Abstract
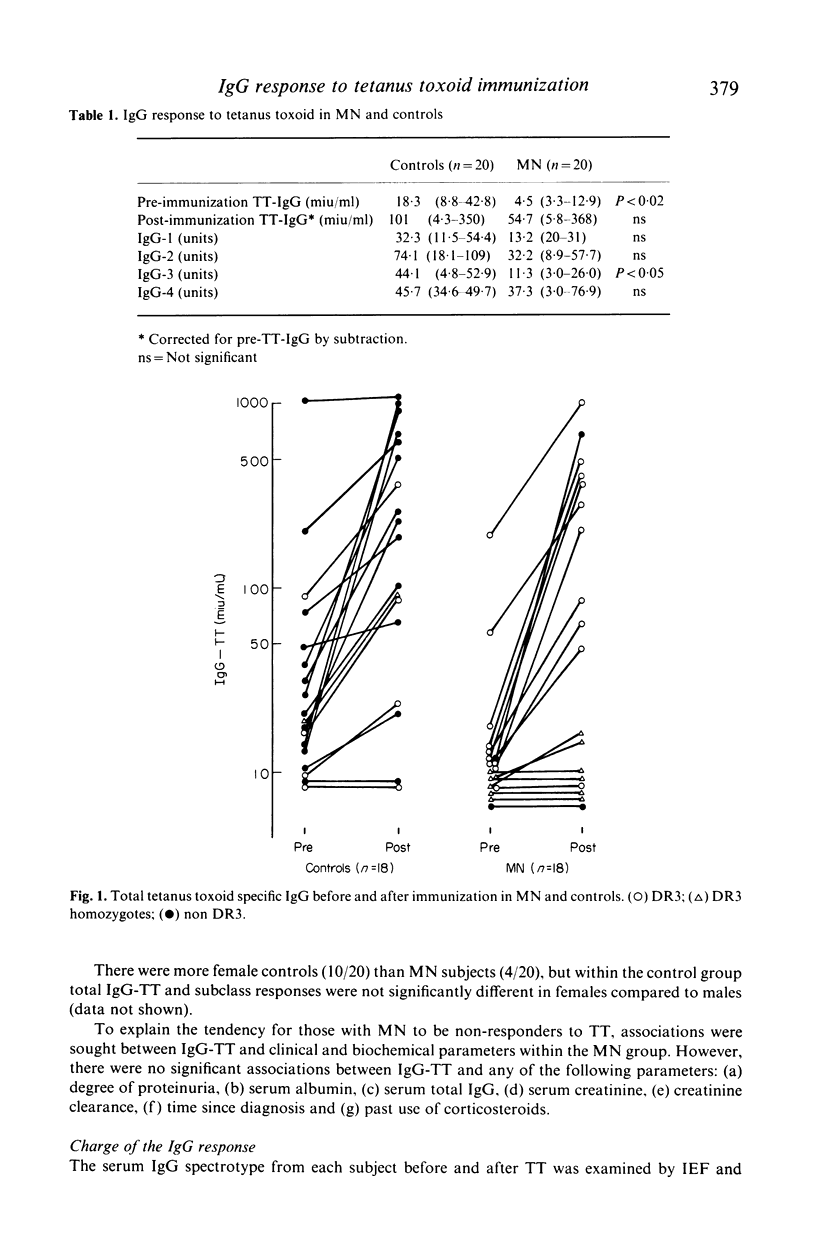
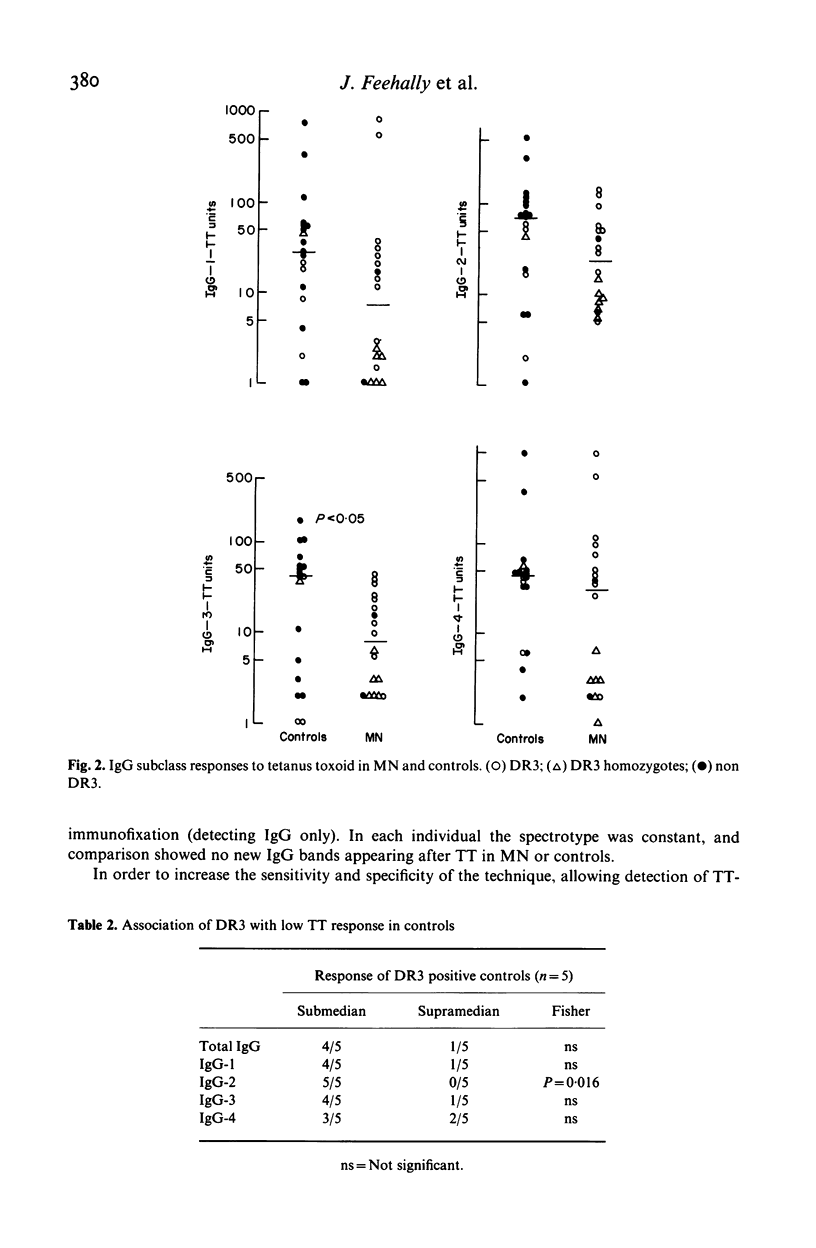
The IgG response to tetanus toxoid (TT) immunization was quantitated by by radioimmunoassay in patients with membranous nephropathy (MN) and healthy controls. Variation in subclass (ELISA) and electrical charge (isoelectric focussing, immunofixation & autoradiography) of the IgG response were also assessed. Total IgG and igG subclass responses were impaired in MN compared to controls, although this was only significant for IgG-3 (P less than 0 X 05). Non responders to TT were more common in MN, and response was independent of disease activity. No distinctive pattern of IgG subclass response or IgG spectrotype was seen in MN. Impaired response to TT was associated with HLA-DR3 among controls, and in MN (88 X 8% of whom were DR3) markedly depressed responses occurred in apparent DR3 homozygotes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder J. N., Chiorazzi N., Gibofsky A., Fotino M., Kunkel H. G. Special characteristics of cellular immune function in normal individuals of the HLA-DR3 type. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister K. M., Howarth G. S., Clarkson A. R., Woodroffe A. J. Glomerular IgG subclass distribution in human glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Apr;19(4):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley P., Feehally J., Doré P., Coupes B., Short C. D., Pumphrey R. S., Mallick N. P. Gm allotypes in membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 1;309(9):556–557. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309013090914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney G., Walls R. S., George C. R., Payne J. E., Newland R. C., Lawrence J. R. Immunological function in glomerulonephritis. Aust N Z J Med. 1980 Oct;10(5):502–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1980.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Salant D. J. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Principato M. A., Thompson G. S., Teichman F. Antigen-specific and polyclonal immunoglobulin production induced by a cloned tetanus toxoid-specific T cell line. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1164–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Webster A. D., Pattison J., Doniach D., Kennedy L. A., Batchelor J. R. Enhanced antibody responses in active chronic hepatitis: relation to HLA-B8 and HLA-B12 and porto-systemic shunting. Lancet. 1976 May 1;1(7966):930–934. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Presence of auto-anti-idiotypic antibody during the normal human immune response to tetanus toxoid antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Presence of circulating anti-idiotype-bearing cells after booster immunization with tetanus toxoid (TT) and inhibition of anti-TT antibody synthesis by auto-anti-idiotypic antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1634–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto S., Tomino S., Mitsuya H., Fujiwara H., Tsuda H. Age-related decline in the in vitro and in vivo syntheses of anti-tetanus toxoid antibody in humans. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2347–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klouda P. T., Manos J., Acheson E. J., Dyer P. A., Goldby F. S., Harris R., Lawler W., Mallick N. P., Williams G. Strong association between idiopathic membranous nephropathy and HLA-DRW3. Lancet. 1979 Oct 13;2(8146):770–771. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Hall R. P., Fauci A. S., Katz S. I., Hamburger M. I., Frank M. M. Defective Fc-receptor functions associated with the HLA-B8/DRw3 haplotype: studies in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis and normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 22;304(4):185–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101223040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Balaban S. Quantitative method for determining human G allotype antigens (Gm). II. Differences in Gm gene expression for G1 and G3 H chains in sera. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):991–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs C. C., Michalski J. P. Lymphocyte abnormality associated with HLA-B8 in healthy young adults. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):936–941. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies K., Boyer R., Stevens R., Louie J. Anti-tetanus toxoid antibody synthesis after booster immunization in systemic lupus erythematosus. Comparison of the in vitro and in vivo responses. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Dec;23(12):1343–1350. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oite T., Batsford S. R., Mihatsch M. J., Takamiya H., Vogt A. Quantitative studies of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by planted, cationized antigen. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):460–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Kohno Y., Iwamoto I., Tanimura M., Naito S. Association between an HLA haplotype and low responsiveness to tetanus toxoid in man. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):359–361. doi: 10.1038/272359b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. Human IgG subclasses in health and disease. (A review). Part I. Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Jul-Sep;10(3):463–479. doi: 10.1007/BF02938793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Allyn S. P., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced in vitro antibody production in humans: tetanus toxoid-specific antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls R. S., Godfrey P., Newland R. C., Carney G., Lawrence J. R. Affinity of tetanus toxoid antibody in glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Sep;24(3):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Giessen M., Groenboer-Kempers O. The subclasses of human IgG antibodies against tetanus toxoid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):117–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



