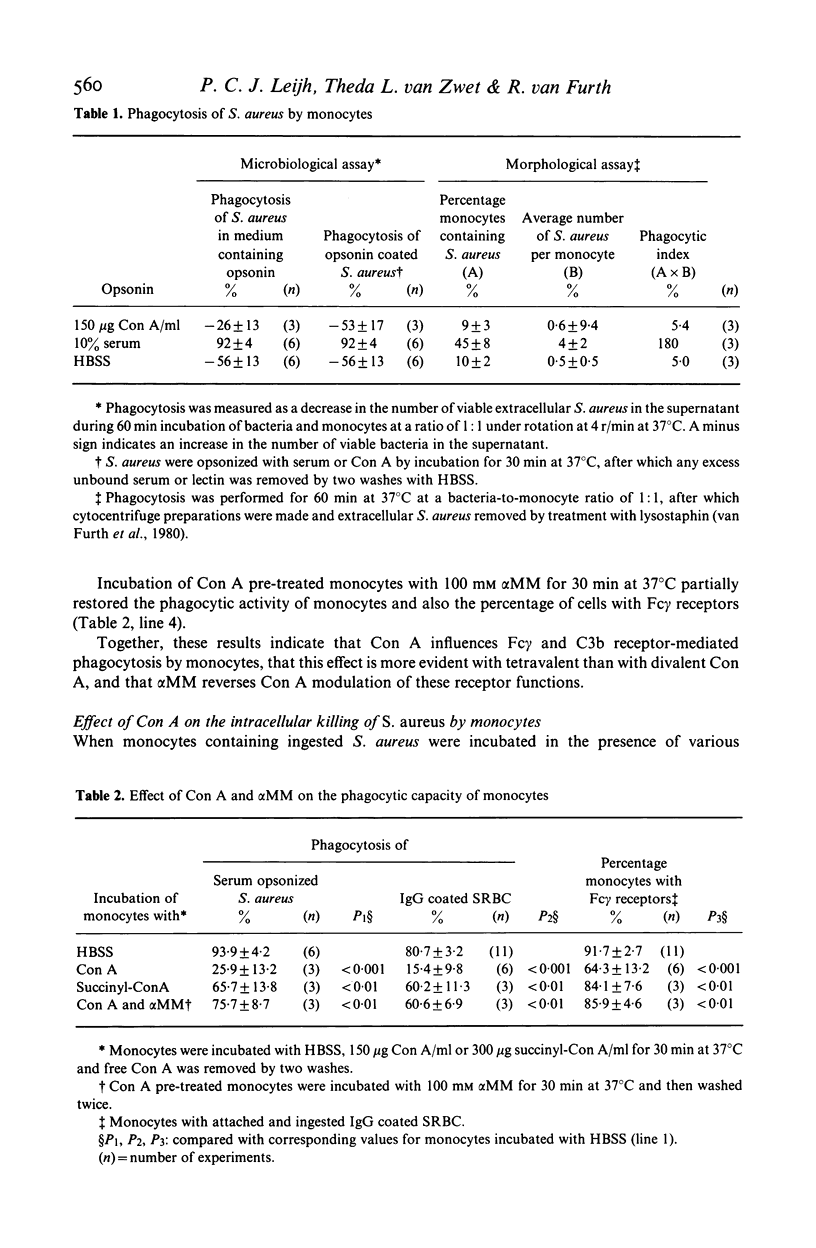
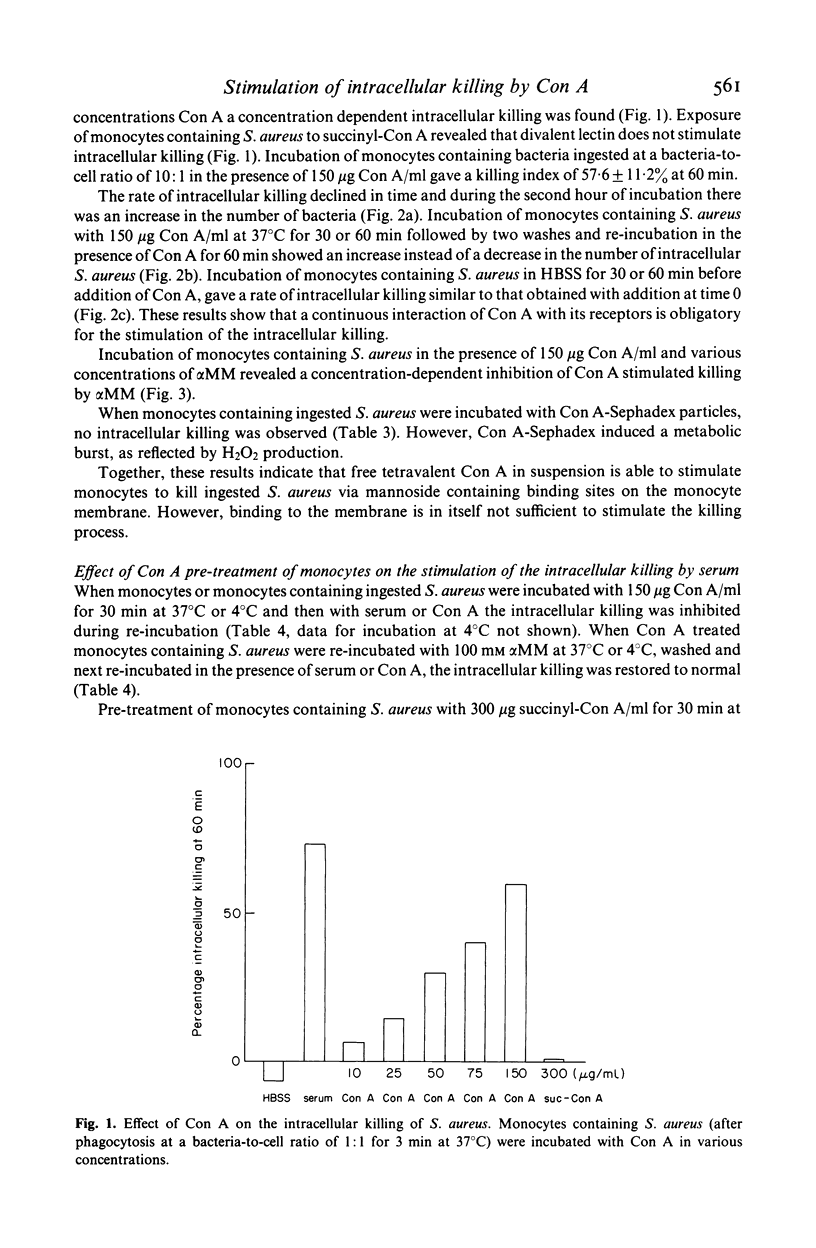
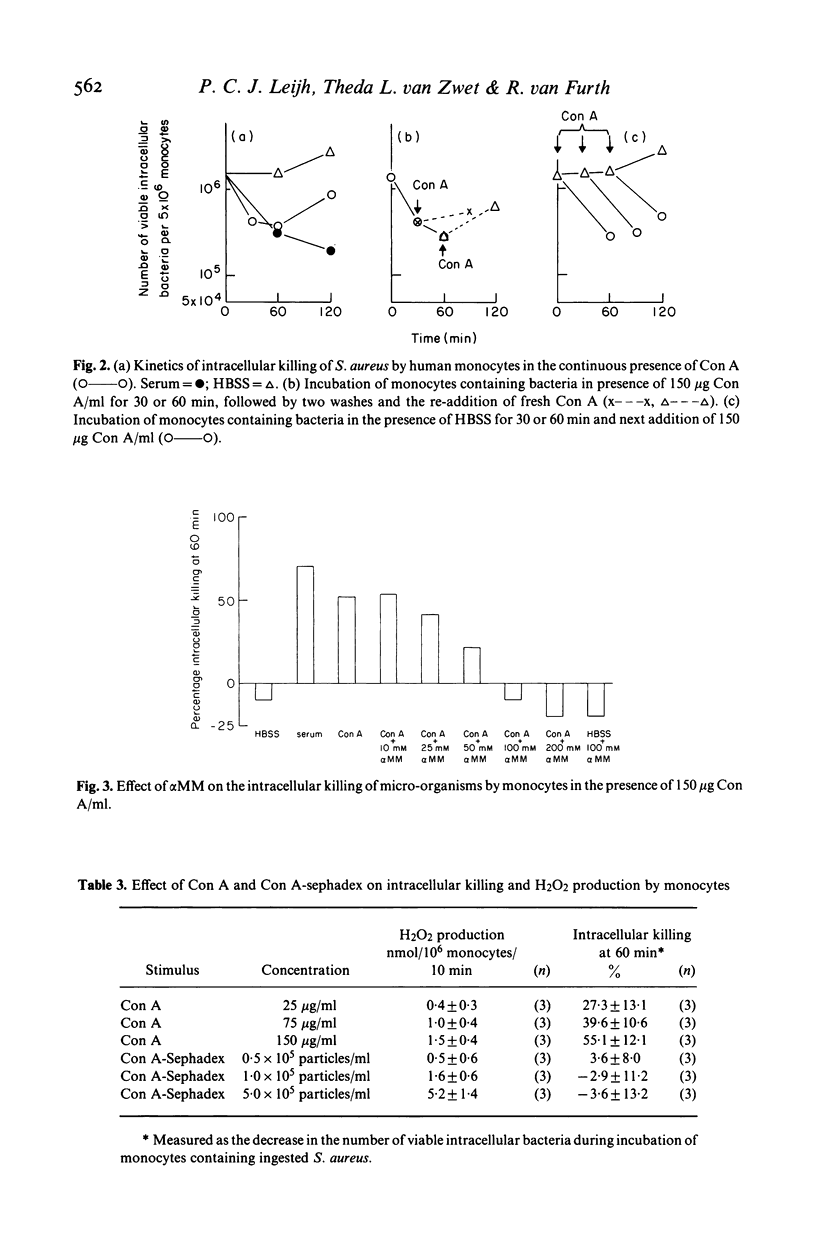
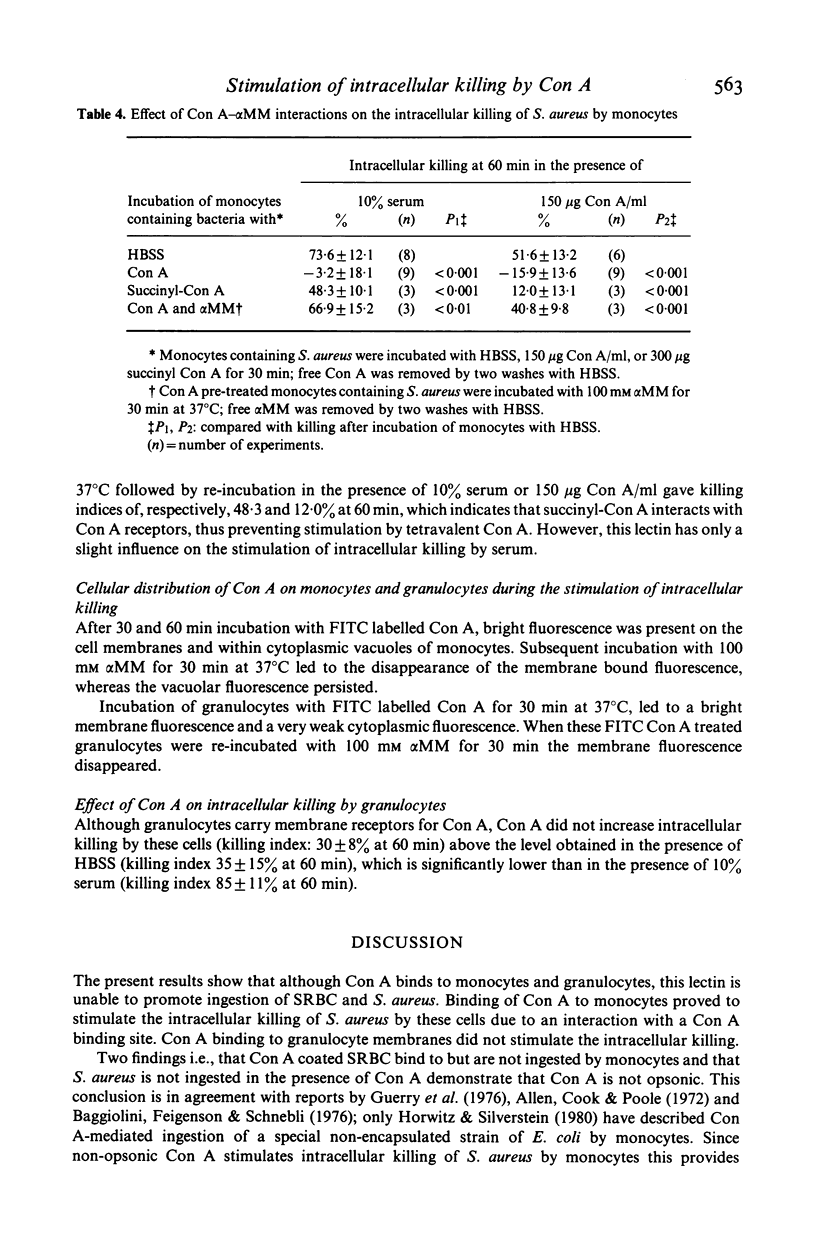
This study concerns the influence of concanavalin A (Con A) on phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human monocytes and granulocytes. Con A binds to S. aureus, monocytes, and granulocytes, and is not opsonic. Con A stimulates the killing of intracellular serum opsonized S. aureus by monocytes, but not by granulocytes. This stimulation of intracellular killing was inhibited by alpha-methyl-mannoside, indicating that the process occurs via Con A specific membrane binding sites. Unlike (tetravalent) Con A, divalent succinyl-Con A does not stimulate intracellular killing, indicating that the lectin valency is important for this stimulation. Con A bound to Sephadex particles, that can not be ingested by monocytes, does not stimulate intracellular killing of S. aureus either, although it, like free Con A, stimulates H2O2 production. Pre-incubation of monocytes with Con A inhibited Fc gamma and C3b-mediated ingestion of S. aureus as well as stimulation of the killing by serum. Divalent Con A had no effect on these functions. This inhibition by Con A is in all probability due to a steric impedance of Con A with respect to the interaction of IgG and C3b with their membrane receptors. Fluorescence techniques showed that Con A was localized on the membrane and in the cytoplasm of the monocytes, whereas granulocytes had only membrane bound lectin. Taken together, these findings suggest that cell penetration by the lectin is obligatory for the stimulation of intracellular killing.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Cook G. M., Poole A. R. Action of concanavalin A on the attachment stage of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Oct;68(2):466–467. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Feigenson M. E., Schnebli H. P. Ricin- and concanavalin A-binding sites on the surface of polymorphonuclear leukocytes have no receptor function in phagocytosis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1976 Oct 2;106(40):1371–1372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D. Effect of concanavalin A on phagocytosis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):44–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio235044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Metcalf J. A., Root R. K. Regulation of oxygen metabolism in human granulocytes: relationship between stimulus binding and oxidative response using plant lectins as probes. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1003–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofton R. W., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. M., van Furth R. The origin, kinetics, and characteristics of the Kupffer cells in the normal steady state. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):1–17. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Cohn Z. A. Effects of concanavalin A on mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Stimulation of endocytic activity and inhibition of phago-lysosome formation. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1364–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Sharon N., Lotan R. A differential response elicited in macrophages on interaction with lectins. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):408–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry D., Kenna M. A., Schrieber A. D., Cooper R. A. Concanavalin A-mediated binding and sphering of human red blood cells by homologous monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1695–1700. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van Zwet T. L., van Furth R. Effect of extracellular serum in the stimulation of intracellular killing of streptococci by human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):421–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.421-426.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Participation of immunoglobulins and complement components in the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):714–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.714-724.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Requirement of extracellular complement and immunoglobulin for intracellular killing of micro-organisms by human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):772–784. doi: 10.1172/JCI109362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Zabucchi G., Berton G., Schneider C. Metabolic stimulation of polymorphonuclear leucocytes: effects of tetravalent and divalent concanavalin A. J Membr Biol. 1978 Dec 29;44(3-4):321–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01944227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh K., Sato N., Kikuchi K. Effect of concanavalin A on the cytotoxicity of rat peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jan;25(1):17–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Diesselhoff-den Dulk M. M. Method to prove investigation of particles by macrophages with light microscopy. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(3):265–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


