Abstract
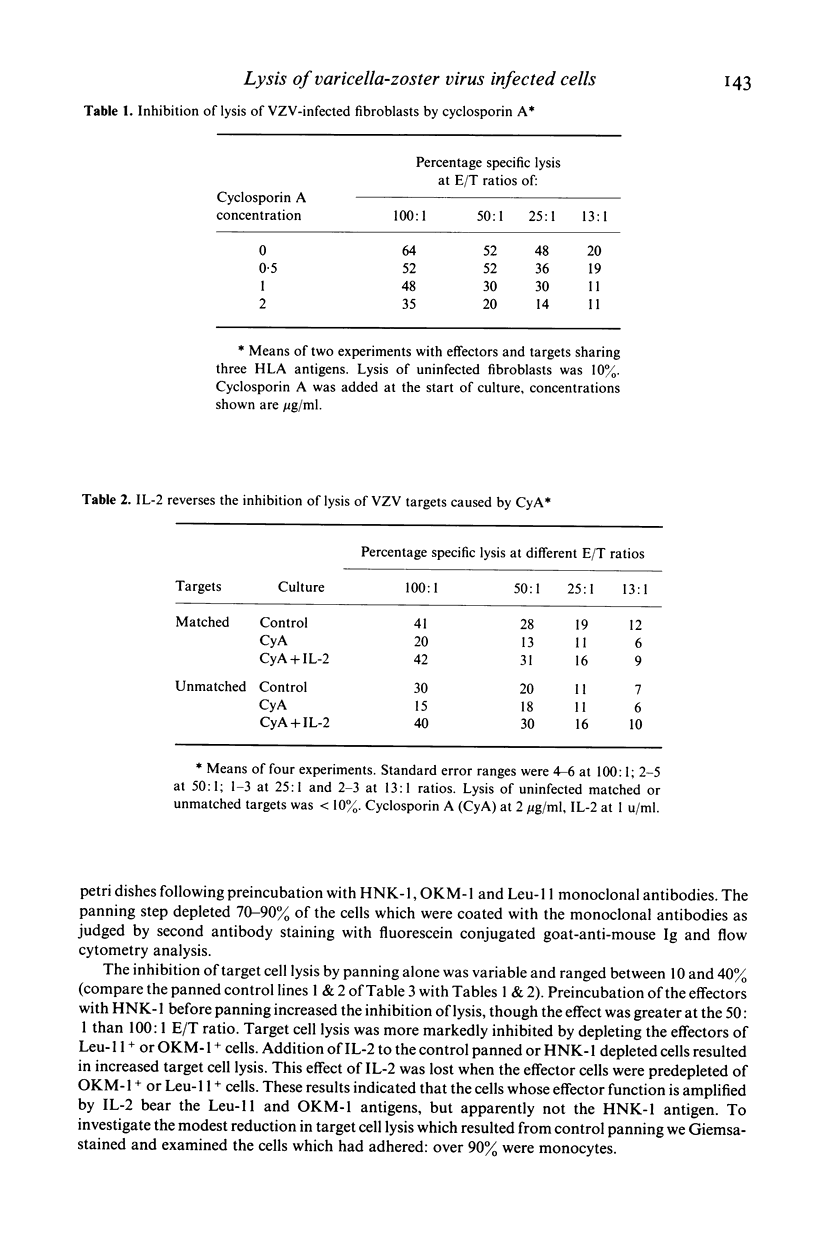
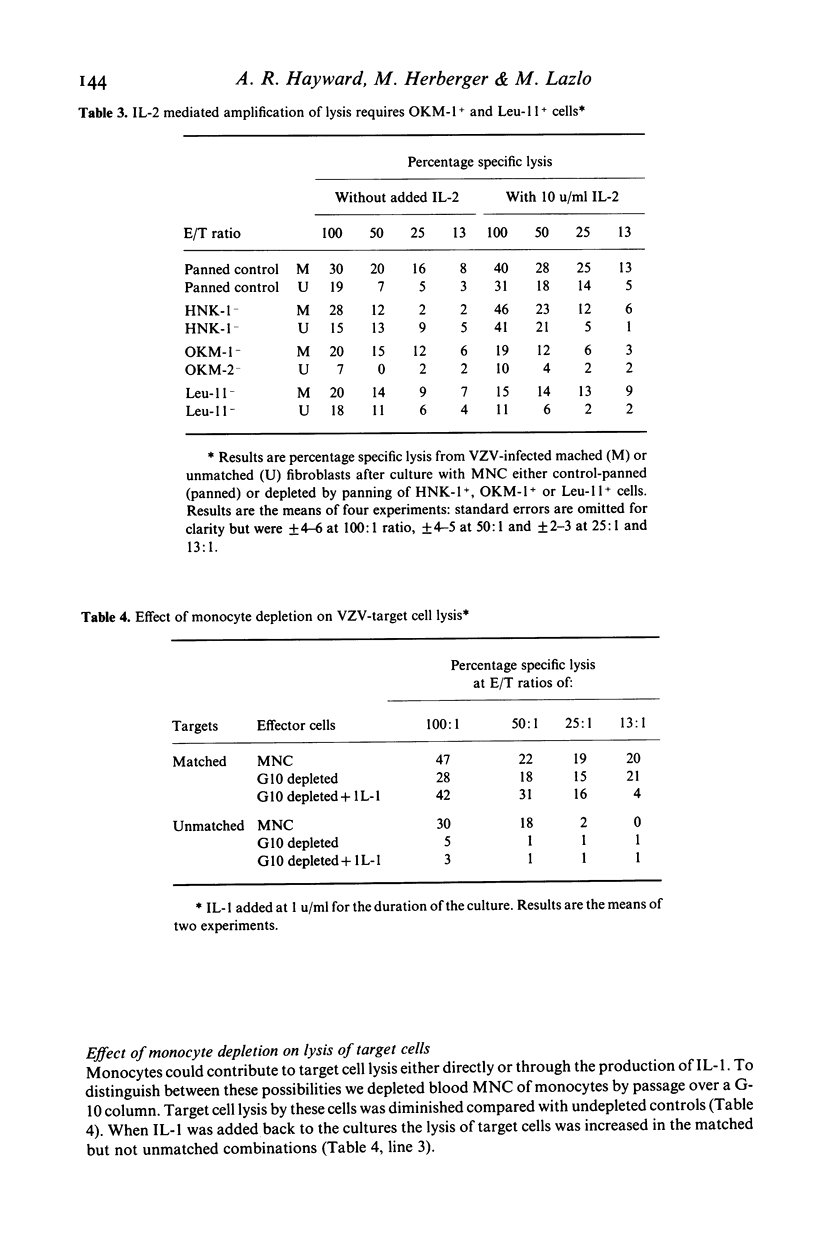
The in vitro lysis of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infected human fibroblasts by blood mononuclear cells (MNC) is inhibited by cyclosporin A, whether or not the effector and target cells chare HLA A or B antigens. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) reversed the inhibition by cyclosporin A (CyA) and also induced a further increase in target cell lysis by MNC in the absence of CyA. MNC depleted of OKM-1+ or Leu-11+ cells showed reduced lysis of VZV infected fibroblasts and this reduction was not overcome by adding IL-2. Depletion of monocytes from the MNC effectors reduced target cell lysis and this effect was reversed by adding Interleukin 1 (IL-1). The results indicate that NK cells contribute to the lysis of VZV infected cells and suggest that IL-2 release by T cells, as a result of HLA matching or antigen representation, may amplify this mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrus L., Lafferty K. J. Inhibition of T-cell activity by cyclosporin A. Scand J Immunol. 1981 May;15(5):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Glorioso J. C., Schwartz S. A. Relationship between expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and susceptibility of target cells to human natural killer activity. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1544–1561. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden R. A., Levin M. J., Giller R. H., Tubergen D. G., Hayward A. R. Lysis of varicella zoster virus infected cells by lymphocytes from normal humans and immunosuppressed pediatric leukaemic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden R. A., McGavren L., Hayward A. R., Levin M. J. Use of bone marrow fibroblasts to prepare targets for an HLA restricted-cytotoxicity assay system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.696-700.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G. Reversible induction of natural killer cell activity in cloned murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):155–158. doi: 10.1038/305155a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. A., Evans R., Kirkpatrick D., Lopez C. Heterogeneity of human NK cells: comparison of effectors that lyse HSV-1-infected fibroblasts and K562 erythroleukemia targets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1663–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. D., Tutschka P. J. Effect of cyclosporin A on human lymphocyte responses in vitro. I. CsA allows for the expression of alloantigen-activated suppressor cells while preferentially inhibiting the induction of cytolytic effector lymphocytes in MLR. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2601–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Allavena P., Spreafico F., Mantovani A. Inhibition of human natural killer activity by cyclosporin A. Transplantation. 1981 Feb;31(2):113–116. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198102000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Esber E., Saral R., Manischewitz J. F., Rogers J. L., Rook A. H., Santos G. W., Burns W. H. HLA-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte and nonthymic cytotoxic lymphocyte responses to cytomegalovirus infection of bone marrow transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2036–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmage D. W., Woolnough J. A., Hemmingsen H., Lopez L., Lafferty K. J. Activation of cytotoxic T cells by nonstimulating tumor cells and spleen cell factor(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4610–4614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda N., Yasuda Y. Biological and immunological studies of bovine hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 2):183–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Shiroguchi T., Kobayashi Y. HLA-restricted T lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against herpes simplex virus-infected cells in humans. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.190-197.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. I. Lysis restricted by HLA class II MB and DR antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


