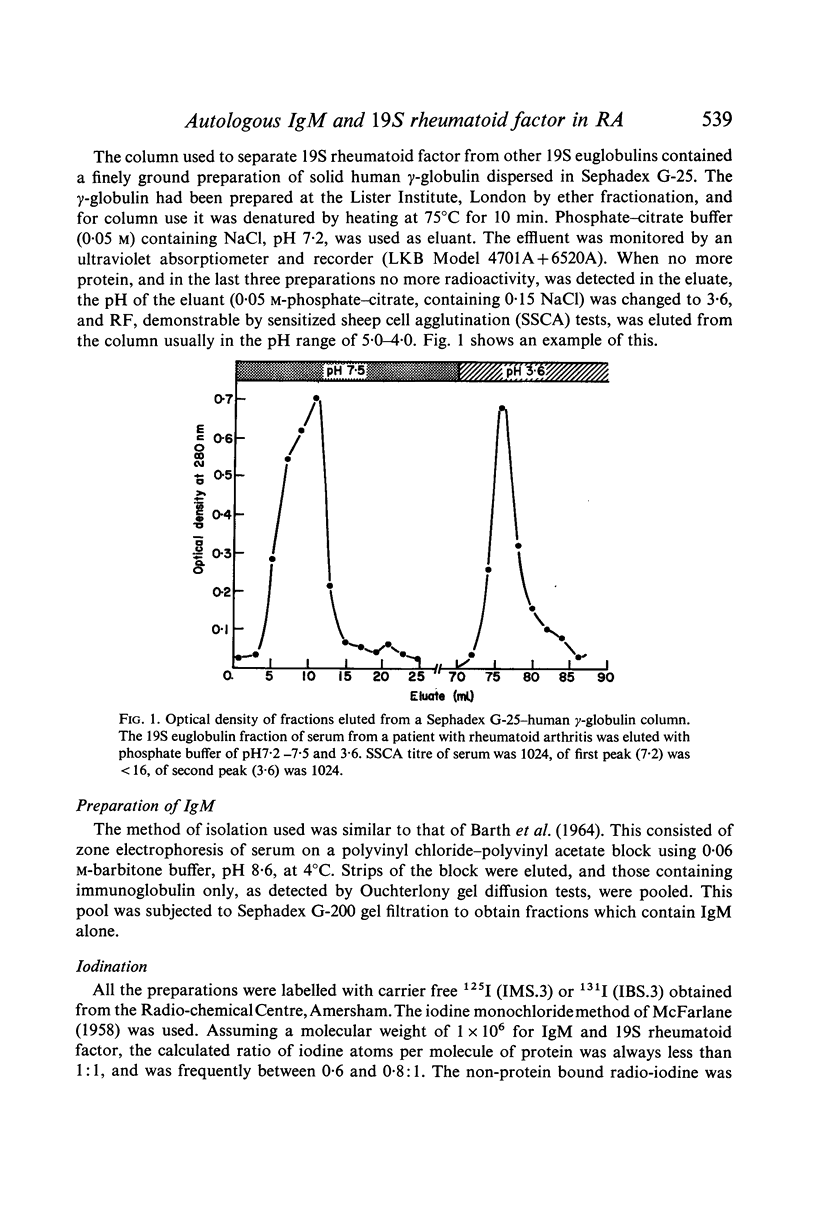
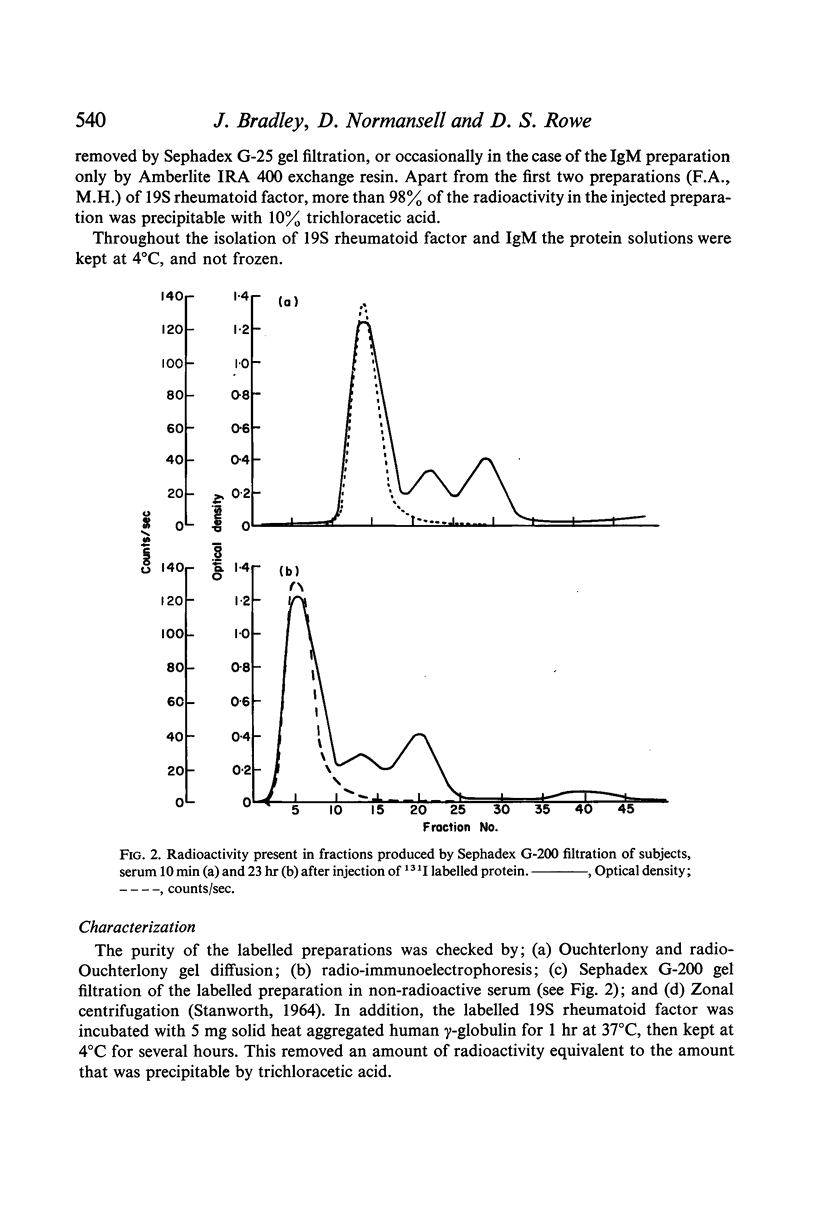
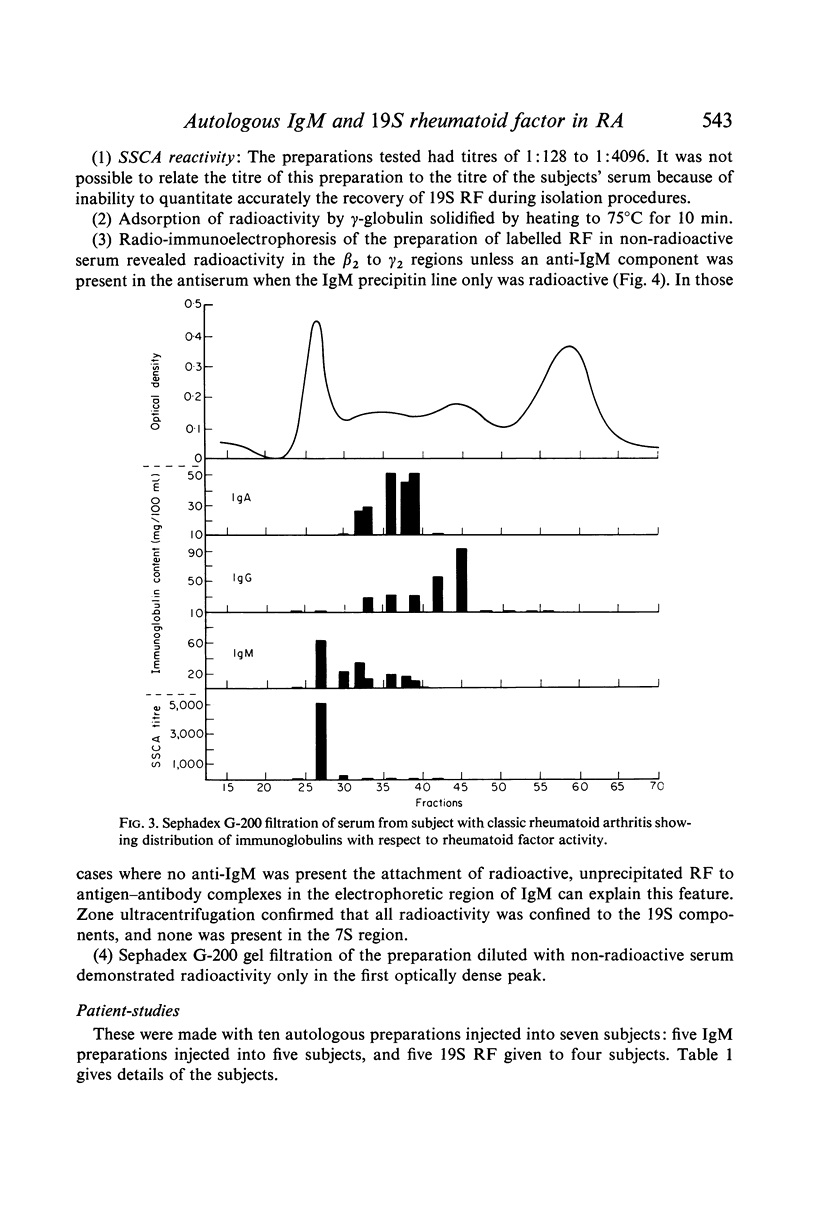
Abstract
The turnover of autologous preparations of radio-iodine labelled IgM and 19S rheumatoid factor was studied and compared in patients with severe rheumatoid disease. The IgM was isolated by block electrophoresis and column chromatography. 19S rheumatoid factor was isolated by a combination of euglobulin precipitation, column chromatography, and absorption onto and acid-elution from solid aggregated IgG.
Ten studies were made in seven patients, five with IgM, and five with 19S rheumatoid factor. In two patients the turnovers of 19S rheumatoid factor and IgM were studied simultaneously.
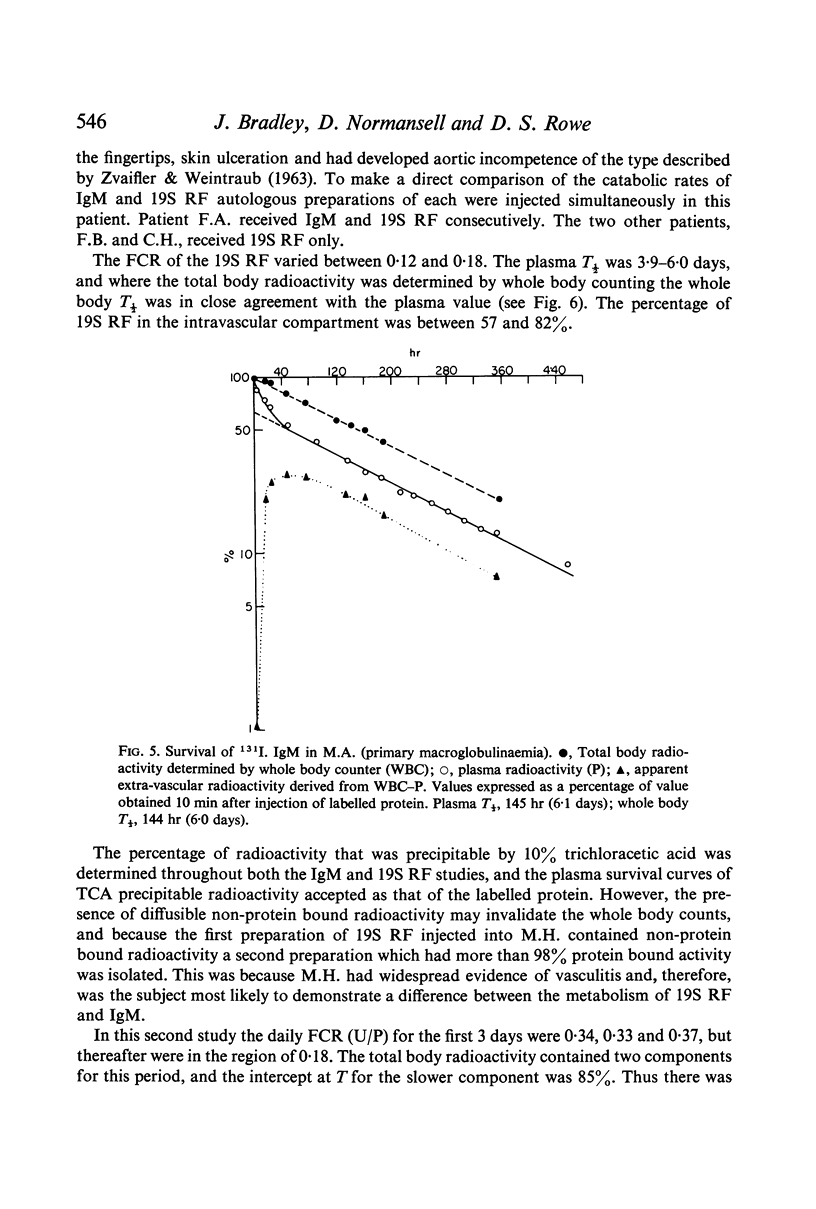
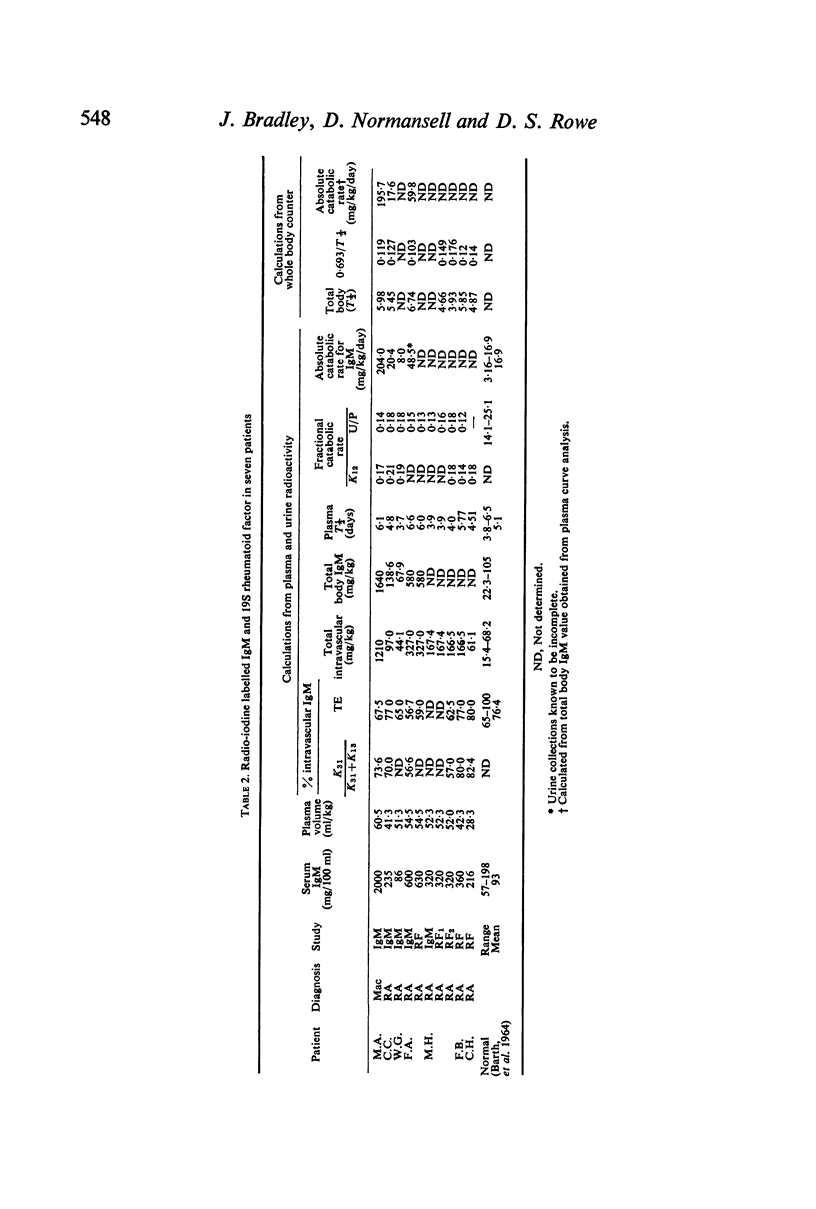
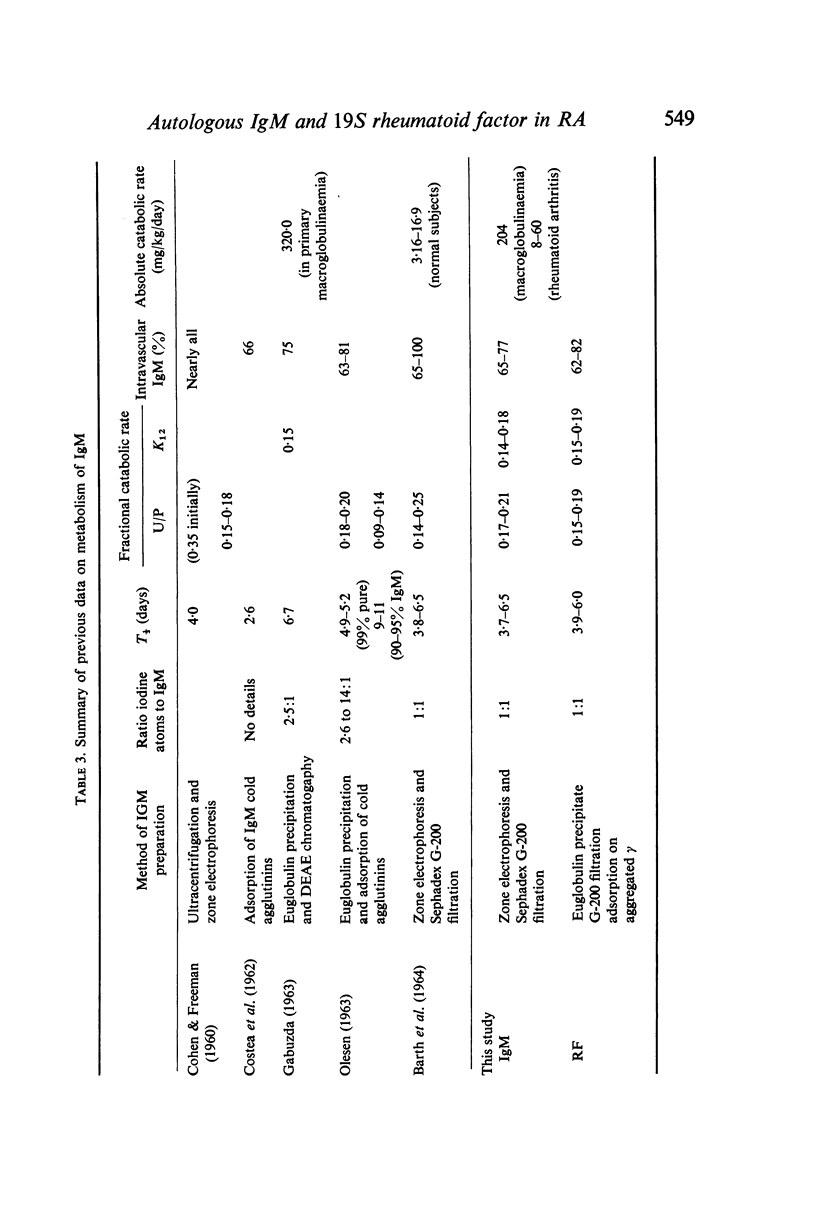
The turnover of IgM was similar to that reported for normal subjects and patients with other diseases: fractional catabolic rate 0·14–0·18, plasma and whole body T½ 3·7–6·5 days, with 65–77% intravascular localization. The absolute catabolic rate for IgM was elevated (8–60 mg/kg/day).
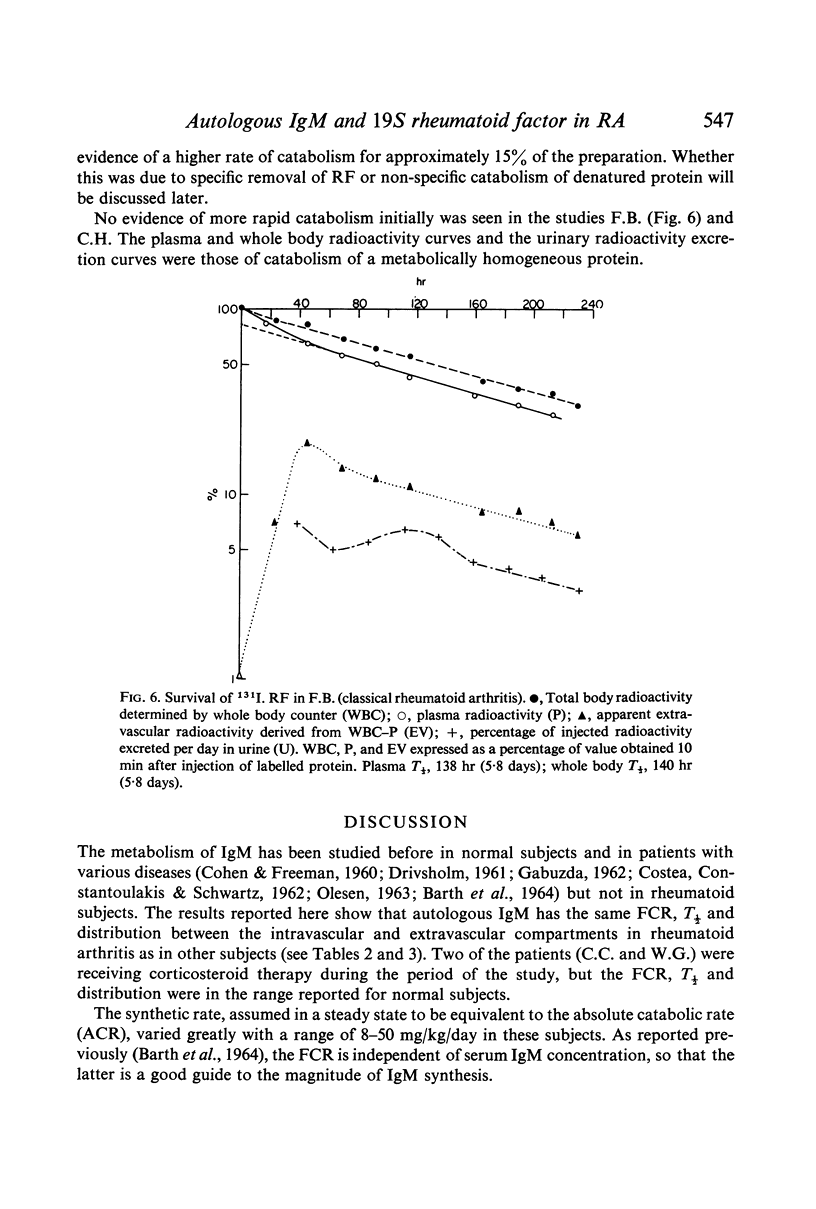
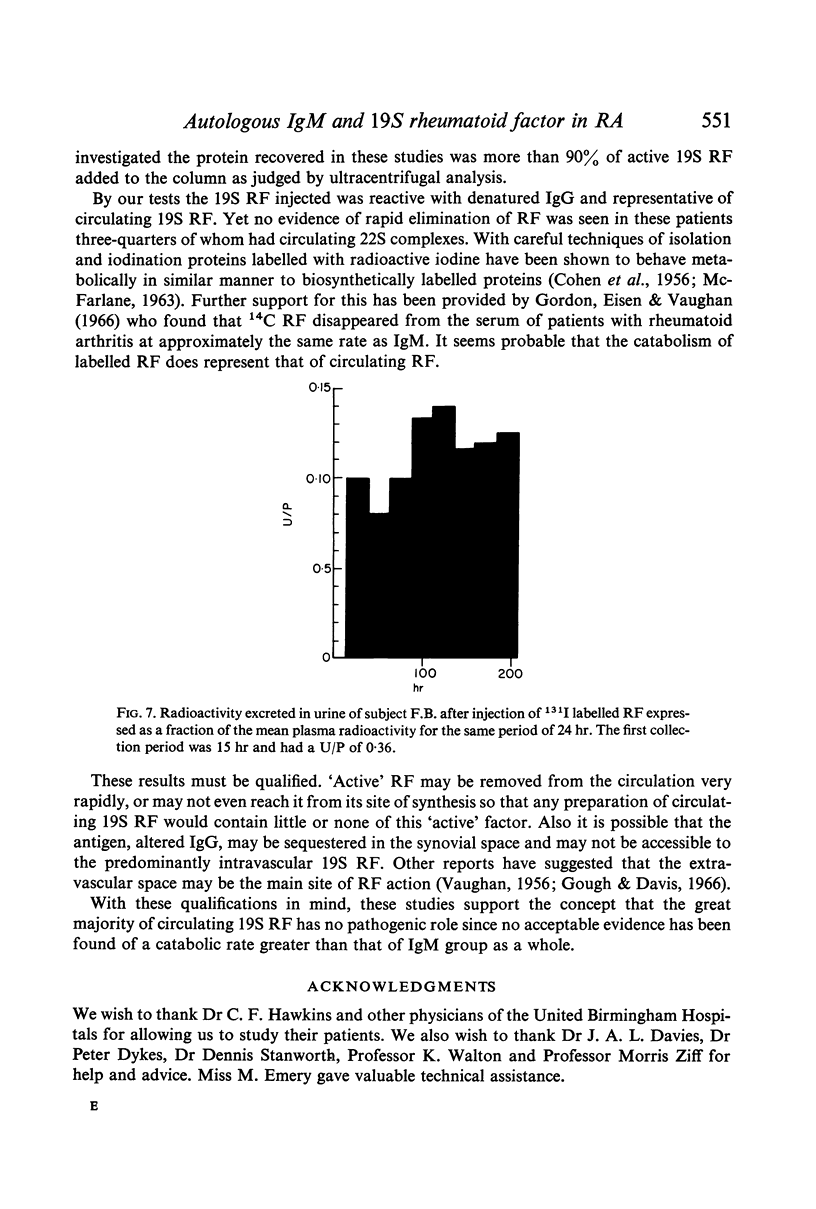
The turnover of 19S rheumatoid factor isolated from serum was comparable in fractional catabolic rate (0·15–0·19) plasma and whole body T½ (3·9–6·0 days) and intravascular localization (62–88%). No evidence of rapid catabolism of the `immune' elimination type was obtained.
Full text
PDF



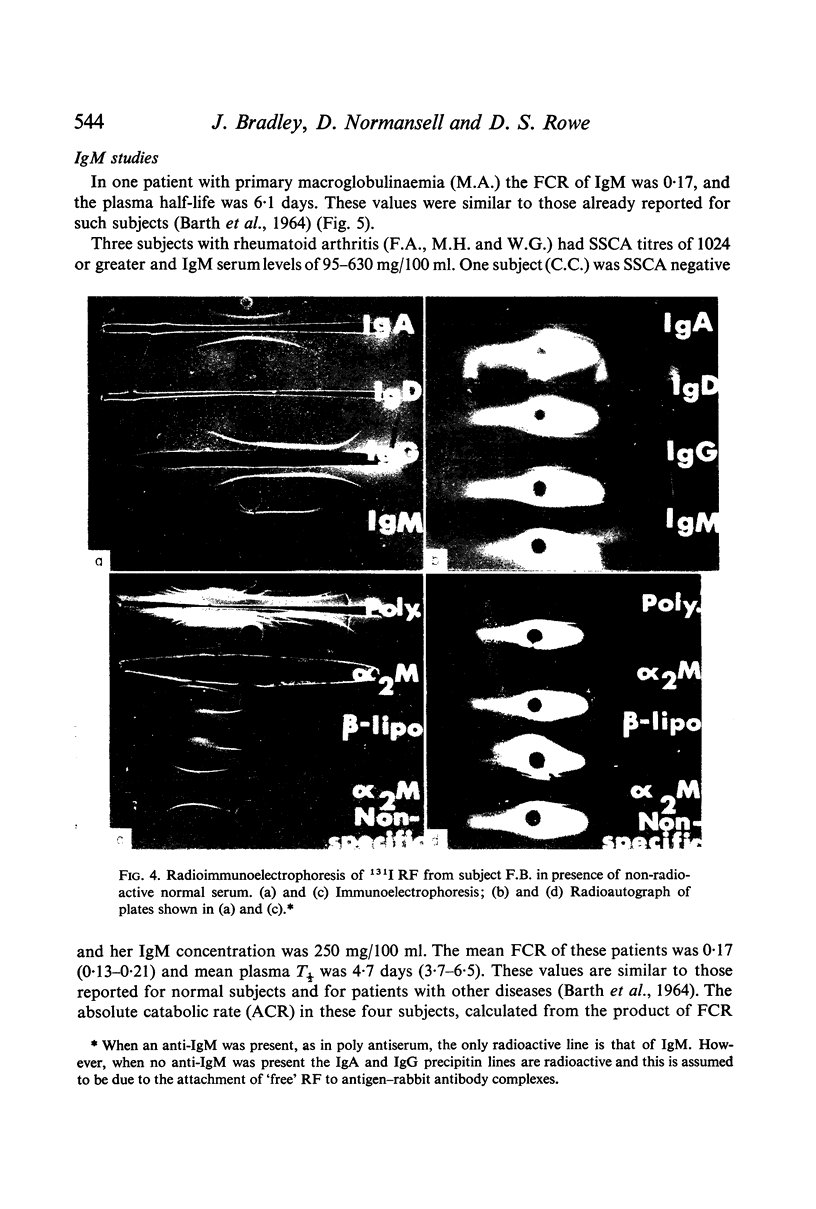
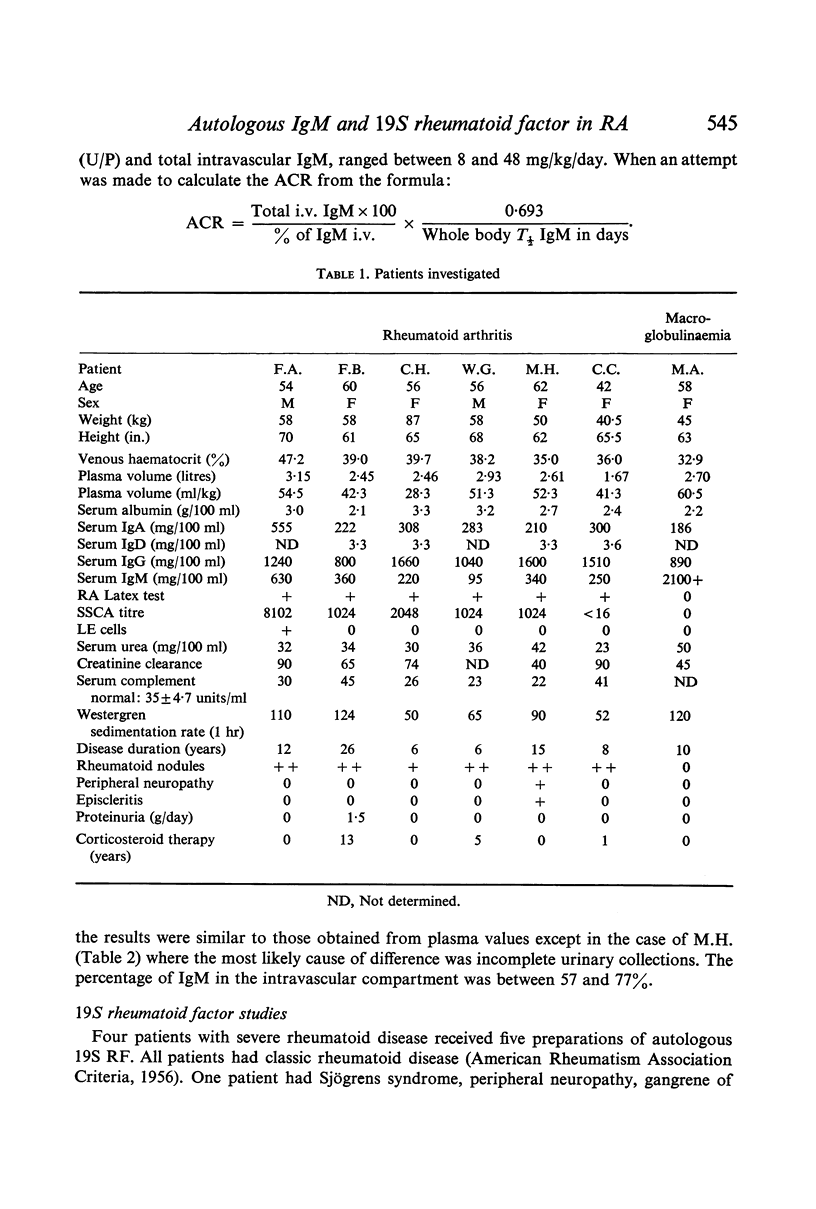



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTH W. F., WOCHNER R. D., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. METABOLISM OF HUMAN GAMMA MACROGLOBULINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1036–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI104987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., SCHREIBER S. S., POST J. Tracer experiments with I131 labeled human serum albumin: distribution and degradation studies. J Clin Invest. 1953 Aug;32(8):746–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI102789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYWATERS E. G., SCOTT J. T. THE NATURAL HISTORY OF VASCULAR LESIONS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Aug;16:905–914. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., FREEMAN T. Metabolic heterogeneity of human gamma-globulin. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:475–487. doi: 10.1042/bj0760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., HOLLOWAY R. C., MATTHEWS C., MCFARLANE A. S. Distribution and elimination of 131 I- and 14C-labelled plasma proteins in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):143–154. doi: 10.1042/bj0620143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J. THE ROLE OF ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES IN DISEASE. Harvey Lect. 1963;58:21–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRIVSHOLM A. Turnover rate of myeloma proteins in serum and urine determined after intravital labelling with glycine--1--C--14. Acta Med Scand. 1961 May;169:503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN G. M., KUNKEL H. G., FRANKLIN E. C. Interaction of the rheumatoid factor with antigen-antibody complexes and aggregated gamma globulin. J Exp Med. 1958 Jul 1;108(1):105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN W. V., ENGLEMAN E. P. The relation of the rheumatoid factor content of serum to clinical neurovascular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1959 Jun;2(3):250–258. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(195906)2:3<250::aid-art1780020306>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., KUNKEL H. G., WARD J. R. Clinical studies of seven patients with rheumatoid arthritis and uniquely large amounts of rheumatoid factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Oct;1(5):400–409. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABUZDA T. G. The turnover and distribution of I-131-labeled myeloma and macroglobulin proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jan;59:65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUBB R. Agglutination of erythrocytes coated with incomplete anti-Rh by certain rheumatoid arthritic sera and some other sera; the existence of human serum groups. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(3):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough W. W., Davis J. S., 4th Effects of rheumatoid factor on complement levels in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Aug;9(4):555–565. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J., VAUGHAN J. H. Transfusion studies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1961 Feb;4:47–55. doi: 10.1002/art.1780040105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMER R., NOSENZO C. J. PSEUDOGLOBULIN RHEUMATOID FACTORS. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:502–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES K., FELIX-DAVIES D., STANWORTH D. R. Studies on the isolation of rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1961 Dec;20:369–385. doi: 10.1136/ard.20.4.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., SIMON H. J., FUDENBERG H. Observations concerning positive serologic reactions for rheumatoid factor in certain patients with sarcoidosis and other hyperglobulinemic states. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Aug;1(4):289–296. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLUSKEY R. T., BENACERRAF B., POTTER J. L., MILLER F. The pathologic effects of intravenously administered soluble antigen-antibody complexes. I. Passive serum sickness in mice. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:181–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. S. IN VIVO BEHAVIOR OF I-FIBRINOGEN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42(3):346–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI104721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E., Stanworth D. R. Ultracentrifugal studies of the reactions of rheumatoid factor with native human gamma-G-globulin. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):527–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLESEN H. TURNOVER STUDIES WITH IODINE-LABELED GAMMA-MACROGLOBULIN AND ALBUMIN. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:497–510. doi: 10.1080/00365516309079778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIKE R. M., SULKIN S. E., COGGESHALL H. C., BURDETTE R. I. Serological reactions in rheumatoid arthritis. IV. Persistence of the serum factor which agglutinates sensitized sheep cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Jun;41(6):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP J. T., CALKINS E., COHEN A. S., SCHUBART A. F., CALABRO J. J. OBSERVATIONS ON THE CLINICAL, CHEMICAL, AND SEROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS, BASED ON THE COURSE OF 154 CASES. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Jan;43:41–58. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOKOLOFF L., BUNIM J. J. Vascular lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. J Chronic Dis. 1957 Jun;5(6):668–687. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(57)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrohenloher R. E. Characterization of the gamma-globulin complexes present in certain sera having high titers of anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):501–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI105364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER M. V., VAUGHAN J. H. Use of anti-Rh sera for demonstrating agglutination activating factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 May;92(1):198–200. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. SEPARATION OF RHEUMATOID FACTORS OF DIFFERENT SPECIFICITIES USING COLUMNS CONJUGATED WITH GAMMA-GLOBULIN. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Dec;6:665–675. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIFF M., BROWN P., LOSPALLUTO J., BADIN J., MCEWEN C. Agglutination and inhibition by serum globulin in the sensitized sheep cell agglutination reaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Apr;20(4):500–509. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZVAIFLER N. J., WEINTRAUB A. M. Aortitis and aortic insufficiency in the chronic rheumatic disorders--a reappraisal. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Jun;6:241–245. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]