Abstract
The immunocytoadherence (rosette) technique has been adapted to study the immune response to varying doses of type III pneumococcal polysaccharide (SIII). Syngeneic erythrocytes coated with SIII were incubated with washed spleen cell suspensions isolated 0·5–39 days after i.v. injection into CBA strain mice of immunogenic (0·5 or 5·0 μg) or paralysing (500 μg) doses of SIII; the immunizing or paralysing effect of these doses of SIII was confirmed by a passive haemagglutination technique. The number of rosette-forming cells per spleen was significantly increased above the background range in twenty-seven out of forty-two, twenty-four out of thirty-seven and forty-one out of forty-six animals injected with 0·5, 5·0 and 500 μg SIII, respectively. Not only was there a greater incidence of `positive' values in the paralysed group, but the response was better maintained than in the immunized groups.
In view of the apparent lack of central inhibition in these experiments, paralysis with SIII was considered to be attributable to the antibody-neutralizing effect of persisting undegraded antigen. It is suggested that the phenomenon of polysaccharide paralysis may be the expression of more than one mechanism.
Full text
PDF



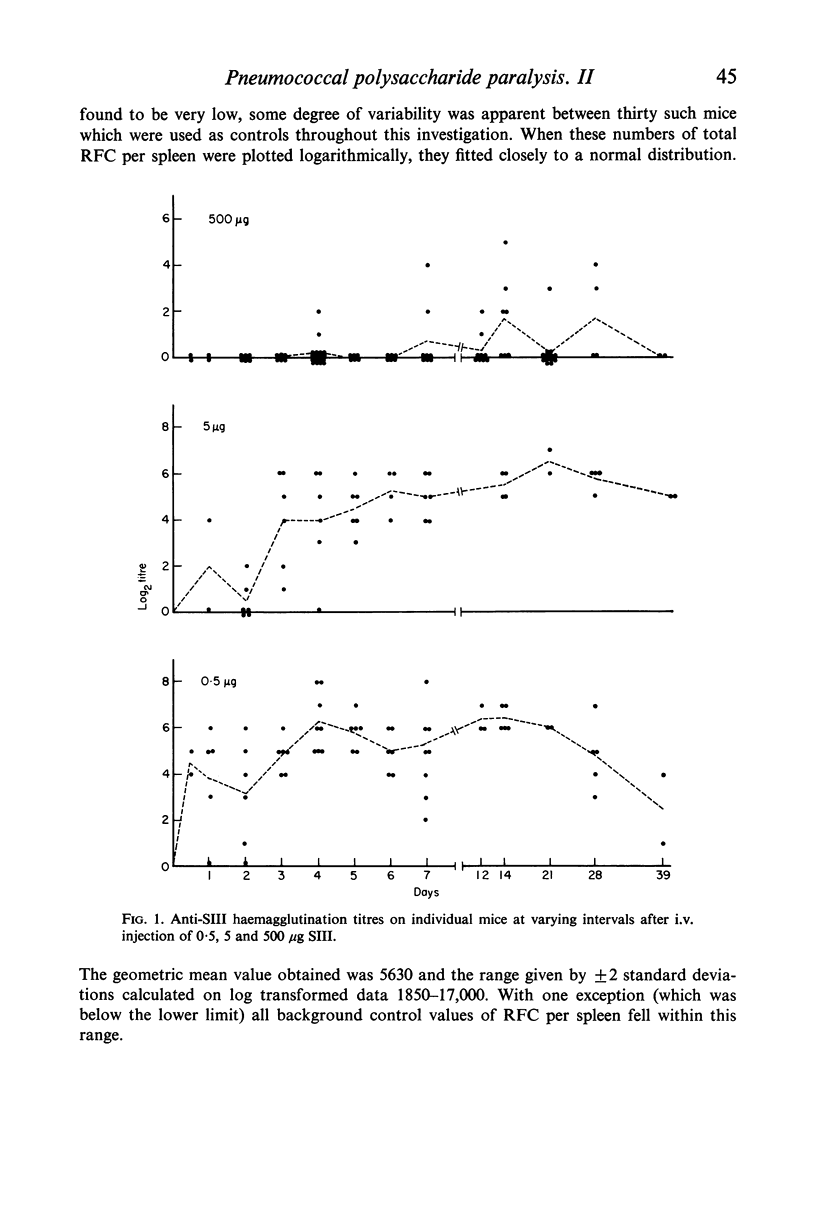
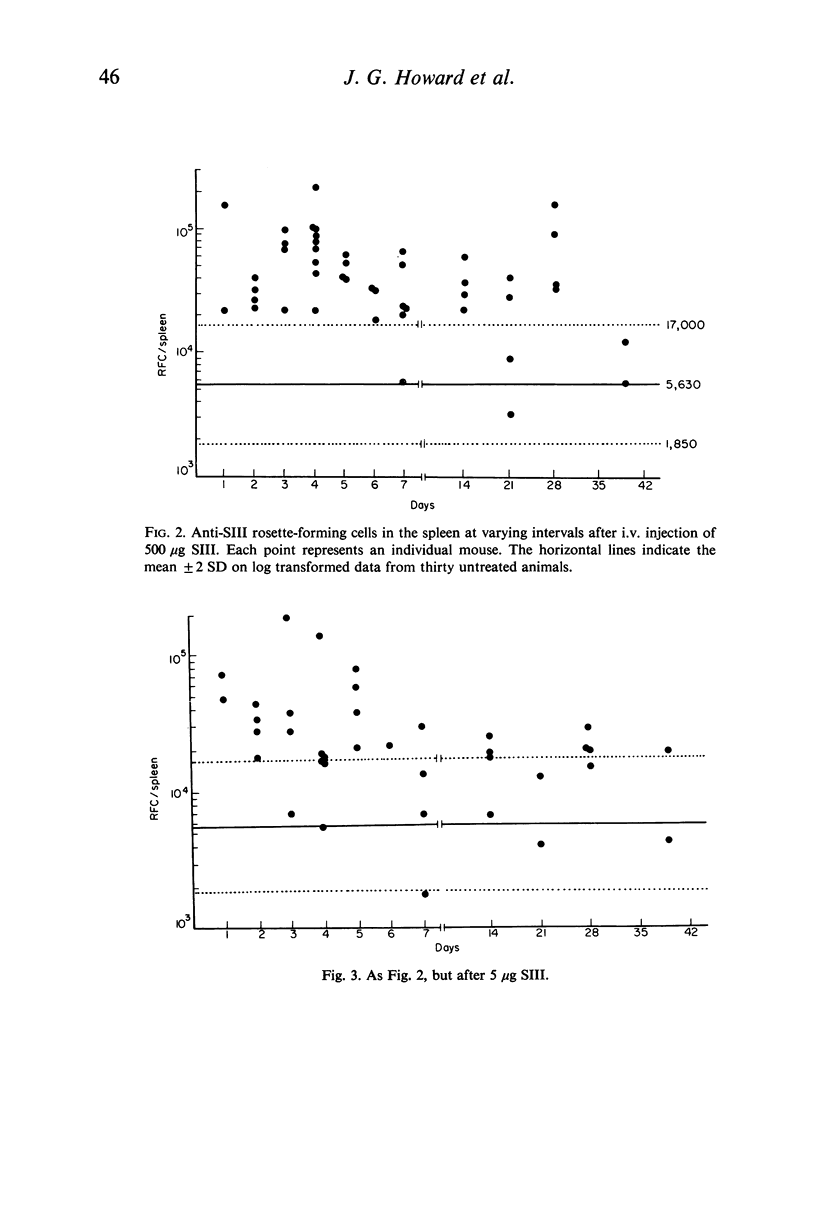
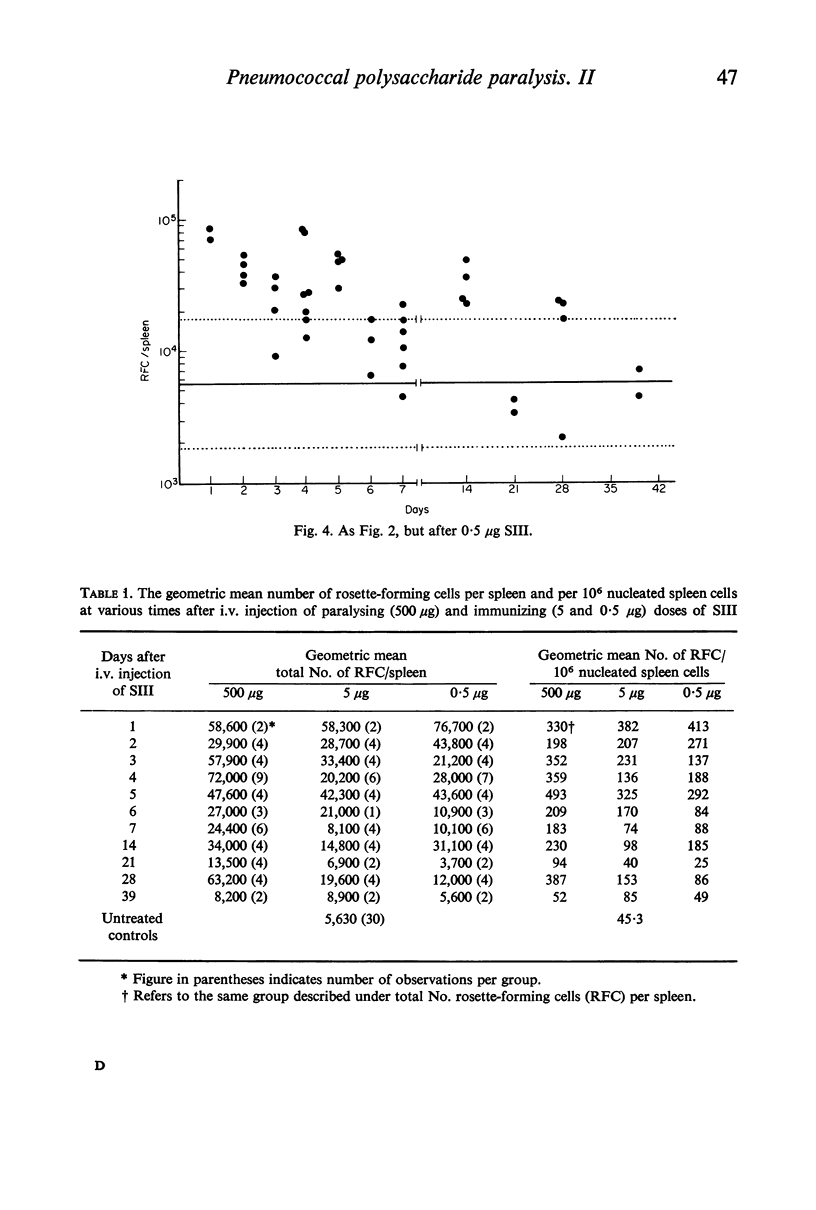






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A., FARTHING C. P., HUMPHREY J. H. The significance of multiple antibody components in serum of immunized rabbits. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:336–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATSHON B. A., BAER H., SHAFFER M. F. Immunologic paralysis produced in mice by Klebsiella pneumoniae type 2 polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1963 Jan;90:121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Bernstein M., Pasanen V., Landy M. Detection and enumeration of antibody-producing cells by specific adherence of antigen-coated bentonite particles. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):767–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Landy M. Brevity of the inductive phase in the immune response of mice to capsular polysaccharide antigens. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):687–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biozzi G., Stiffel C., Mouton D., Liacopoulosbriot M., Decreusefond C., Bouthillier Y. Etude du phénomène de l'immuno-cyto-adhérence au cours de l'immunisation. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3 Suppl):7–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. S. A hemagglutination test and a specific depolymerase for studying immunologic paralysis in mice. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):358–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. S. Studies on the induction, specificity, prevention and breaking of immunologic paralysis and immunity to pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., MAURER P. H., WEIGLE W. O. Immunologic activity of pneumococcal polysaccharide fixed in the tissues of the mouse. J Immunol. 1955 Mar;74(3):188–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELTON L. D., KAUFFMANN G., PRESCOTT B., OTTINGER B. Studies on the mechanism of the immunological paralysis induced in mice by pneumococcal polysaccharides. J Immunol. 1955 Jan;74(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S., Weigle W. O. Studies on the induction of immunologic unresponsiveness. II. Kinetics. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):624–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Siskind G. W. Studies on immunological paralysis. I. A consideration of macrophage involvement in the induction of paralysis and immunity by type II pneumococcal polysaccharide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):29–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. Immunological paralysis induced by brief exposure of cells to protein antigens. Immunology. 1968 Oct;15(4):531–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEPER C. A. MECHANISMS OF IMMUNOLOGIC PARALYSIS BY PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE. 3. IMMUNOLOGIC PARALYSIS IN RELATION TO MATURATION OF THE IMMUNOLOGIC RESPONSE OF MICE. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEPER C. A., SEASTONE C. V. MECHANISMS OF IMMUNOLOGIC PARALYSIS BY PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE. I. STUDIES OF ADOPTIVELY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY TO PNEUMOCOCCAL INFECTION IN IMMUNOLOGICALLY PARALYZED AND NORMAL MICE. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:374–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOTA N. R., LIACOPOULOS-BRIOT M., STIFFEL C., BIOZZI G. L'IMMUNO-CYTO-ADH'ERENCE: UNE M'ETHODE SIMPLE ET QUANTITATIVE POUR L'ETUDE IN VITRO DES CELLULES PRODUCTRICES D'ANTICORPS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 3;259:1277–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B., Ovary Z. Secondary antibody responses in haptenic systems: cell population selection by antigen. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERCARZ E., COONS A. H. Specific inhibition of antibody formation during immunological paralysis and unresponsiveness. Nature. 1959 Oct 3;184(Suppl 14):1080–1082. doi: 10.1038/1841080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISKIND G. W., PATERSON P. Y. A BIOASSAY FOR ESTIMATION OF PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE IN UNRESPONSIVE (PARALYZED) MICE. J Immunol. 1964 Sep;93:489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISKIND G. W., PATERSON P. Y., THOMAS L. INDUCTION OF UNRESPONSIVENESS AND IMMUNITY IN NEWBORN AND ADULT MICE WITH PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE. J Immunol. 1963 Jun;90:929–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARK O. K. Studies on pneumococcal polysaccharide. II. Mechanism involved in production of immunological paralysis by type I pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1955 Feb;74(2):130–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Howard J. G. Studies on the induction of immunological unresponsiveness to pneumococcal polysaccharide in mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):417–429. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. G., Trice K. L. Influence of cellular factors on immune unresponsiveness induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae capsular antigen. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):896–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.896-901.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAALBERG O. B. A SIMPLE METHOD FOR DETECTING SINGLE ANTIBODY-FORMING CELLS. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1231–1231. doi: 10.1038/2021231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


