Abstract
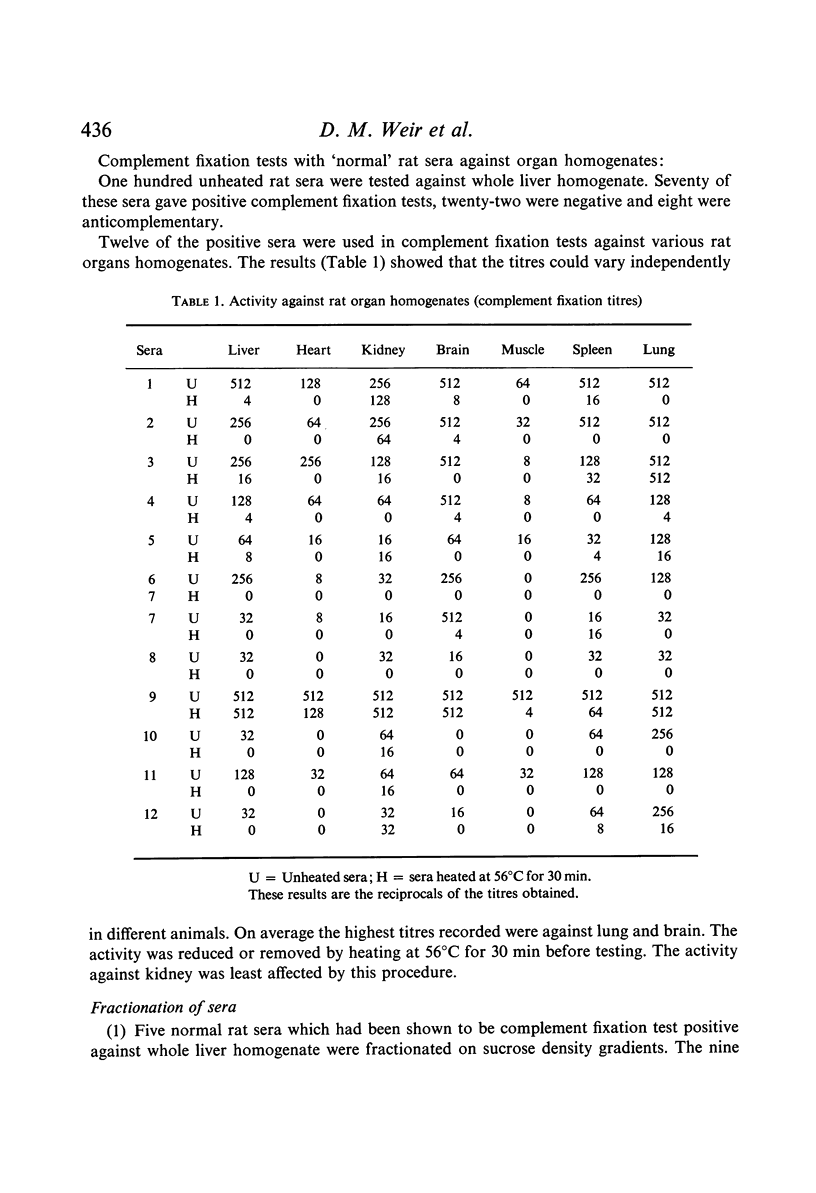
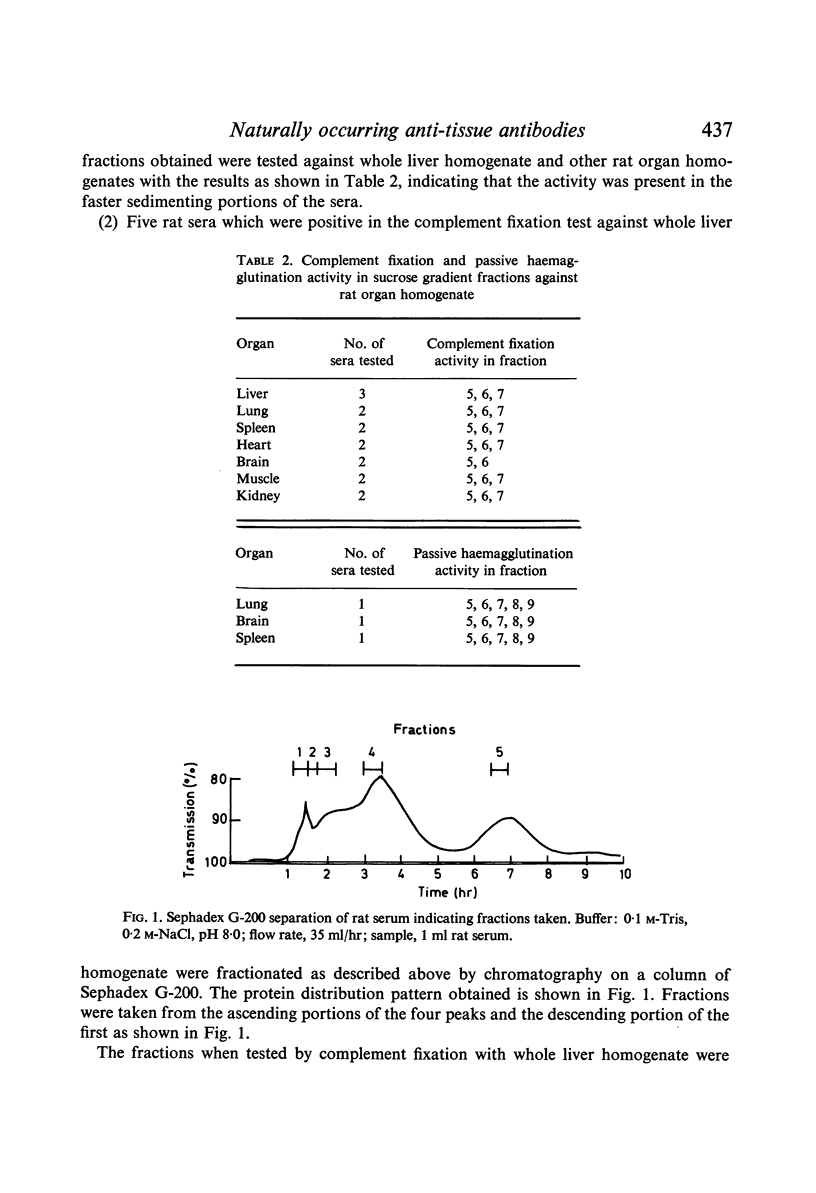
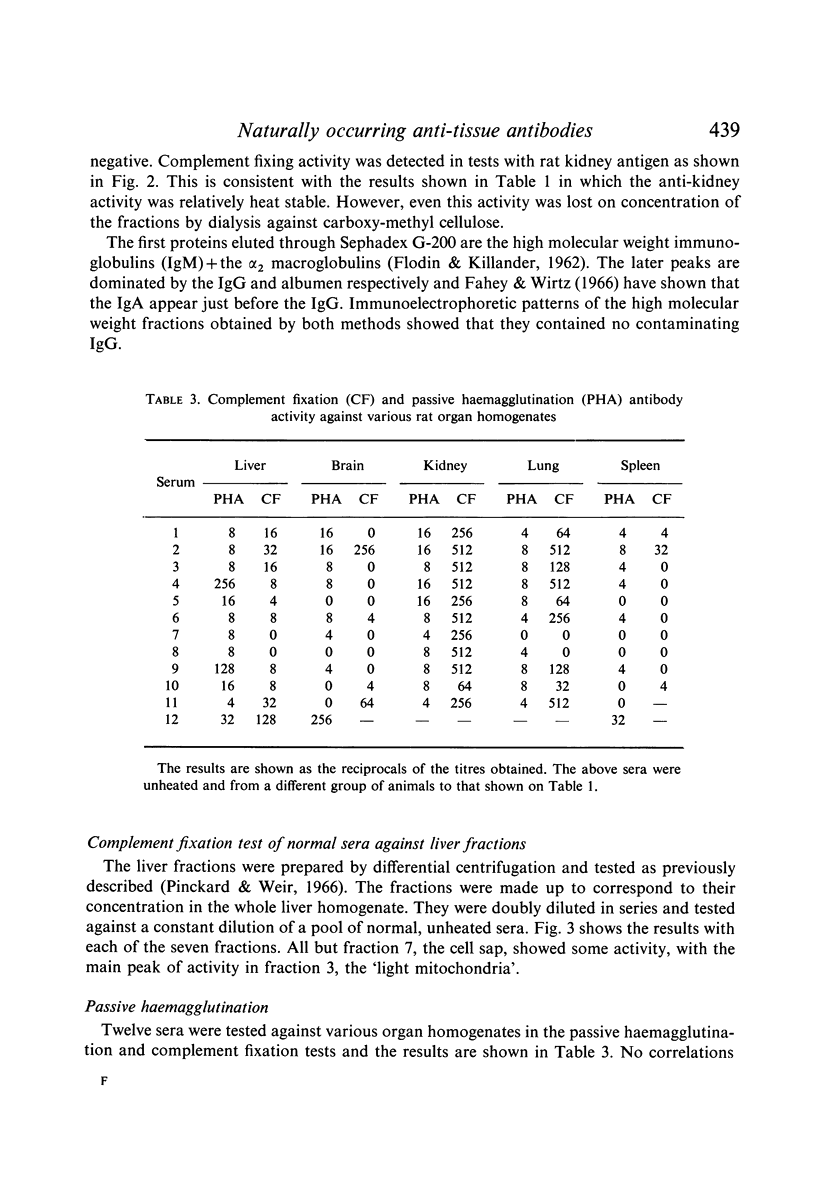
Seventy per cent of normal rat sera have been shown to contain heat labile serum component(s) active against various rat organ homogenates as demonstrated by haemolytic complement fixation and passive haemagglutination tests. The main antigenic activity in rat liver has been found in the mitochondrial fractions.
It was also demonstrated by the indirect fluorescent antibody technique that both guinea-pig complement and high molecular weight rat globulins were fixed to rat organ sections.
Chemotactic activity has also been observed with rat serum and rat liver mitochondria and it is suggested that these naturally occurring antibodies may be implicated in the removal of tissue breakdown products.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNASON B. G., SALOMON J. C., GRABAR P. ANTICORPS ANTIFOIE ET IMMUNOGLOBULINES S'ERIQUES CHEZ LES SOURIS CLASSIQUES ET AX'ENIQUES; 'ETUDE COMPARATIVE APR'ES N'ECROSE H'EPATIQUE AIGUUE PROVOQU'EE PAR LE T'ETRACHLORURE DE CARBONE (CCL4) C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 21;259:4882–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASHERSON G. L., ROSE M. E. Autoantibody production in rabbits. III. The effect of infection with Eimeria stiedae and its relation to natural antibody. Immunology. 1963 May;6:207–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Holborow E. J. Autoantibody production in rabbits. VII. Autoantibodies to gut produced by the injection of bacteria. Immunology. 1966 Feb;10(2):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGBY J. W., LOEWI G. A COMPLEMENT FIXATION REACTION BETWEEN RAT SERA AND RAT KIDNEY. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:372–374. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREESMAN G., LARSON C., PINCKARD R. N., GROYON R. M., BENEDICT A. A. ANTIBODY ACTIVITY IN DIFFERENT CHICKEN GLOBULINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:292–296. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Roitt I. M., Walker J. G., Sherlock S. Tissue antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis, active chronic (lupoid) hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis and other liver diseases and their clinical implications. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):237–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. N., Gery I., Davies A. M. Specific antibodies in heart-disease. Lancet. 1961 May 27;1(7187):1138–1141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAGAJUNIOR C., DE TOLEDO J., TOLEDO J., LIMA A. O. CIRCULATING ANTI-LIVER ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH LIVER DISEASES. Hospital (Rio J) 1964 Apr;65:683–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLEY J. V. Incubation of serum with tissue extracts as a cause of chemotaxis of granulocytes. Nature. 1963 Jun 22;198:1212–1213. doi: 10.1038/1981212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAMER N. C., WATT M. F., HOWE J. H., PAR RISH A. E. Circulating antihuman kidney antibodies in human renal disease. Am J Med. 1961 Jan;30:39–45. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Sorkin E. Studies on chemotaxis. II. The significance of normal sera for chemotaxis induced by various agents. Immunology. 1965 Nov;9(5):441–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY I. R., GAJDUSEK D. C. An autoimmune reaction against human tissue antigens in certain acute and chronic diseases. II. Clinical correlations. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Jan;101(1):30–46. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00260130044004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Weir D. M. Antibodies against the mitochondrial fraction of liver after toxic liver damage in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jan;1(1):33–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STIFFEL C., BIOZZI G., MOUTON D., BOUTHILLIER Y., DECREUSEFOND C. STUDIES ON PHAGOCYTOSIS OF BACTERIA BY THE RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM IN A STRAIN OF MICE LACKING HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:246–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER J. G., DONIACH D., ROITT I. M., SHERLOCK S. SEROLOGICAL TESTS IN DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS. Lancet. 1965 Apr 17;1(7390):827–831. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIR D. M. IMMUNOLOGICAL REACTIONS AFTER TISSUE DAMAGE. Lancet. 1964 Apr 4;1(7336):749–750. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92855-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIR D. M. LIVER AUTOANTIBODIES IN THE RAT. Immunology. 1963 Nov;6:581–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


