Abstract
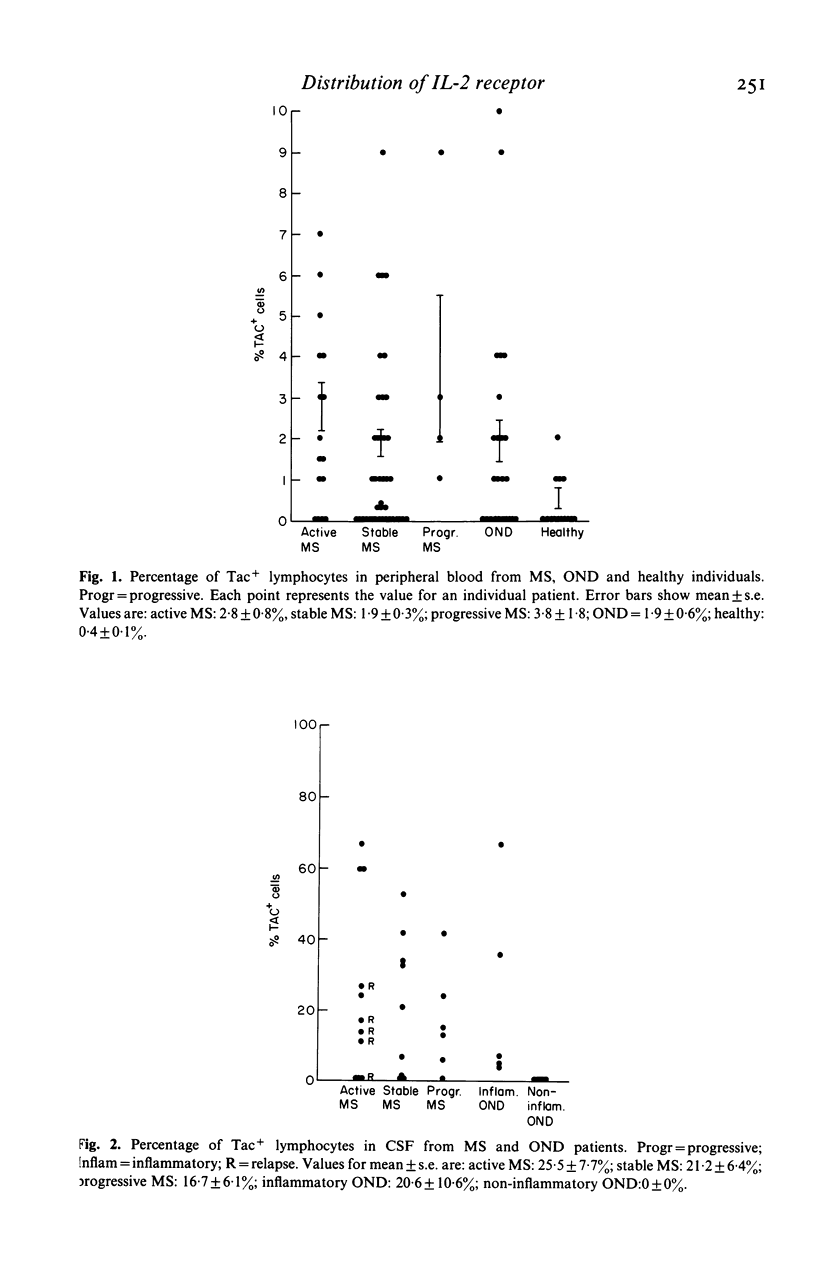
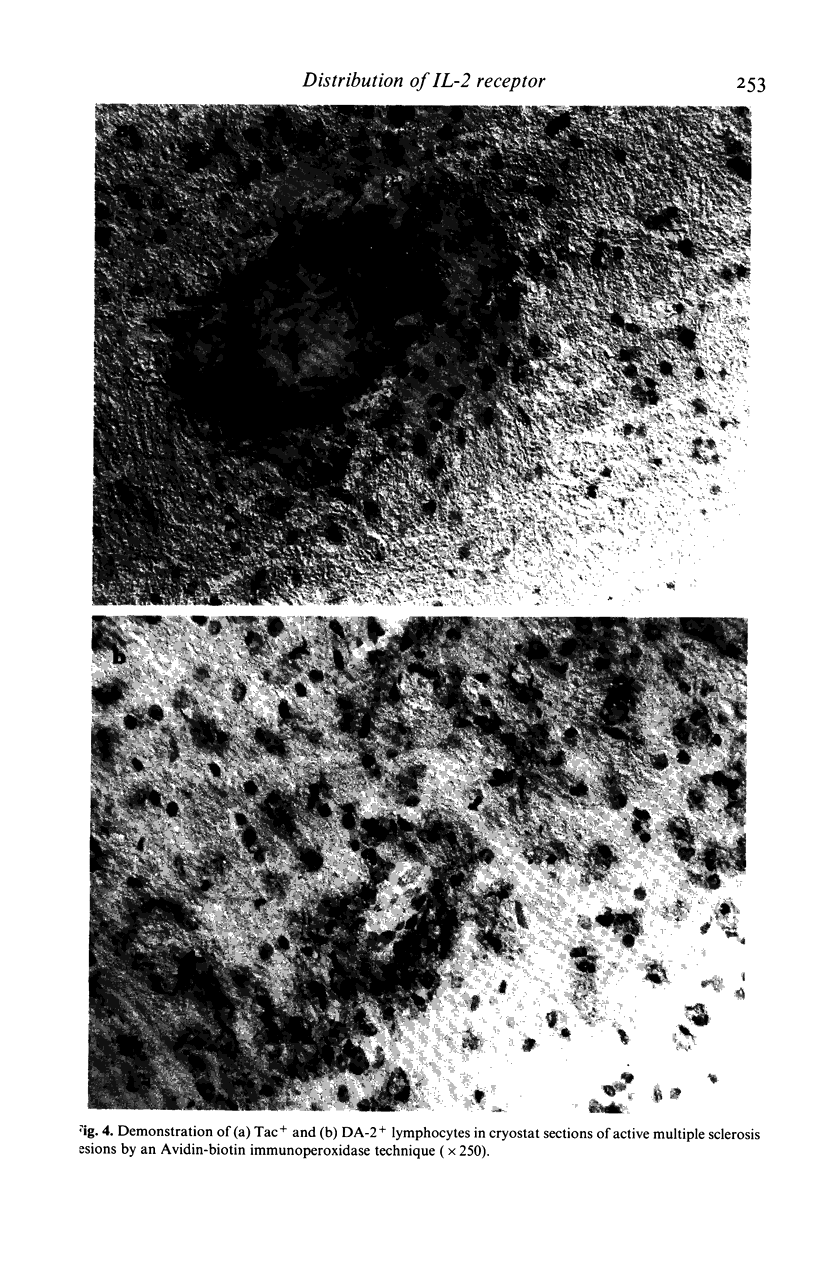
The identification of T cells in the brain using monoclonal antibodies has suggested a role for T cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS). In the present study the monoclonal antibody anti-Tac, shown to react with interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptors expressed on activated T cells, was used to determine levels of recently activated T cells in blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and brain sections from MS patients at different stages of disease. The CSF of MS patients contained much higher numbers of IL-2 receptor positive lymphocytes (up to 67%) than blood cells from the same patients, or the CSF of patients with non-inflammatory neurological diseases. In histological sections of the brain of MS patients with active disease, perivascular lymphocytes expressing IL-2 receptors were detected, as were lymphocytes containing IL-2. In contrast, these were absent in brain sections from patients with chronic MS, secondary demyelination or from normal controls. These observations in CSF and brain suggest that in multiple sclerosis, T-cell activation is occurring within the CNS and not in peripheral lymphoid tissue.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson T. C., 3rd, Fox R. I., Frisman D. M., Howell F. V. Immunohistologic analysis of lymphoid infiltrates in primary Sjogren's syndrome using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booss J., Esiri M. M., Tourtellotte W. W., Mason D. Y. Immunohistological analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in the central nervous system in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dommasch D., Grüninger W., Schultze B. Autoradiographic demonstration of proliferating cells in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol. 1977 Jan 13;214(2):97–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02430348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Fong S., Sabharwal N., Carstens S. A., Kung P. C., Vaughan J. H. Synovial fluid lymphocytes differ from peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):351–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle J. D., Farrands P. A., Balfour T. W., Chamberlain J., Amar S. S., Sheldon M. G. Controlled trial of faecal occult blood testing in the detection of colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1983 Jul 2;2(8340):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrosu M. G., Ennas M. G., Murru M. R., Marrosu G., Cianchetti C., Manconi P. E. Surface markers on lymphocytes from human cerebrospinal fluid. Identification by monoclonal antibodies. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Dec;5(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. I., Halliday A. M. Diagnosis and classification of multiple sclerosis. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):4–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naparstek Y., Ben-Nun A., Holoshitz J., Reshef T., Frenkel A., Rosenberg M., Cohen I. R. T lymphocyte lines producing or vaccinating against autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Functional activation induces peanut agglutinin receptors and accumulation in the brain and thymus of line cells. Eur J Immunol. 1983 May;13(5):418–423. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha A. B., Richman D. P., Arnason B. G. Detection of in vivo stimulated cerebrospinal-fluid lymphocytes by flow cytometry in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 25;303(13):713–717. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009253031301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Grant B. W., Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Immune cell populations in cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reunanen M. I. Spontaneous proliferation of cerebrospinal fluid mononuclear cells in multiple sclerosis. A longitudinal study. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Dec;3(4):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Agostini C., Trentin L., Zambello R., Chilosi M., Cipriani A., Ossi E., Angi M. R., Morittu L., Pizzolo G. Evidence of cells bearing interleukin-2 receptor at sites of disease activity in sarcoid patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Reinherz E. L., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis. Distribution of T cells, T cell subsets and Ia-positive macrophages in lesions of different ages. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Jun;4(3):201–221. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Uchiyama T., Uchino H. Expression of Tac antigen on activated normal human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):612–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Nelson D. L., Fleisher T. A., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. II. Expression of Tac antigen on activated cytotoxic killer T cells, suppressor cells, and on one of two types of helper T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1398–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachie A., Miyawaki T., Uwadana N., Ohzeki S., Taniguchi N. Sequential expression of T cell activation (Tac) antigen and Ia determinants on circulating human T cells after immunization with tetanus toxoid. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa Y., Fukui M., Ohta H., Kitamura K. 3H-thymidine autoradiography of the CSF cells in cases of non-neoplastic disease. J Neurol. 1976 Feb 13;211(3):195–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00313230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



