Abstract
The effect of prolonged treatment with anti-lymphocytic IgG raised in horses on cell mediated (homograft rejection) and humoral type immune responses has been investigated simultaneously in the same animal. The rejection of skin homografts precedes the development of circulating antibodies against alum precipitated bovine serum albumin but may follow the formation of agglutinating antibodies against sheep erythrocytes. High levels of antibodies against horse IgG are frequently detected prior to graft rejection.
Full text
PDF

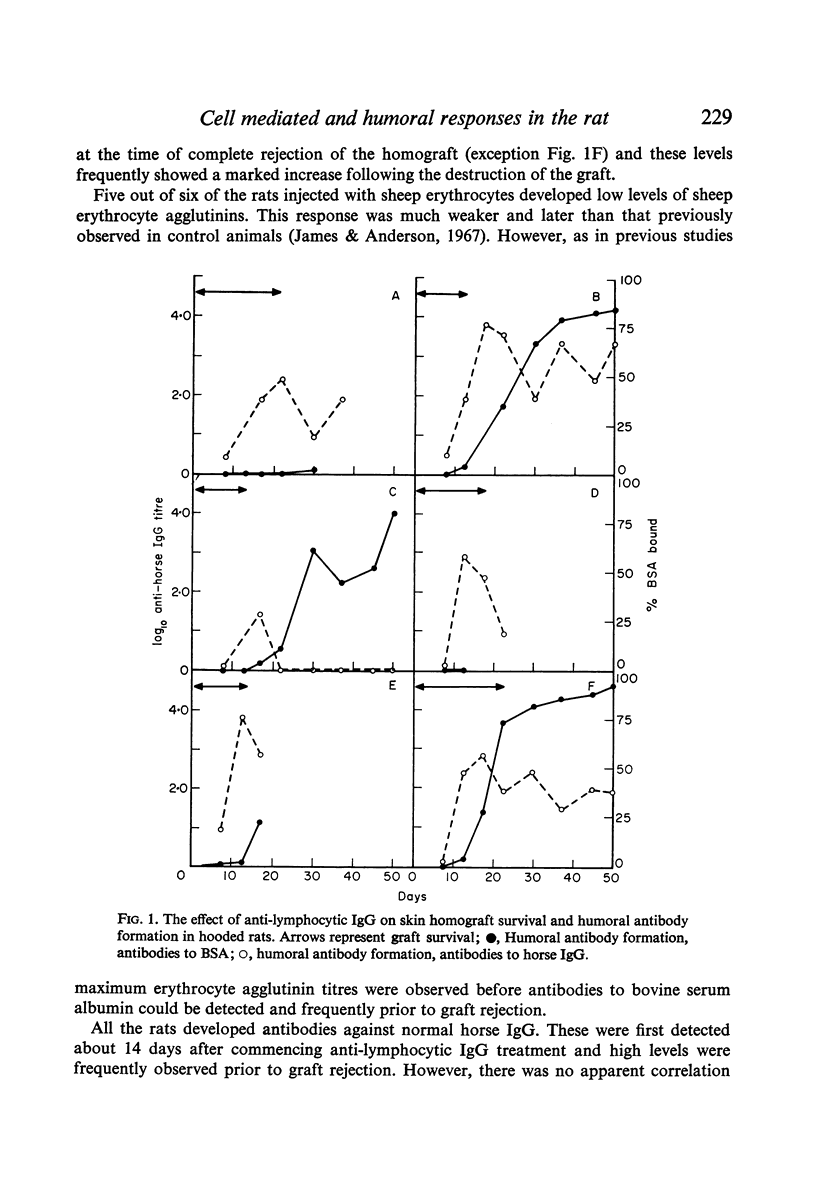
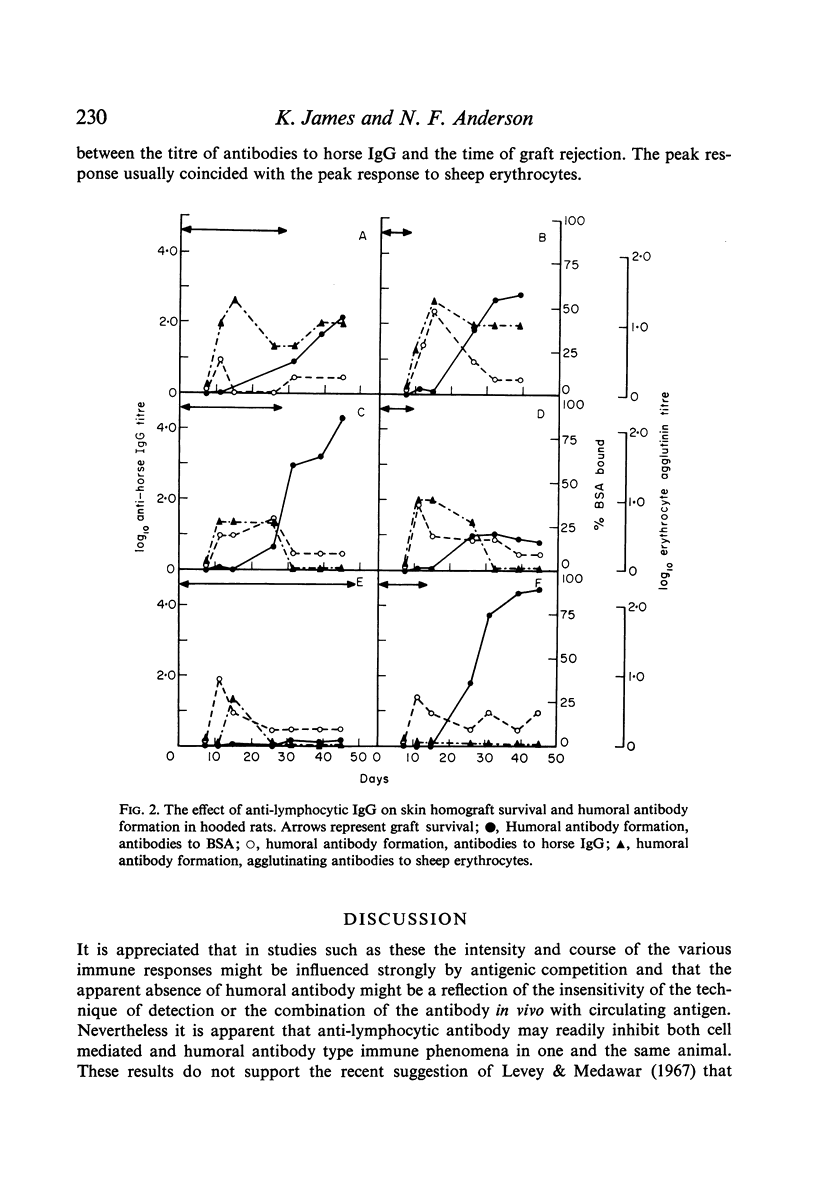


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. F., James K., Woodruff M. F. Effect of antilymphocytic antibody and antibody fragments on skin-homograft survival and the blood-lymphocyte count in rats. Lancet. 1967 May 27;1(7500):1126–1128. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91706-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., James K., Woodruff M. F. Elimination of normal horse IgG labelled with Iodine-131 in rats receiving horse anti-rat lymphocytic IgG. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):869–870. doi: 10.1038/215869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey H. L., Ziff M. Suppression of experimentally induced polyarthritis in the rat by heterologous anti-lymphocyte serum. Lancet. 1966 Oct 22;2(7469):889–891. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91984-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K. Anti-lymphocytic antibody--a review. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Nov;2(6):615–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K., Jubb V. S. Effect of anti-rat lymphocyte antibody on humoral antibody formation. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):367–371. doi: 10.1038/215367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy H. F. Immunological studies on the rat thymectomized in adult life. Immunology. 1965 Nov;9(5):417–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R. The attachment of proteins to aldehyde-tanned cells. Br J Haematol. 1961 Jul;7:299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1961.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H., Medawar P. B. Further experiments on the action of antilymphocytic antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):470–477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Weir D. M., McBride W. H. Factors influencing the immune response. I. Effects of the physical state of the antigen and of lymphoreticular cell proliferation on the response to intravenous injection of bovine serum albumin in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 May;2(3):331–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODRUFF M. F., SIMPSON L. O. Experimental skin grafting in rats; with special reference to split skin grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1955 Jun;15(6):451–458. doi: 10.1097/00006534-195506000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


