Abstract
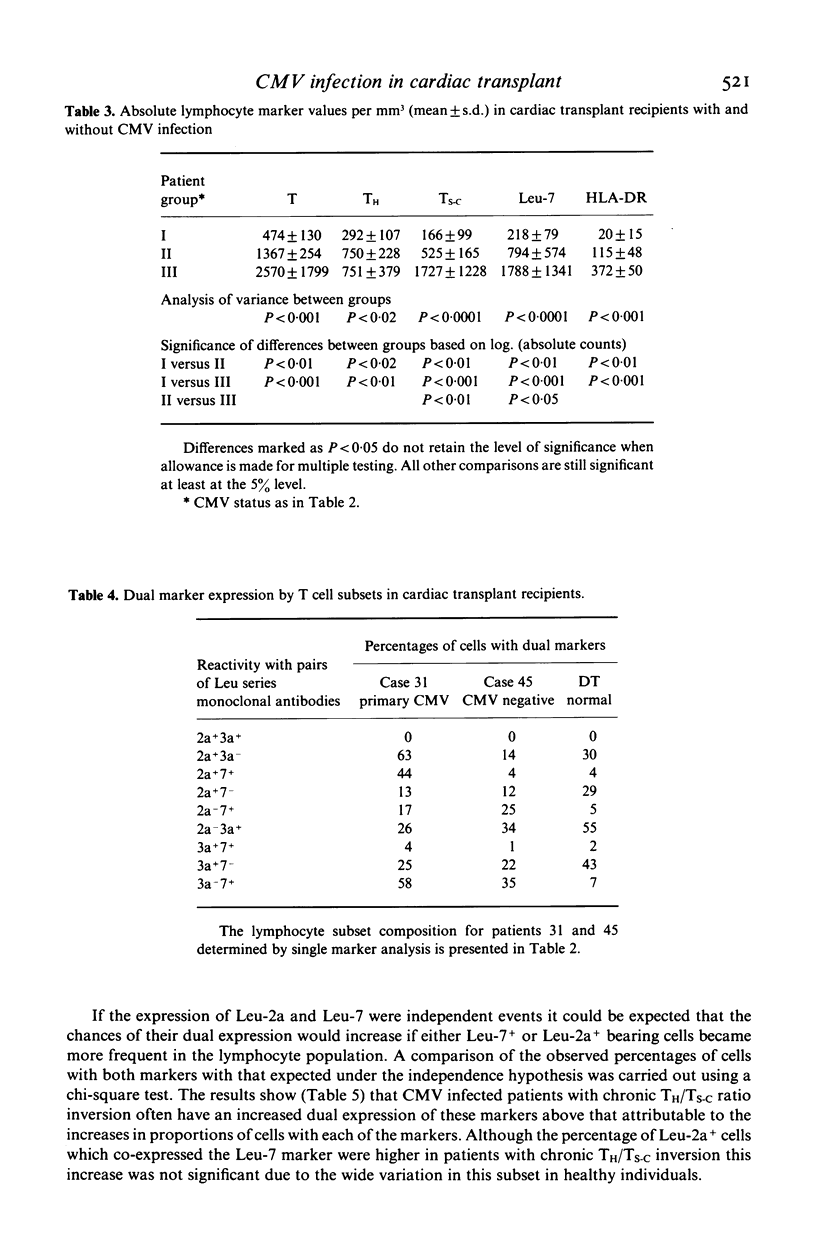
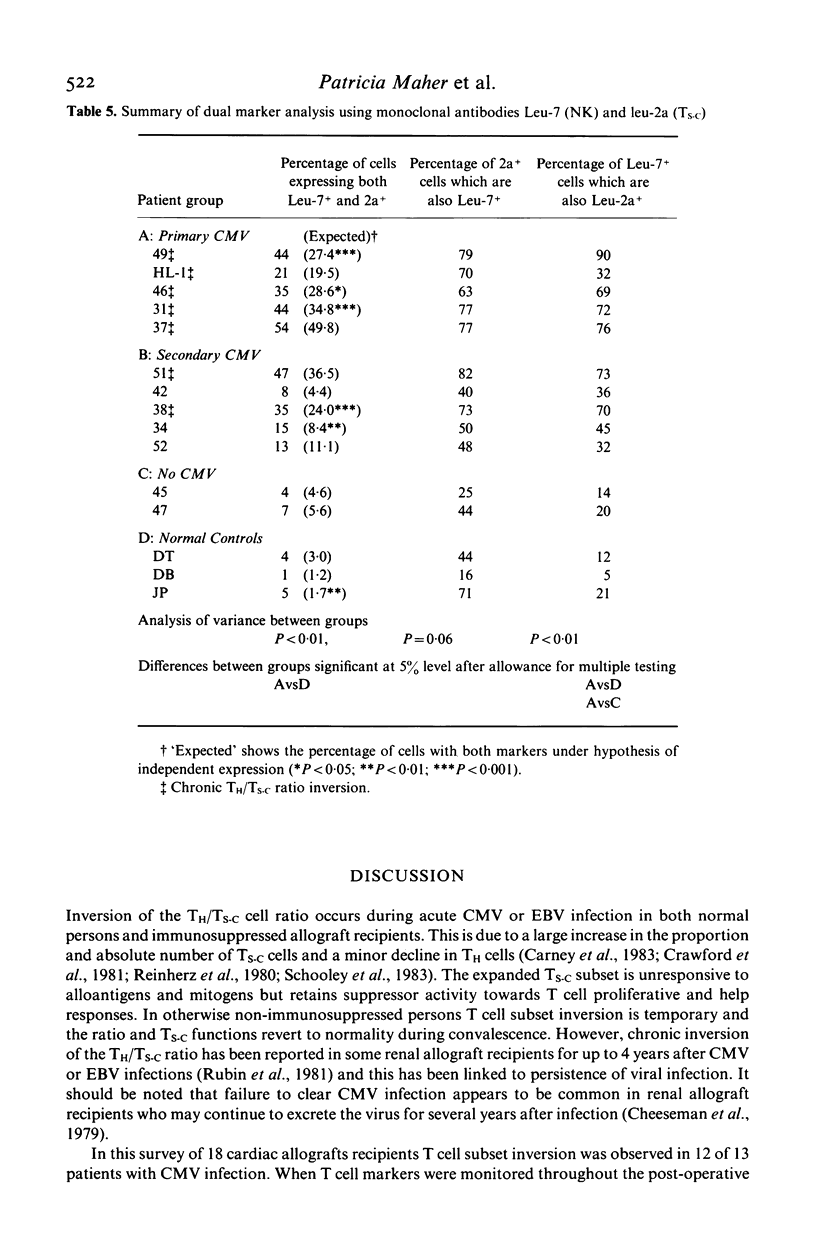
Lymphocyte subsets were analysed in 18 patients during the first 3 years after cardiac transplantation. The patients received Cyclosporin A and prednisolone for maintenance immunosuppression. Serological evidence of active cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection was found in 13 cases (72%), and in 12 of these an inversion usually of the T helper/T suppressor-cytotoxic ratio (TH/TS-C) was detected. T subset inversion usually preceded the diagnostic rise in CMV antibody titre. In 69% of patients with CMV the TH/TS-C ratio remained inverted throughout follow-up (245-951 days). Persistent T subset inversion was not found in all five patients who lacked serological evidence of active CMV. Chronic inversion consisted of an average increase in TS-C of 152% and an average decline in TH cells of 31% as compared to CMV negative patients. The proportion of lymphoid cells reacting with a phenotypic marker for natural killer (NK) cells (Leu-7) was increased by 83%. These alterations were also reflected in the absolute numbers of cells with these markers. Two-colour immunofluorescence analysis revealed that the expanded TS-C population present during chronic inversion was predominantly Leu-7+. As TS-C+ Leu-7+ cells in healthy persons may be hyporesponsive NK cells, a sustained increase in this cell type in allograft recipients could further reduce immunocompetence, thereby predisposing to superinfection or malignancy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Miller C. A., Gartland G. L., Balch C. M. Differentiation stages of human natural killer cells in lymphoid tissues from fetal to adult life. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):273–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Iacoviello V., Hirsch M. S. Functional properties of T lymphocytes and their subsets in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):390–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H., Stewart J. A., Winkle S., Cosimi A. B., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Russell P. S., Baker G. P., Herrin J., Rubin R. H. Cytomegalovirus excretion 2-14 years after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1979 Mar;11(1):71–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Brickell P., Tidman N., McConnell I., Hoffbrand A. V., Janossy G. Increased numbers of cells with suppressor T cell phenotype in the peripheral blood of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):291–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dummer J. S., Ho M., Rabin B., Griffith B. P., Hardesty R. L., Bahnson H. T. The effect of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infection on T lymphocyte subsets in cardiac transplant patients on cyclosporine. Transplantation. 1984 Oct;38(4):433–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Grumet F. C., Evans R. L. Activation of human T lymphocyte subsets: helper and suppressor/cytotoxic T cells recognize and respond to distinct histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2124–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Faldetta T. J., Humphreys R. E., Pratt D. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Peripheral human T cells sensitized in mixed leukocyte culture synthesize and express Ia-like antigens. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1440–1445. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. Cytomegalovirus infections following renal transplantation. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1151–1178. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Cooper D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Morimoto C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Immunoregulatory human T lymphocytes triggered as a consequence of viral infection: clonal analysis of helper, suppressor inducer and suppressor effector cell populations. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1167–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole C. M., Carvalho G. S., Cranage M. P., Large S. Immune responses in cardiac transplantation. I. Detection of activated TIa+ cells in the blood during herpes virus infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Sep;57(3):671–678. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn I. Cancer in immunosuppressed patients. Transplant Proc. 1984 Apr;16(2):492–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. A human NK and K cell subset shares with cytotoxic T cells expression of the antigen recognized by antibody OKT8. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., O'Brien C., Rosenthal P., Schlossman S. F. The cellular basis for viral-induced immunodeficiency: analysis by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1269–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Carney W. P., Schooley R. T., Colvin R. B., Burton R. C., Hoffman R. A., Hansen W. P., Cosimi A. B., Russell P. S., Hirsch M. S. The effect of infection on T lymphocyte subpopulations: a preliminary report. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1981;3(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(81)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S., Colvin R. B., Cosimi A. B., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., McCluskey R. T., Burton R. C., Russell P. S., Herrin J. T., Delmonico F. L. Association of herpesvirus infections with T-lymphocyte-subset alterations, glomerulopathy, and opportunistic infections after renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 10;308(6):307–313. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302103080603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilden A. B., Abo T., Balch C. M. Suppressor cell function of human granular lymphocytes identified by the HNK-1 (Leu 7) monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1171–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonck L. F., de Gast G. C. Is cytomegalovirus infection a major cause of T cell alterations after (autologous) bone-marrow transplantation? Lancet. 1984 Apr 28;1(8383):932–935. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. The human Ia system. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:221–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


