Abstract
The serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis, in presence of human complement, caused destruction of glial cells and myelin in cultured nervous tissue, particularly in the acute stage of the disease. Cytotoxicity of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was not wholly specific for multiple sclerosis, being observed also in cases of encephalitis and certain viral diseases. The degree of cytotoxicity of the CSF correlated with the increase in γ-globulin (IgG) in the cerebrospinal fluid. Immunoelectrophoresis studies of the CSF showed the presence in 50% of cases of an abnormal fast γ-globulin component.
These findings have two important implications. Firstly they support the concept that demyelination in multiple sclerosis and related diseases is the result of an autoimmune process. Secondly they are useful for the laboratory diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and its differentiation from non-demyelinating disorders of the nervous system.
Full text
PDF

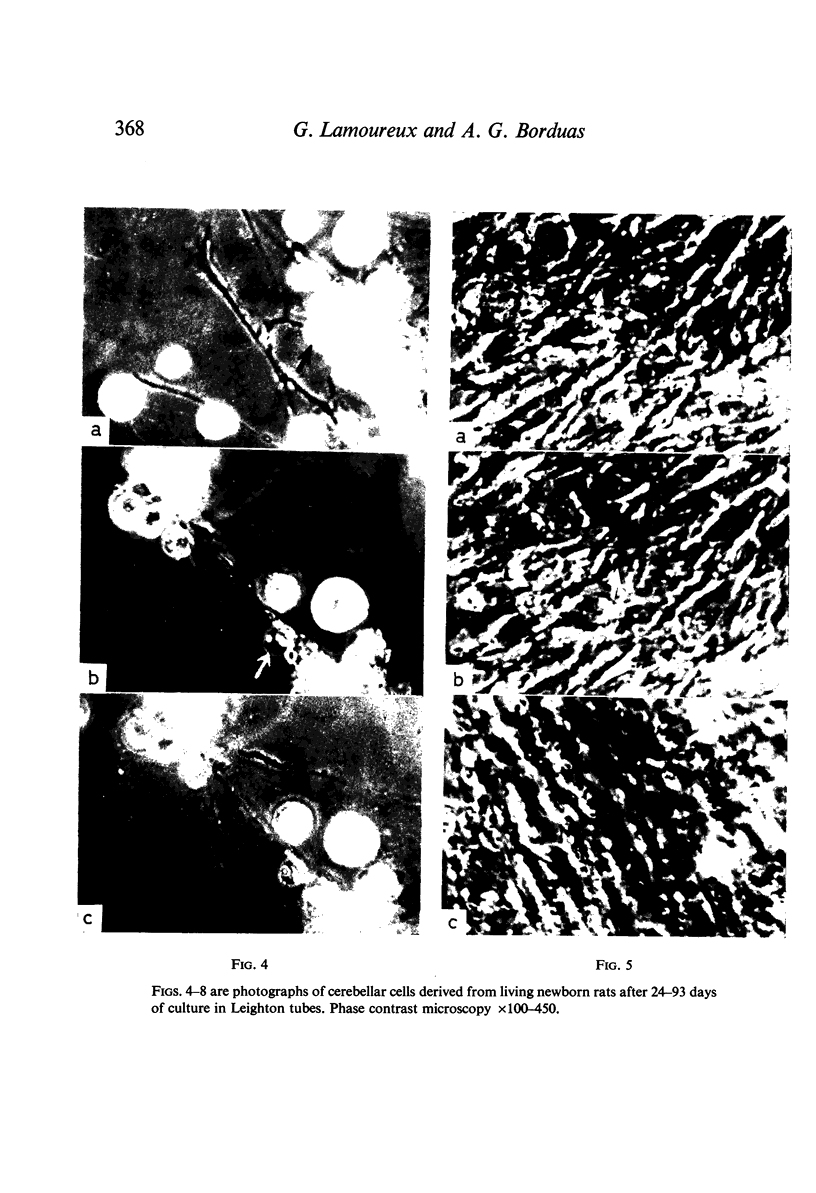
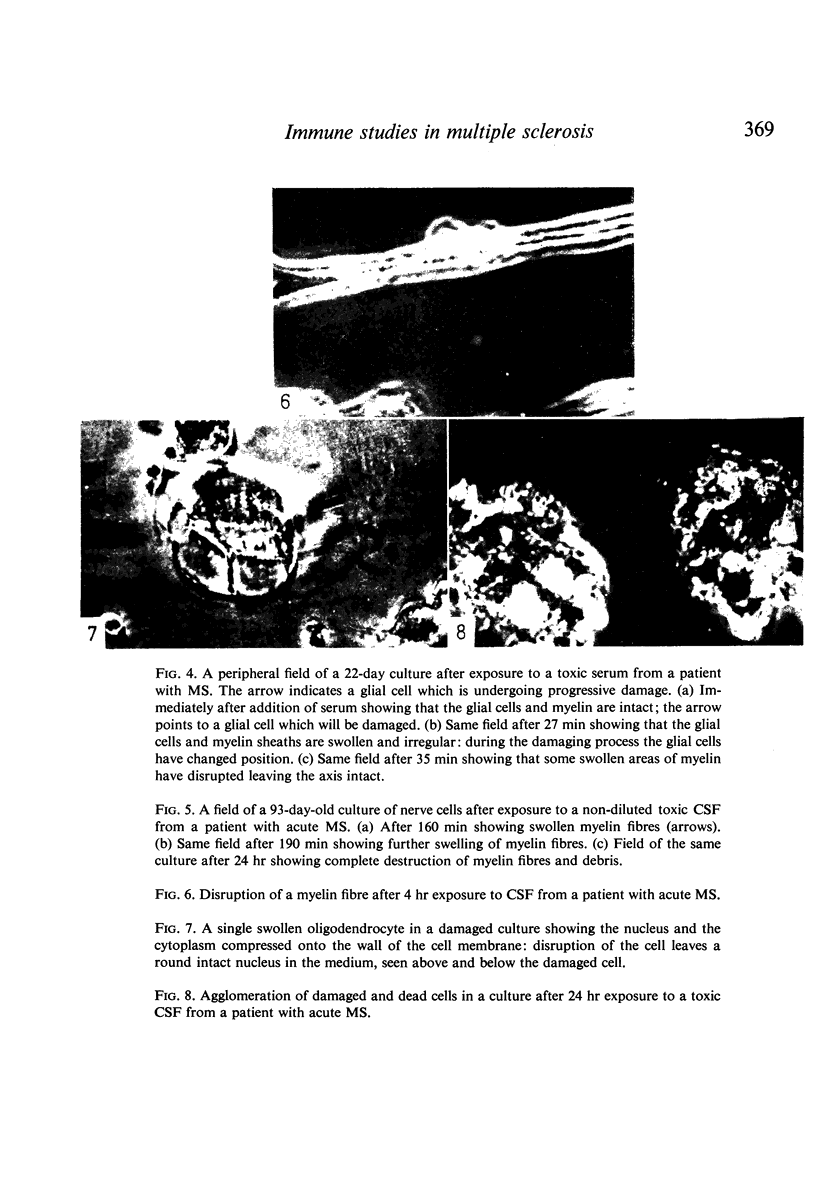
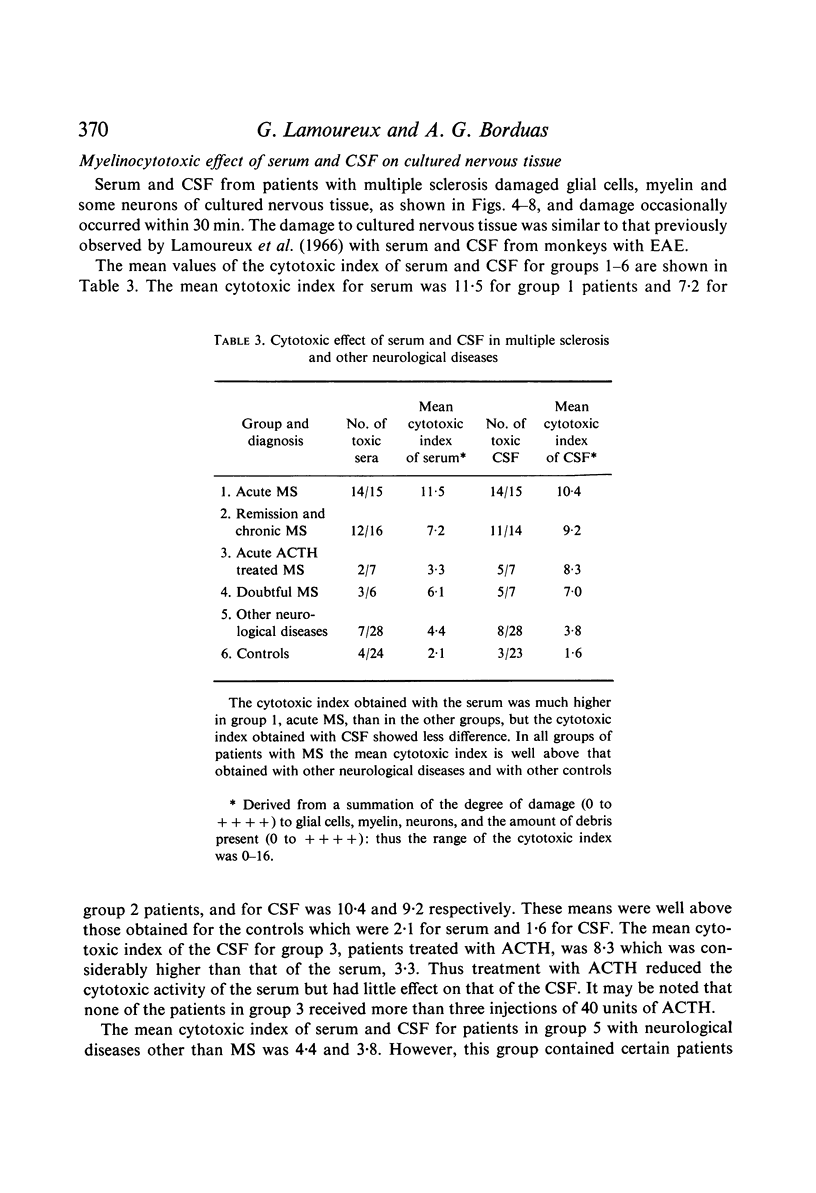
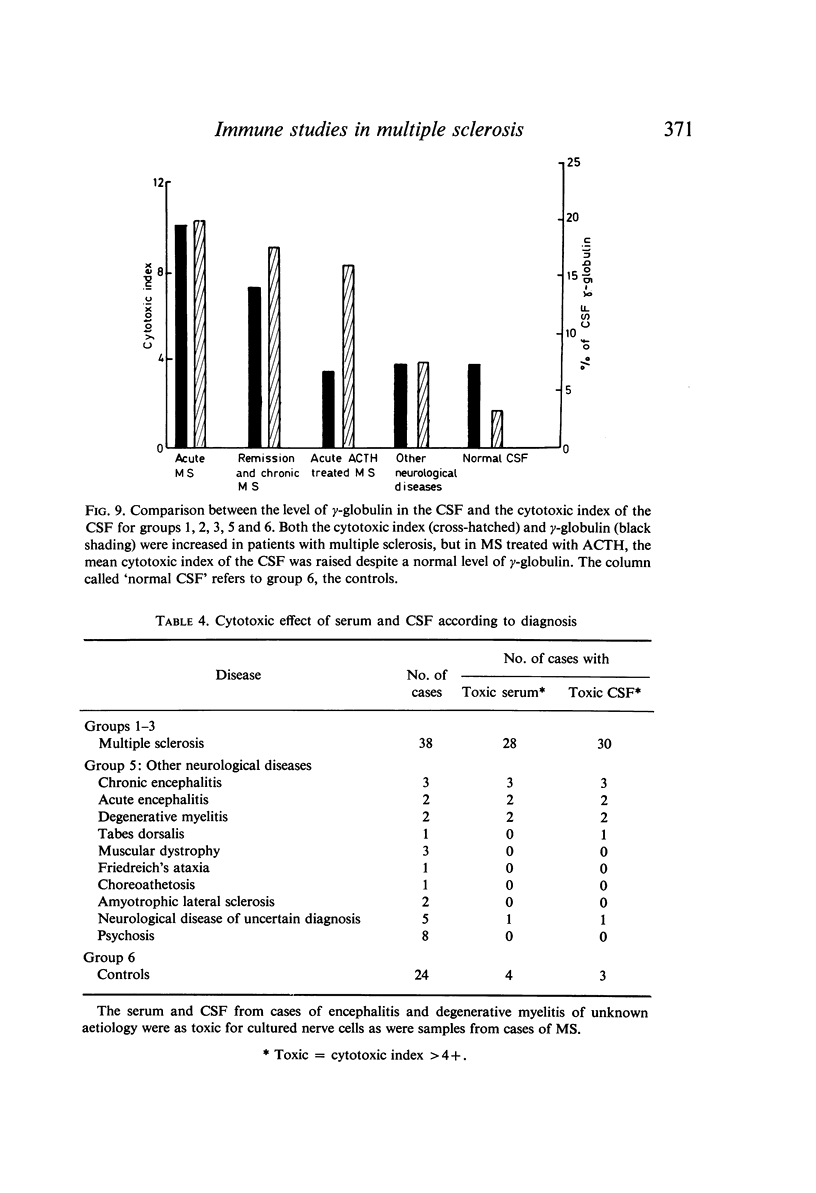
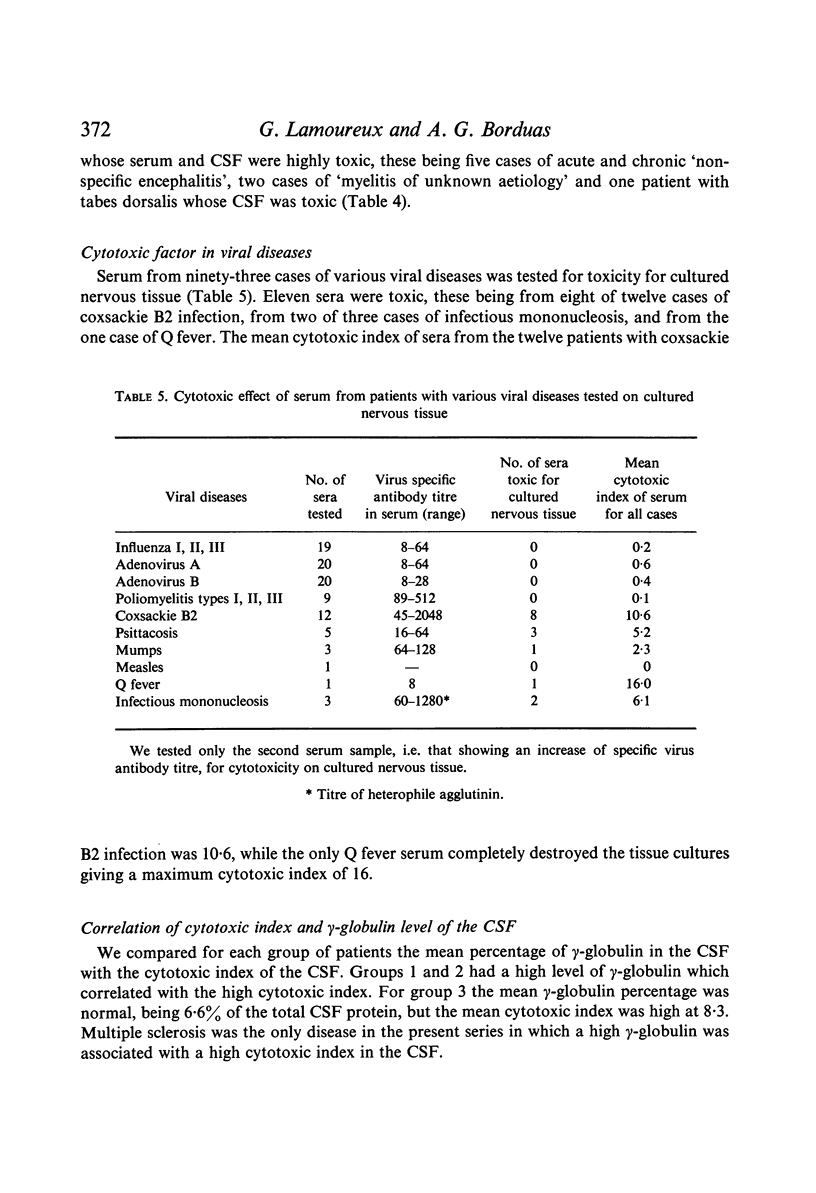




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUER H., HEITMANN R. Chemische und serologische Untersuchungen bei der multiplen Sklerose. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1958;178(1):47–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER H. Zur Frage der Identität der Liquorproteine mit den Eiweisskörpern des Blutserums. I. Besonderheiten der Liquorproteine hinsichtlich der Vorfraktion, der gamma-Globuline und der proteingebundenen Lipide. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1956;175(4):354–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B., APPEL S. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF DEMYELINATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:280–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEDOROFF S., DOERR J. Effect of human blood serum on tissue cultures. III. A natural cytotoxic system in human blood serum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Aug;29:331–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEDOROFF S., WEBB S. J. Natural cytotoxic antibodies in human blood sera which react with mammalian cells and bacteria. Nature. 1962 Jan 6;193:80–81. doi: 10.1038/193080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD E. J., CASPARY E. A., BALL E. J. Some biological properties of a highly active encephalitogenic factor isolated from human brain. Lancet. 1963 Jul 6;2(7297):11–13. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD E. J., RIDLEY A. Cerebrospinal fluid gamma-globulin in multiple sclerosis. Observations on its nature. Br Med J. 1960 Oct 8;2(5205):1053–1055. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5205.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J., Hughes D. Toxicity of motor neurone disease serum for myelin in tissue culture. Br Med J. 1965 Dec 11;2(5475):1399–1401. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5475.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JELLINGER K., SEITELBERGER F. Akute tödliche Entmarkungs-Encephalitis nach wiederholten Hirntrockenzellen-injektionen. Klin Wochenschr. 1958 May 1;36(9):437–441. doi: 10.1007/BF01478731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABAT E. A., FREEDMAN D. A. A study of the crystalline albumin, gamma globulin and total protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of 100 cases of multiple sclerosis and in other diseases. Am J Med Sci. 1950 Jan;219(1):55–64. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195001000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. H., SVEC K. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RELATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL AND TISSUE ANTIGENS. III. PRESENCE IN HUMAN SERA OF STREPTOCOCCAL ANTIBODY CROSS-REACTIVE WITH HEART TISSUE. ASSOCIATION WITH STREPTOCOCCAL INFECTION, RHEUMATIC FEVER, AND GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:651–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Moore D. H., Landow H. AN ELECTROPHORETIC STUDY OF THE PROTEIN COMPONENTS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO THE SERUM PROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1942 Sep;21(5):571–577. doi: 10.1172/JCI101335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. A HYPERACUTE FORM OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jul;47:61–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux G., Boulay G., Borduas A. G. A cytotoxic antibody for cultured nervous tissue in serum and cerebrospinal fluid from rhesus monkeys with allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):307–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPIRA K., PARK D. C. Gamma globulin studies of multiple sclerosis and their application to the problem of diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1961 May;24:121–124. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.24.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UCHIMURA I., SHIRAKI H. A contribution to the classification and the pathogenesis of demyelinating encephalomyelitis; with special reference to the central nervous system lesions caused by preventive inoculation against rabies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1957 Apr;16(2):139-203; discussion, 203-8. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195704000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOKOYAMA M., EINSTEIN E. R. IMMUNOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:439–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]