Abstract
The stimulatory effect of antigen–antibody–complement complexes on cultured normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes was studied. The donors of the cells had not been sensitized to the antigens used. Two antigens were used: flagellar antigen of Salmonella paratyphi B (SPB) and bovine serum albumin (BSA), with their respective antibodies prepared in rabbits. The addition of such antigen–antibody aggregates to the cultures stimulated the lymphocytes as determined by morphological changes and increased uptake of [14C]thymidine into DNA. Peak of stimulation was observed after 5–6 days of culture incubation. The stimulation appeared to be complement dependent. The lymphocytes showed no response either to the antigen alone or to anti-SPB. When BSA–anti-BSA was centrifuged, most of the stimulatory activity was found in the supernate. The most likely explanation of this stimulation is injury to lymphocyte membranes, possibly from a non-specific attachment of immune complexes to them. A similar mechanism of membrane injury may underlie reactions to all non-specific stimulants, and possibly also to specific antigens to which the cell donor is sensitized.
Full text
PDF


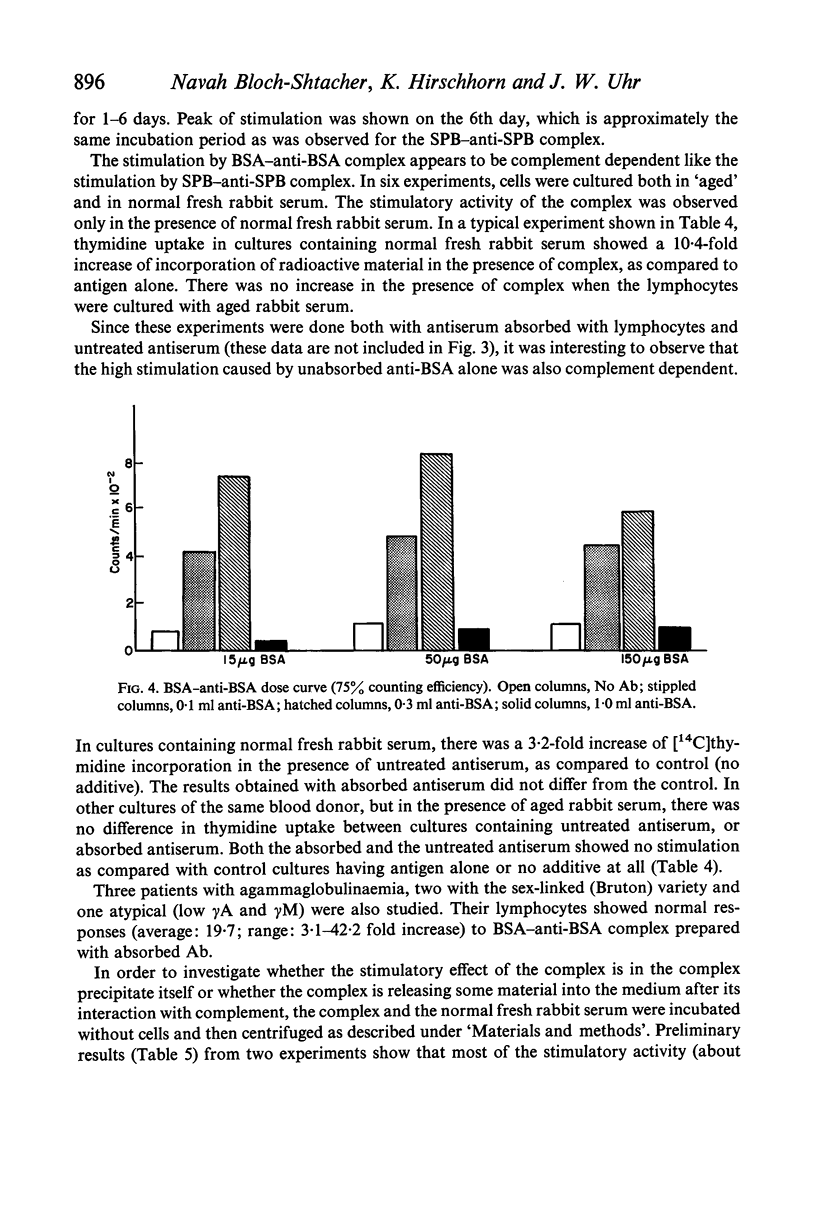
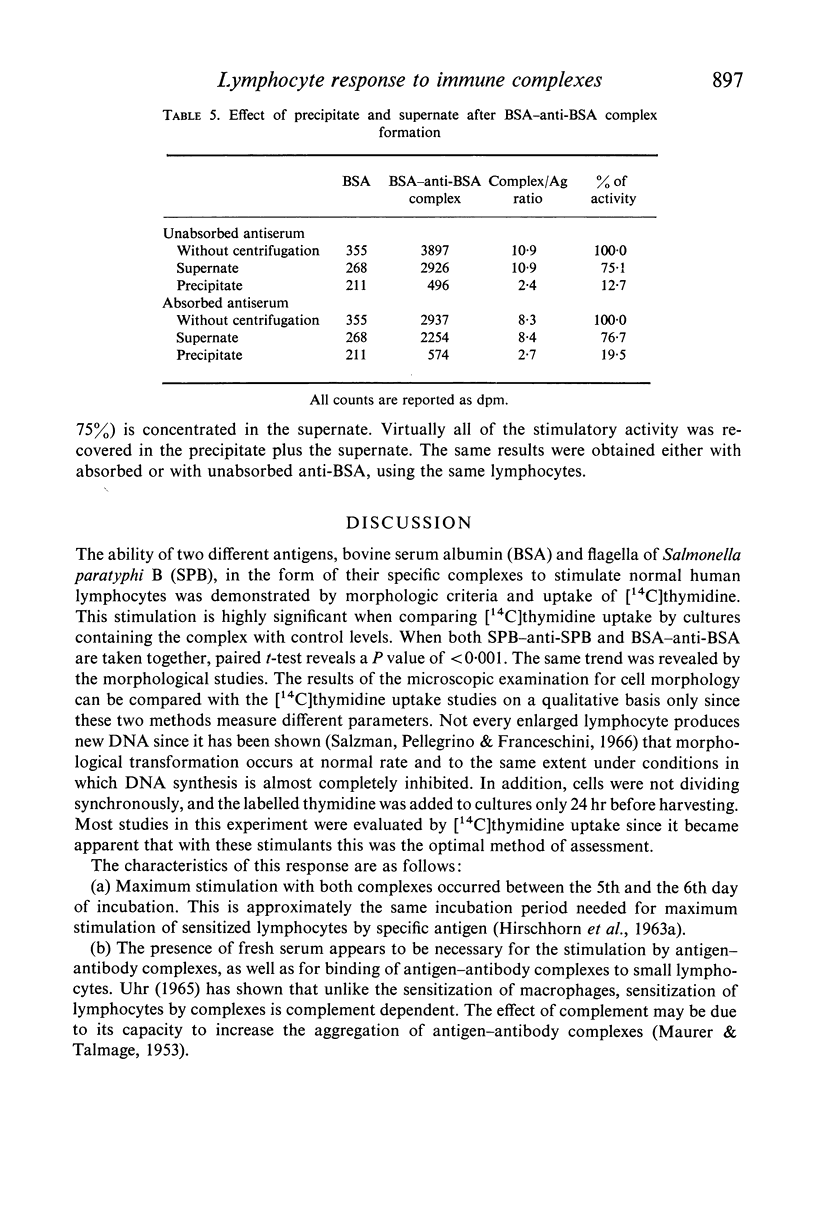


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOPER H. L., RUBIN A. D. RNA METABOLISM IN LYMPHOCYTES STIMULATED BY PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ: INITIAL RESPONSES TO PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:1014–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias Da Silva W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. II. Biological properties of anaphylatoxin prepared with purified components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 May 1;125(5):921–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H., HIRSCHHORN K. AGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA: THE FUNDAMENTAL DEFECT. Science. 1964 Aug 7;145(3632):611–612. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3632.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., BACH F., KOLODNY R. L., FIRSCHEIN I. L., HASHEM N. IMMUNE RESPONSE AND MITOSIS OF HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., KOLODNY R. L., HASHEM N., BACH F. Mitogenic action of phytohaemagglutinin. Lancet. 1963 Aug 10;2(7302):305–306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., SCHREIBMAN R. R., VERBO S., GRUSKIN R. H. THE ACTION OF STREPTOLYSIN S ON PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES OF NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1151–1157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Hirschhorn K., Weissmann G. Appearance of hydrolase rich granules in human lymphocytes induced by phytohemagglutinin and antigens. Blood. 1967 Jul;30(1):84–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., HUSBAND E. M. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Feb 15;1(7329):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURER P. H., TALMAGE D. W. The effect of the presence of complement in rabbit serum on the quantitative precipitin reaction. II. Effect on antigen and antibody precipitation. J Immunol. 1953 May;70(5):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead J. F., McFarland W. Efficiency of scintillation counting of tritium labelled DNA-protein in the mixed leucocyte reaction in vitro. Nature. 1966 Sep 10;211(5054):1157–1159. doi: 10.1038/2111157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C. Phytohemagglutinin: an initiator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1960 May;20:462–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripps C. S., Hirschhorn K. The production of immunoglobulins by human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):377–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman N. P., Pellegrino M., Franceschini P. Biochemical changes in phytohemagglutinin stimulated human lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Oct;44(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Passive sensitization of lymphocytes and macrophages by antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1599–1606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva W. D., Eisele J. W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. 3. Purification of the activity with anaphylatoxin properties generated by interaction of the first four components of complement and its identification as a cleavage product of C'3. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1027–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


