Abstract
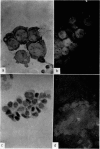
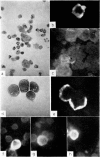
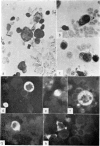
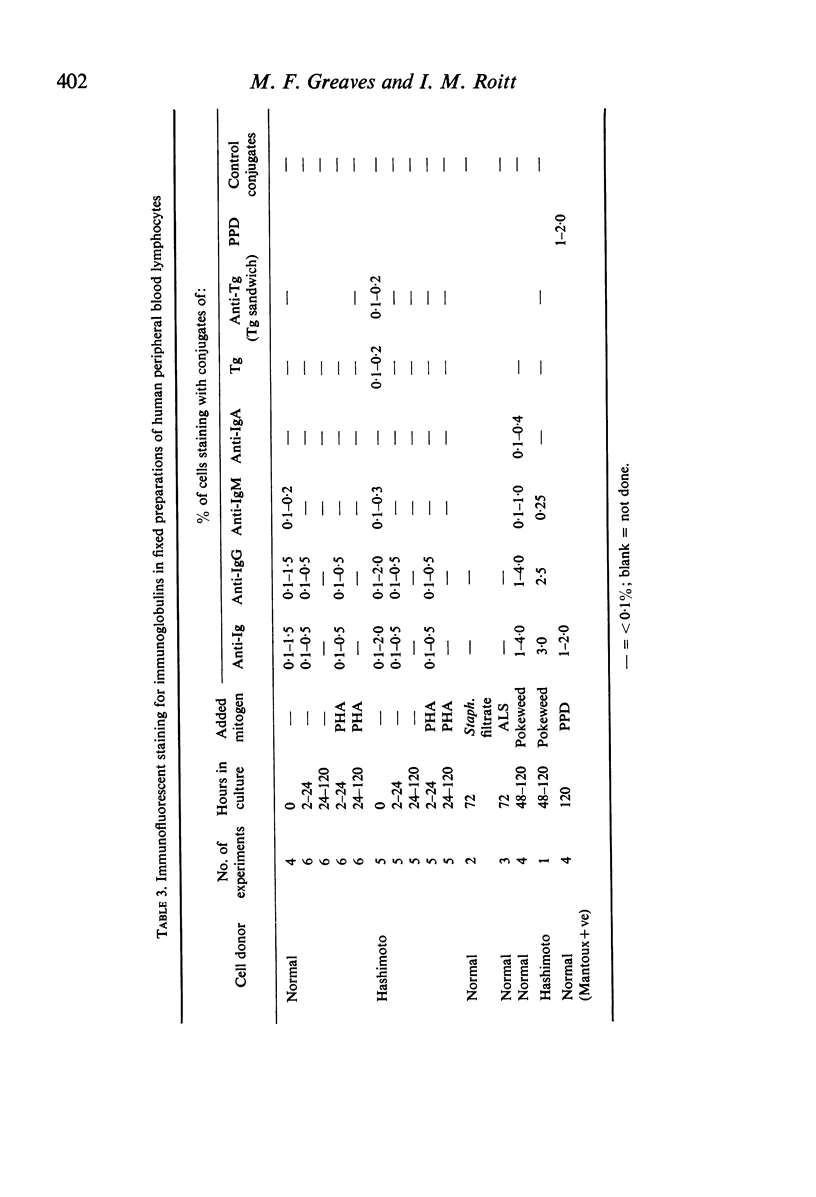
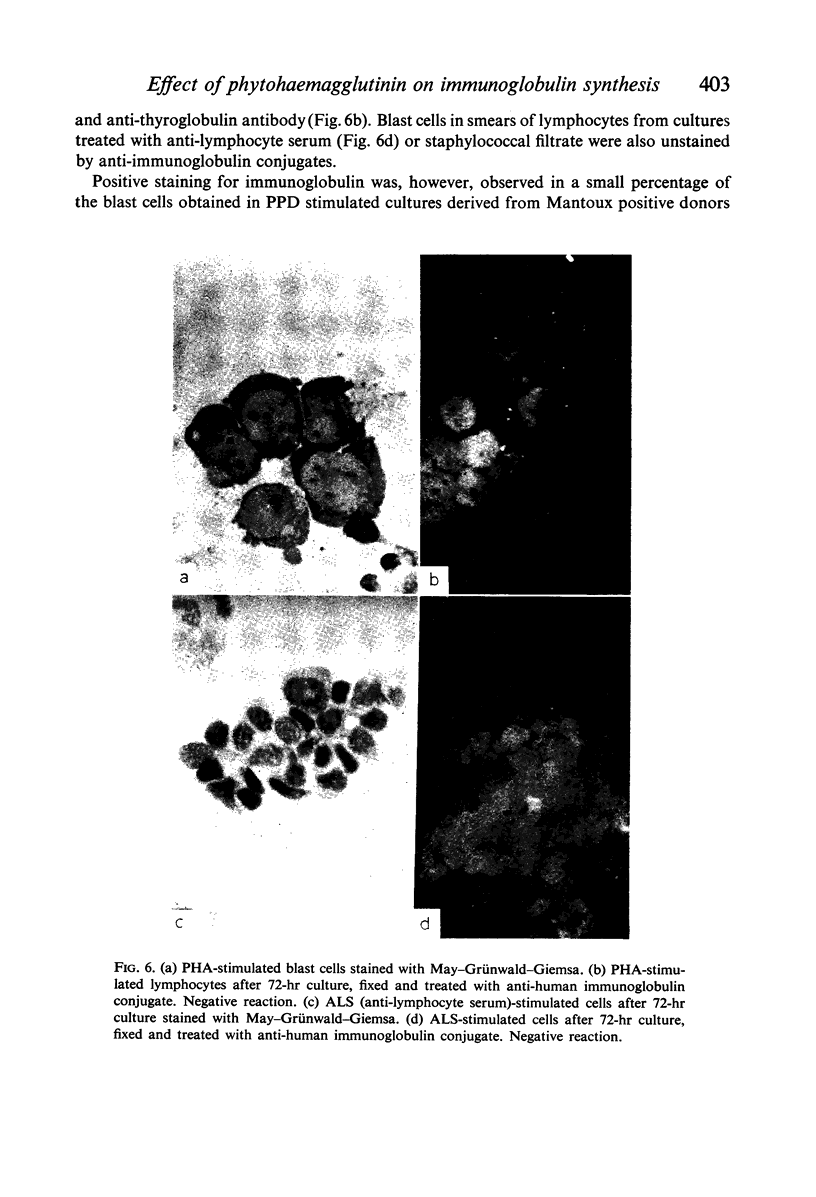
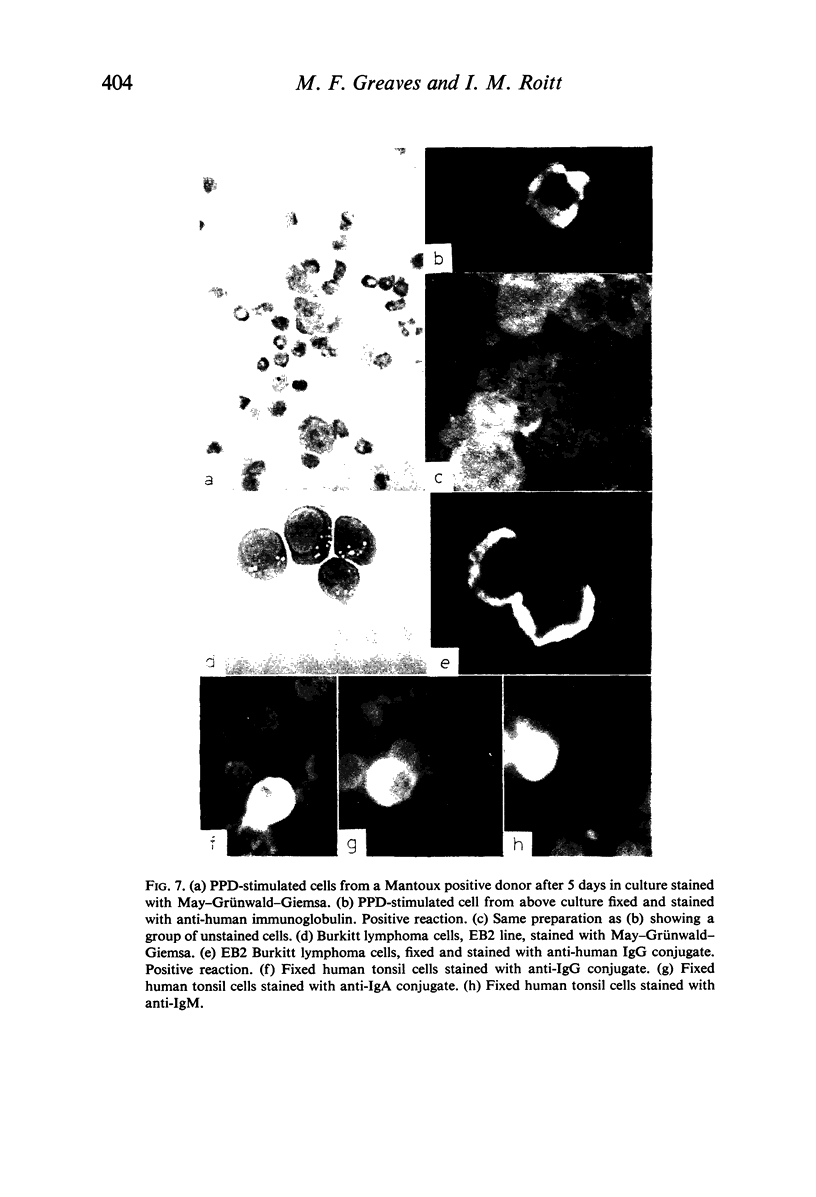
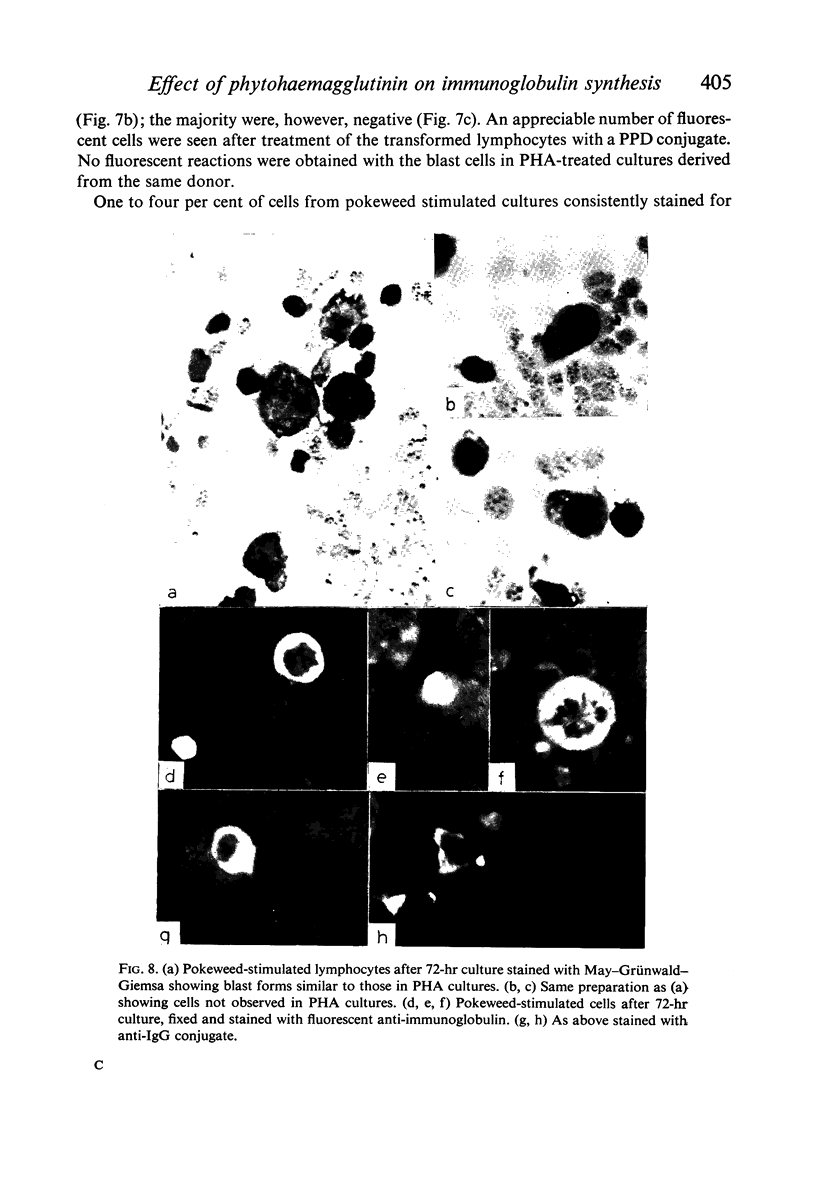
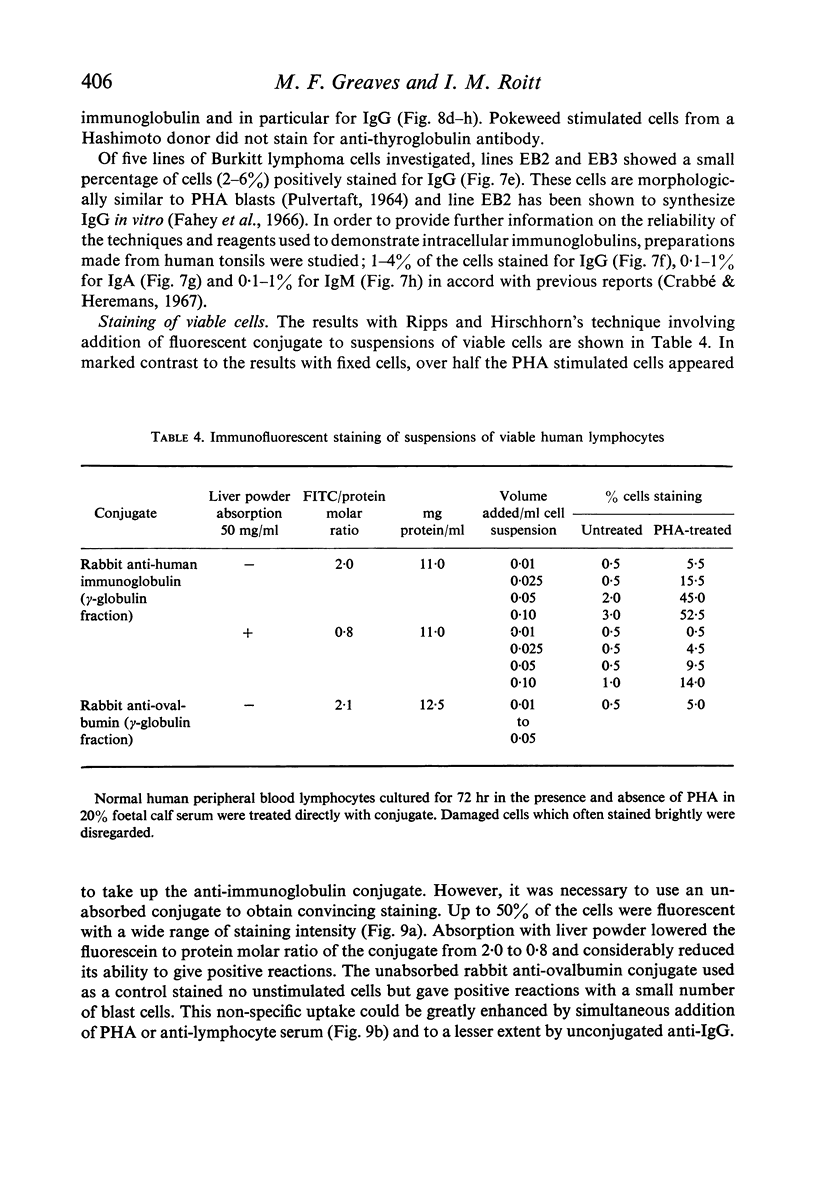
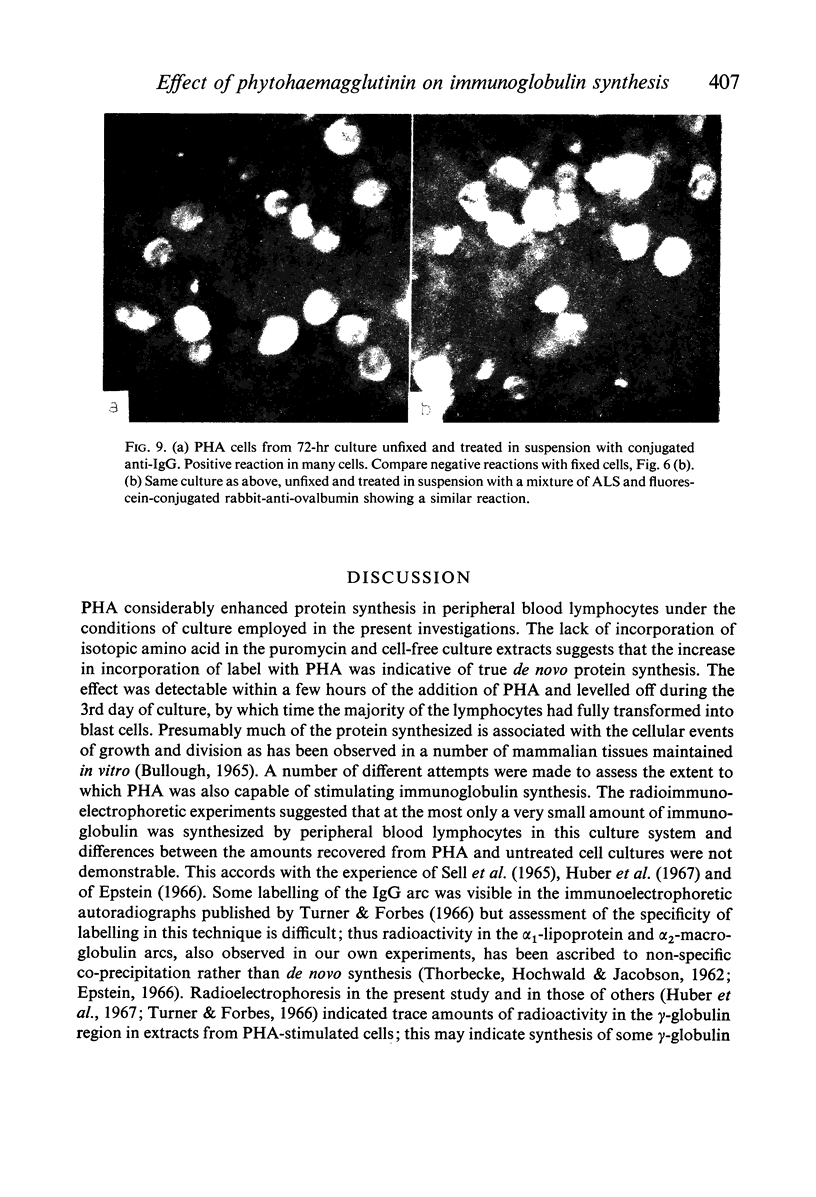
Amino acid incorporation techniques and immunofluorescence have been used to investigate the effect of mitogenic substances on immunoglobulin synthesis by human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Radioelectrophoresis, radioimmunoelectrophoresis and controlled immunological precipitation methods suggest that only a small amount of immunoglobulin is synthesized in the culture system used. Immunofluorescent staining of fixed cell preparations showed that during the first 24 hr in culture only a small percentage of cells reacted positively for immunoglobulin; after 24 hr these cells were no longer demonstrable. This suggests that the small amount of immunoglobulin detected was synthesized during the first few hours in culture by these cells, having the morphological appearance of medium lymphocytes. The slight enhancement of immunoglobulin synthesis obtained in one experiment with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) probably occurred within this same cell type since after 24 hr in vitro no cells in the transformed cultures could be stained by the fluorescent anti-immunoglobulin. Fixed preparations of blast cells obtained by stimulation with anti-lymphocytic serum and staphylococcal filtrate also gave negative reactions. However, using a staining technique with suspensions of viable cells, it was possible to demonstrate positive staining for immunoglobulins with PHA stimulated cells as previously described by Ripps & Hirschhorn (1967). A number of controls suggest that this reaction depends upon the presence of exposed immunoglobulin groups or markers on the cell surface and that intracytoplasmic staining is the result of endocytosis of conjugate.
In contrast with the negative results obtained with PHA-transformed blasts, a small percentage of lymphocytes from cultures stimulated by pokeweed or tuberculin reacted positively when fixed preparations were stained with conjugated anti-immunoglobulin.
Full text
PDF



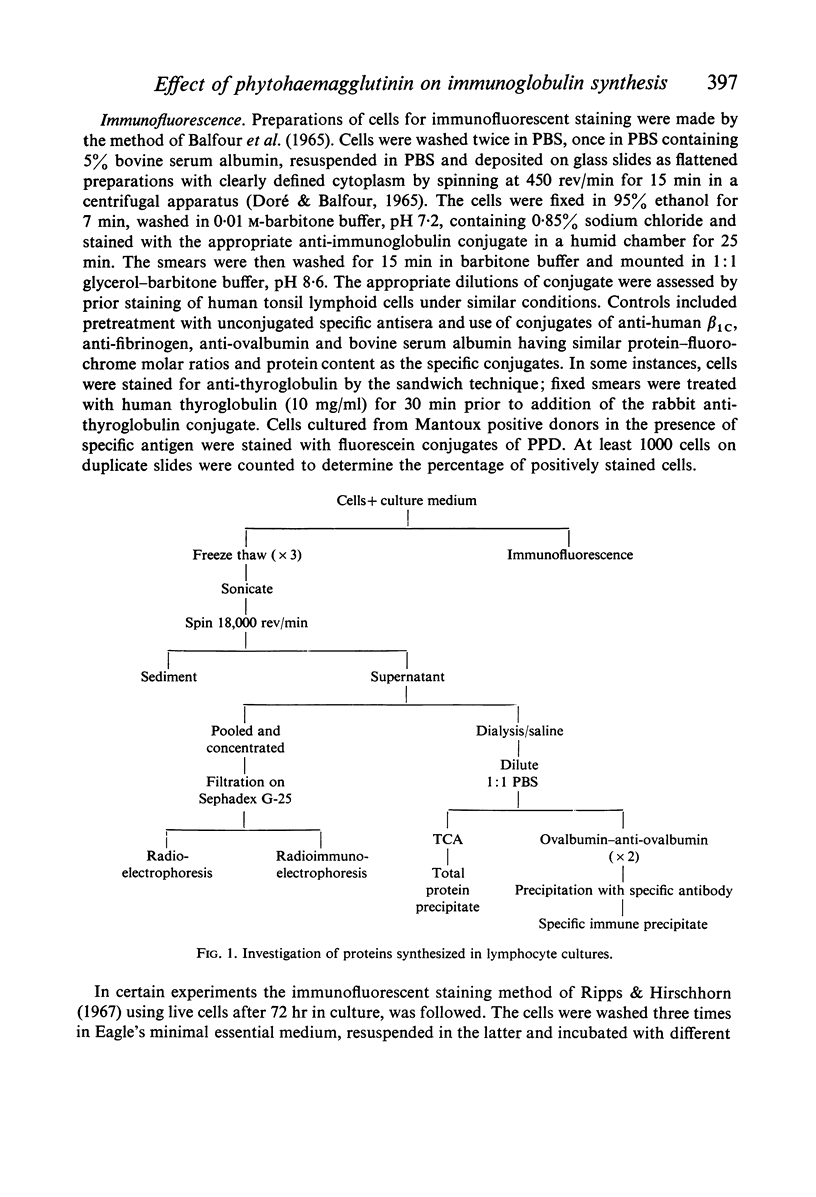

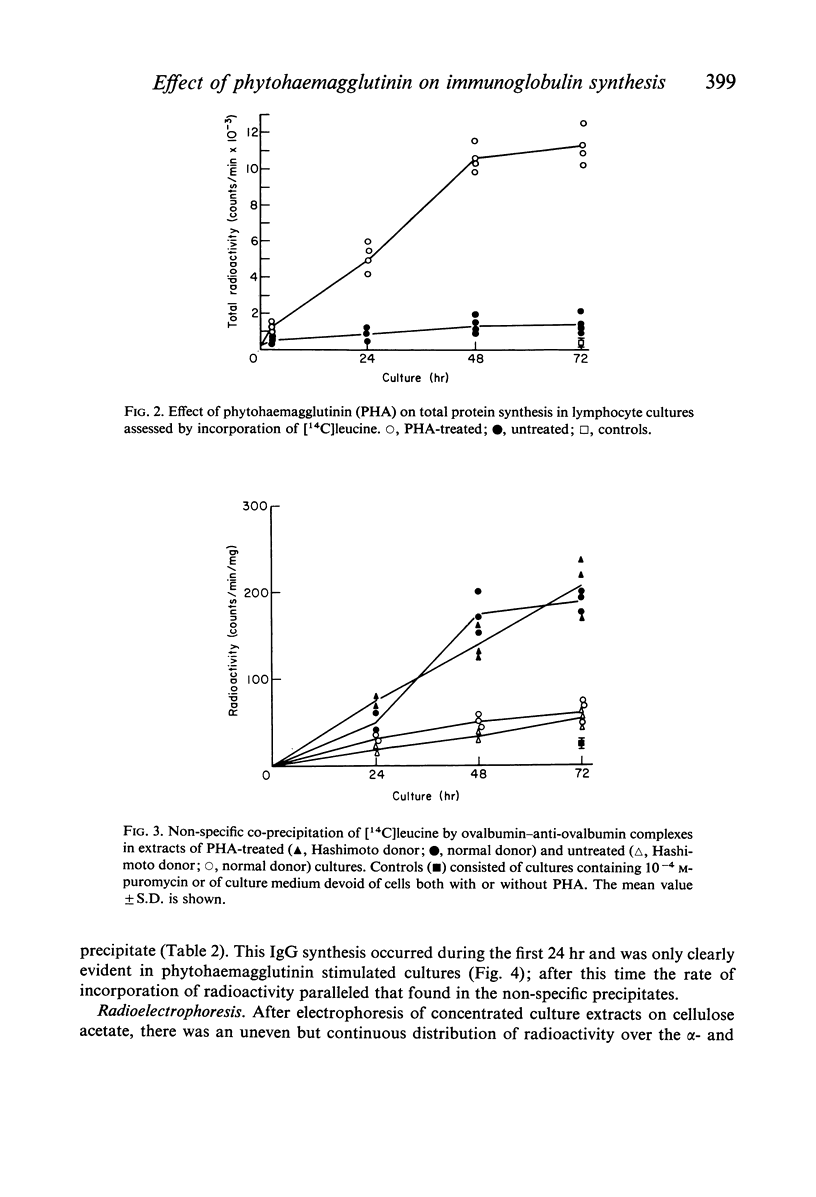
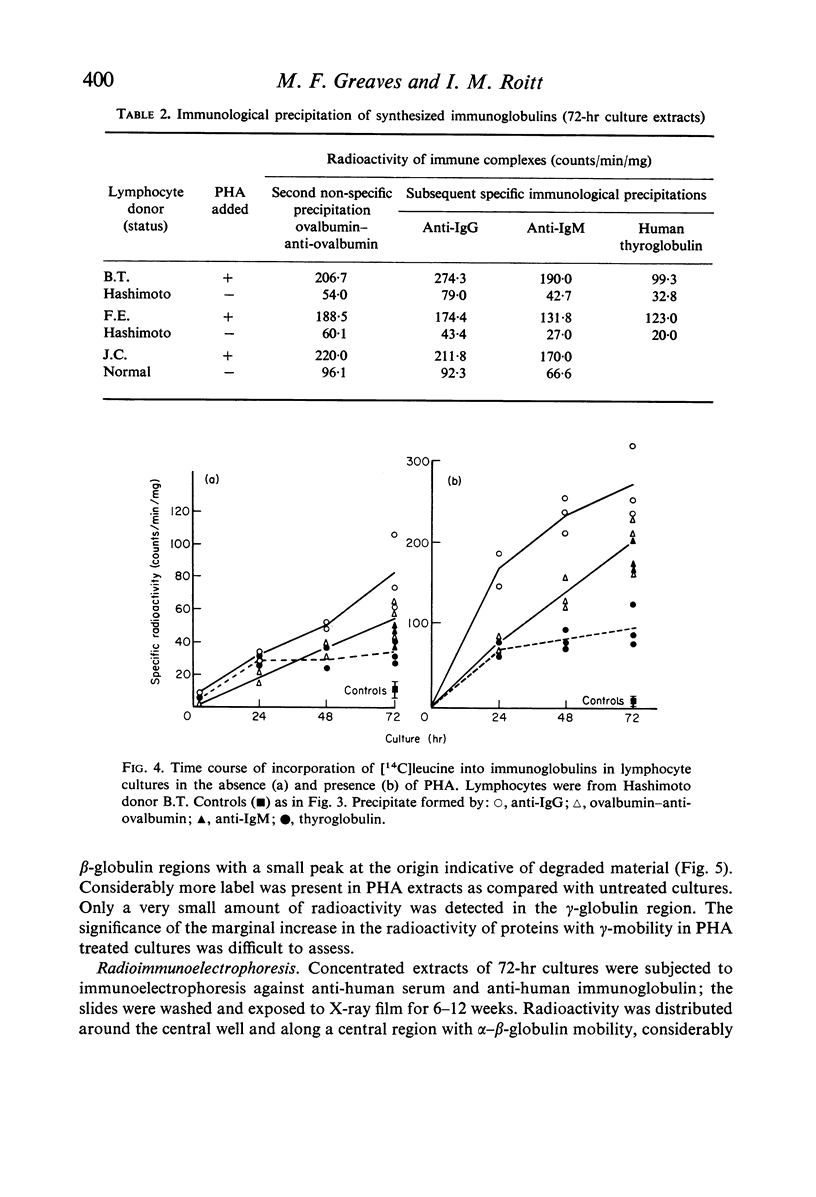
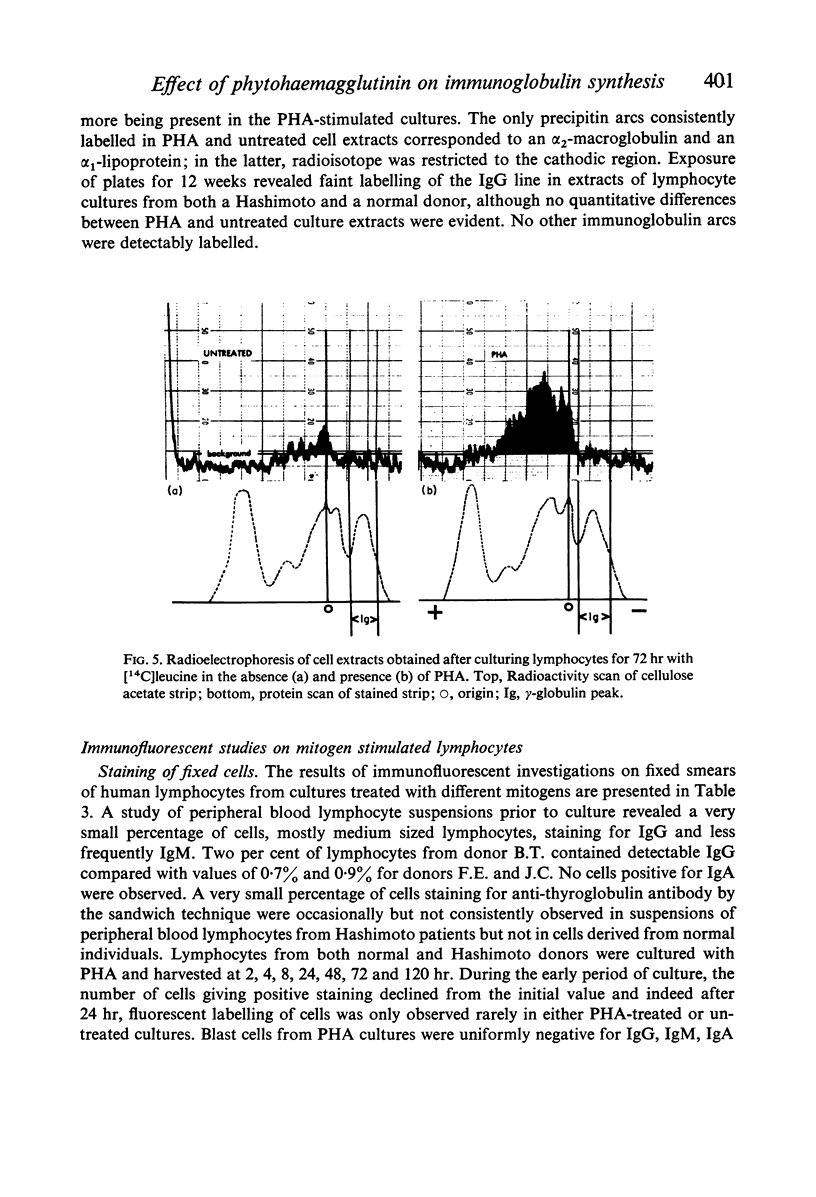





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALFOUR B. M., COOPER E. H., ALPEN E. L. MORPHOLOGICAL AND KINETIC STUDIES ON ANTIBODY-PRODUCING CELLS IN RAT LYMPH NODES. Immunology. 1965 Mar;8:230–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUDZYNSKI A. Z., BRODA E., KELLNER G., FRIMMEL J. S. An examination of HeLa cancer cells for production of gamma-globulin. Nature. 1962 Dec 1;196:892–893. doi: 10.1038/196892a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough W. S. Mitotic and functional homeostasis: a speculative review. Cancer Res. 1965 Nov;25(10):1683–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Börjeson J., Reisfeld R., Chessin L. N., Welsh P. D., Douglas S. D. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. I. Biological and physicochemical properties of the pokeweed mitogen. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):859–872. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N. The biosynthesis of proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:1–38. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Localization of mouse isoantigens on the cell surface as revealed by immunofluorescence. Immunology. 1967 Oct;13(4):395–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Parks E. The regulation of pinocytosis in mouse macrophages. IV. The immunological induction of pinocytic vesicles, secondary lysosomes, and hydrolytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Heremans J. F. Distribution in human nasopharyngeal tonsils of plasma cells containing different types of immunoglobulin polypeptide chains. Lab Invest. 1967 Jan;16(1):112–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doré C. F., Balfour B. M. A device for preparing cell spreads. Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):403–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Borjeson J., Chessin L. N. Studies on human lymphocytes in vitro. IV. Comparative fine structural features of the established Burkitt lymphoma cell lines AL-1, EB-2 and phytomitogen-transformed lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):340–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Hoffman P. F., Borjeson J., Chessin L. N. Studies on human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. 3. Fine structural features of lymphocyte transformation by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EASTON J. M., GOLDBERG B., GREEN H. Demonstration of surface antigens and pinocytosis in mammalian cells with ferritin-antibody conjugates. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:437–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES I. J. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF ANTIBODY SYNTHESIS BY HUMAN LEUCOCYTES IN VITRO. Lancet. 1965 Jan 23;1(7378):198–199. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90979-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Finegold I., Rabson A. S., Manaker R. A. Immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro by established human cell lines. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1259–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Roitt I. M., Zamir R., Carnaghan R. B. Effect of anti-lymphocyte serum on responses of human peripheral-blood lymphocytes to specific and non-specific stimulants in vitro. Lancet. 1967 Dec 23;2(7530):1317–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90909-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRAMOTO R., GOLDSTEIN M. N., PRESSMAN D. Limited fixation of antibody by viable cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Feb;24:255–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., BACH F., KOLODNY R. L., FIRSCHEIN I. L., HASHEM N. IMMUNE RESPONSE AND MITOSIS OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIGER L., SORKIN E. Synthesis of antibodies by blood leucocytes of the rabbit. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:299–299. doi: 10.1038/198299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G., Littleton R. J. The effects of antigens and of phytohemagglutinin on rabbit spleen cell suspensions. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):621–634. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. N., Hummeler K., Harris S. Electron microscopic observations on antibody-producing lymph node cells. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):161–172. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt L. J., Ling N. R., Stanworth D. R. The effect of heterologous antisera and rheumatoid factor on the synthesis of DNA and protein by human peripheral lymphocytes. Immunochemistry. 1966 Sep;3(5):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Winkler H., Reiser G., Huber C., Gabl F., Braunsteiner H. Eigenschaften und subcelluläre Lokalisation neugebildeter Proteine menschlicher Lymphocyten in vitro mit und ohne Phytohämagglutininzusatz. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Feb 15;45(4):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01716909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., SPICER E., JAMES K., WILLIAMSON N. THE ACTIVATION OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES BY PRODUCTS OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy M., Sanderson R. P., Jackson A. L. Humoral and cellular aspects of the immune response to the somatic antigen of Salmonella enteritidis. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):483–504. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A. The immunologic significance of antigen induced lymphocyte transformation in vitro. J Immunol. 1966 Aug;97(2):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C. Phytohemagglutinin: an initiator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1960 May;20:462–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ IN RELATION TO BURKITT'S TUMOUR. (AFRICAN LYMPHOMA). Lancet. 1964 Sep 12;2(7359):552–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90618-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti F., Franceschini P., Forti G., Cepellini R. The effect of phytohaemagglutinin on the metabolism and gamma-globulin synthesis of human lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF THE HUMAN LYMPHOCYTE. Science. 1964 Dec 25;146(3652):1648–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3652.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripps C. S., Hirschhorn K. The production of immunoglobulins by human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):377–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S., GELL P. G. STUDIES ON RABBIT LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. I. STIMULATION OF BLAST TRANSFORMATION WITH AN ANTIALLOTYPE SERUM. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:423–440. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. In vitro production of diphtheria antitoxin by tissues of immunized animals. III. Incorporation of amino acids into antibody; relationship to antibody synthesis and sensitivity relative to other methods. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Dec;39(6):661–673. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Rowe D. S., Gell P. G. Studies on rabbit lymphocytes in vitro. 3. Proteins, RNA, and DNA synthesis by lymphocyte cultures after stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin, with staphylococcal filtrate, with antiallotype serum, and with heterologous antiserum to rabbit whole serum. J Exp Med. 1965 Oct 1;122(4):823–839. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Studies on rabbit lymphocytes in vitro. V. The induction of blast transformation with sheep antisera to rabbit IgG subunits. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):289–301. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner K. J., Forbes I. J. Synthesis of proteins by human leukocytes in vitro. II. Chemical characterization. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):926–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit R. E., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. I. The methods and their specificity. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]