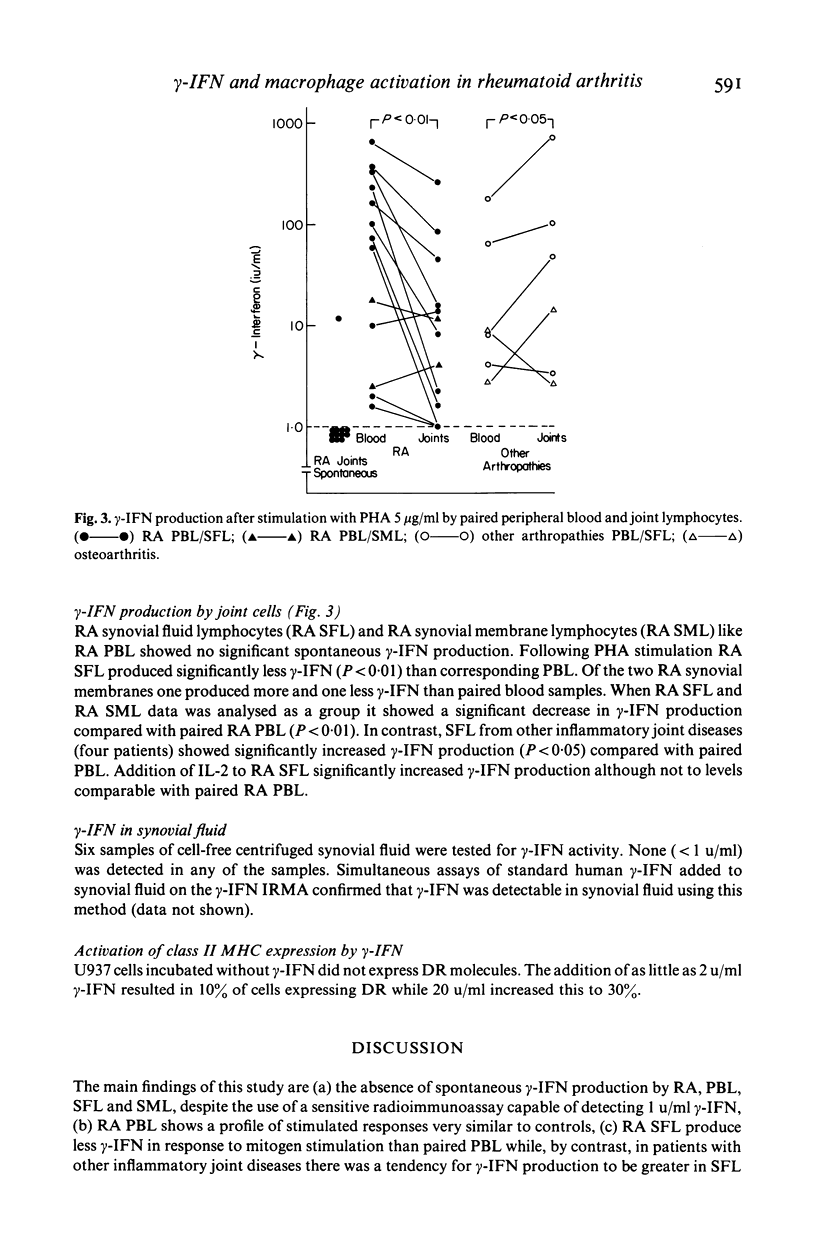
Abstract
Gamma-interferon (gamma-IFN) is a potent inducer of surface expression of class II MHC molecules in vitro. Enhanced HLA-DR expression is a characteristic immuno-histological feature of rheumatoid joints. To assess the possible relevance of gamma-IFN to macrophage (M phi) activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) we investigated the spontaneous and mitogen-induced production of gamma-IFN by RA lymphocytes using a sensitive radioimmunoassay. Synovial fluids (SF) from a variety of inflammatory and non-inflammatory rheumatic diseases did not contain measurable amounts of IFN. RA lymphocytes from peripheral blood (PBL) and joints failed to show spontaneous gamma-IFN production. RA and control PBL were equally responsive to both mitogen stimulation and to the addition of exogenous interleukin 2 (IL-2) as control PBL. SF lymphocytes from RA patients showed a significantly decreased PHA-stimulated gamma-IFN production and this was in contrast to the SF lymphocytes from patients with other inflammatory joint diseases who showed significantly increased gamma-IFN production compared with matched PB lymphocytes. These results show that gamma-IFN production by peripheral blood and joint cells from patients with RA is normal and it remains to be established whether gamma-IFN is the factor responsible for the macrophage activation seen in the disease.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsen T. G., Fróland S. S., Natvig J. B., Pahle J. Antigen and unspecific mitogen stimulation of lymphocytes eluted from rheumatoid inflammatory tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(9):1057–1063. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew P. W., Rees A. D., Scoging A., Dobson N., Matthews R., Whittall J. T., Coates A. R., Lowrie D. B. Secretion of a macrophage-activating factor distinct from interferon-gamma by human T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):962–964. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. II. Enhanced secretion of interleukin 1 by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):437–440. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. D., Panayi G. S. Natural killer cell activity in inflammatory joint disease. Clin Rheumatol. 1983 Sep;2(3):243–249. doi: 10.1007/BF02041398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon T. H., de Vere-Tyndall A., Tyrrell D. A., Denman A. M., Ansell B. M. Interferon system in patients with systemic juvenile chronic arthritis: in vivo and in vitro studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesario T. C., Andrews B. S., Martin D. A., Jason M., Treadwell T., Friou G., Tilles J. G. Interferon in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatic disease. J Rheumatol. 1983 Aug;10(4):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combe B., Pope R. M., Fischbach M., Darnell B., Baron S., Talal N. Interleukin-2 in rheumatoid arthritis: production of and response to interleukin-2 in rheumatoid synovial fluid, synovial tissue and peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):520–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGré M., Mellbye O. J., Clarke-Jenssen O. Immune interferon in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis and related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Dec;42(6):672–676. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.6.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug J. H., Førre O., Kvien T. K., Egeland T., Degré M. Natural killer (NK) cell activity of peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):490–494. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W. An immunohistological analysis of lymphocyte subpopulations and their microenvironment in the synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):22–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke O., Panayi G. S., Janossy G., Poulter L. W., Tidman N. Analysis of T cell subsets in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by means of monoclonal antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):357–361. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure G., Bene M. C., Tamisier J. N., Thomas P. Monoclonal antibody (HNK 1-Leu 7) defined lymphoid cells in the blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Sep;26(9):1173–1175. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Hengartner H., Weber E., Fehr K., Grob P. J., Cohen G. Interleukin 1 activity in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1982;2(2):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00541245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler F., Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J., Epstein L. B. Analysis of the defects responsible for the impaired regulation of Epstein-Barr virus-induced B cell proliferation by rheumatoid arthritis lymphocytes. I. Diminished gamma interferon production in response to autologous stimulation. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):173–188. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley J. A., Nussbaum-Blumenson A., Sheedy D., Grossmayer B. J., Ozer H. Identification of the T cell subset that produces human gamma interferon. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2522–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein K. T., Palladino M. A., Welte K., Vilcek J. Purified human interleukin-2 enhances induction of immune interferon. Cell Immunol. 1983 Aug;80(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Redelman D., Zvaifler N. J., Naides S. Studies of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. I. Evidence for activated natural killer- (NK) like cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1758–1763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L., Perez N., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Devos R. Pure interferon gamma enhances class II HLA antigens on human monocyte cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):106–108. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Recombinant gamma interferon enhances natural killer cell activity similar to natural gamma interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik A., Roberts W. K., Vasil A., Blumenthal E., Larosa F., Leibson H. J., Endres R. O., Graham S. D., Jr, White J., Hill J. Coordinate production by a T cell hybridoma of gamma interferon and three other lymphokine activities: multiple activities of a single lymphokine? J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


