Abstract
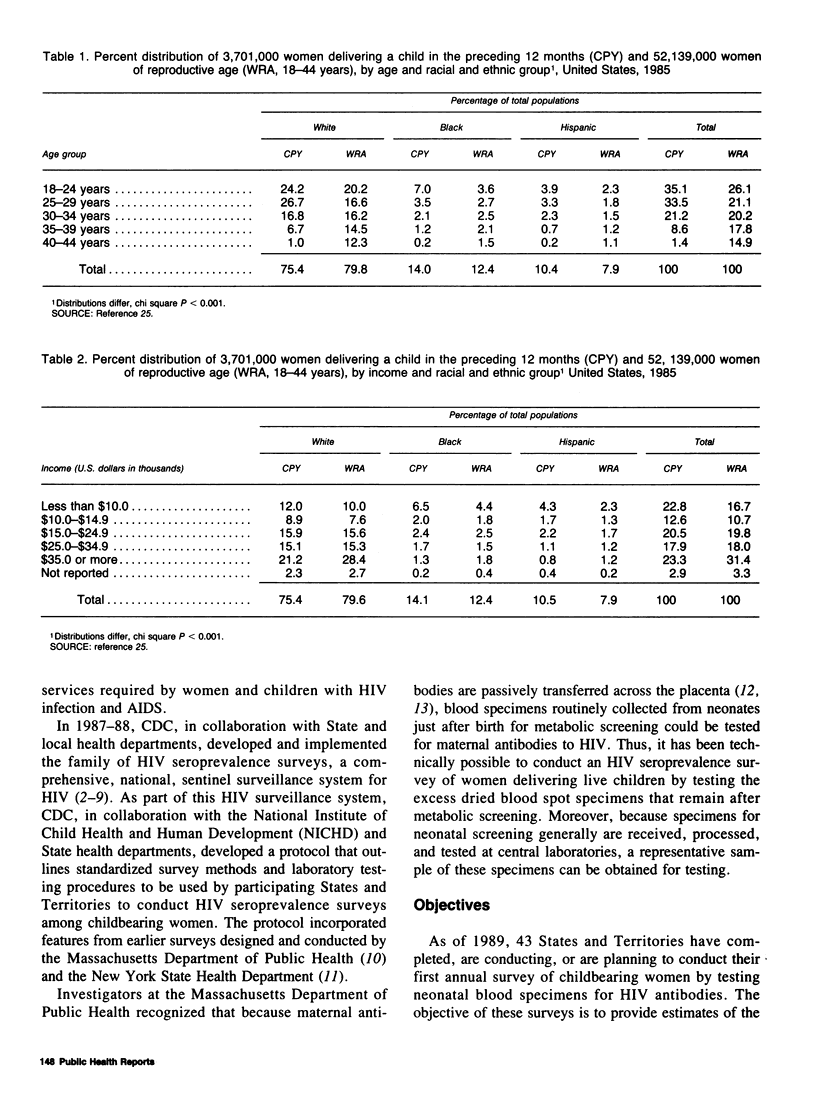
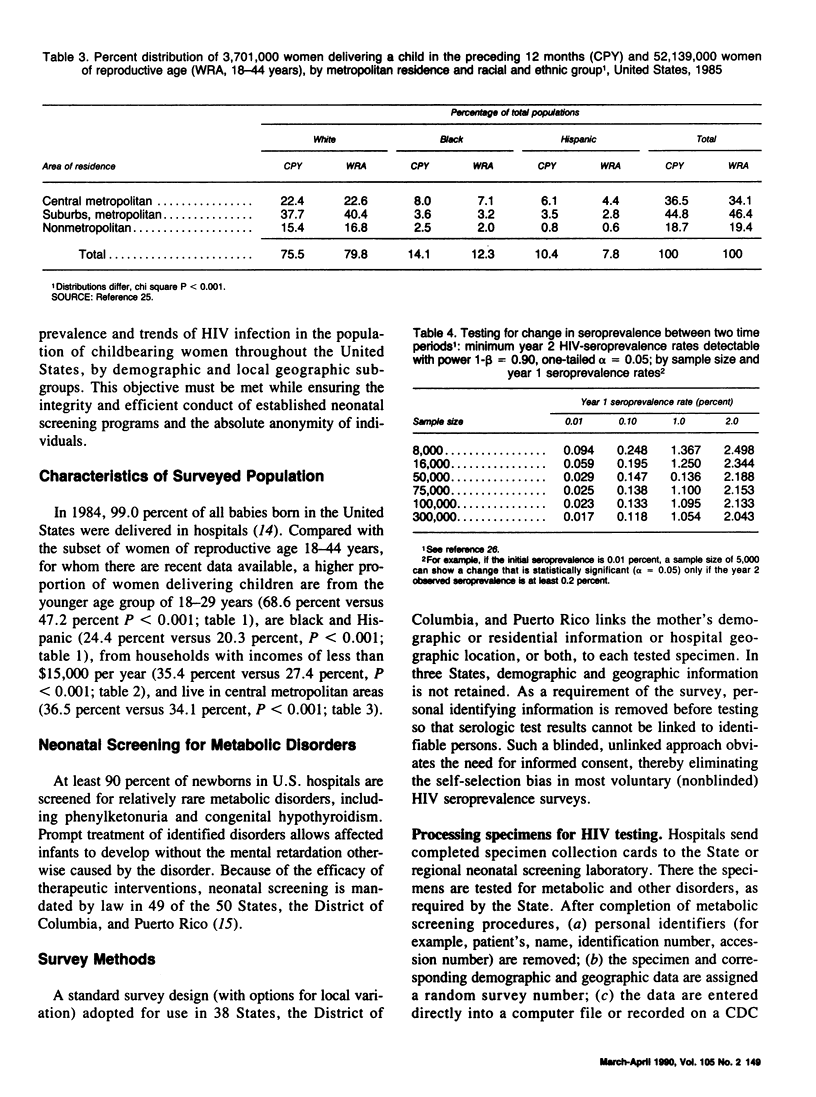
A seroprevalence survey of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) among childbearing women is being conducted in 43 States and Territories as one of the family of HIV seroprevalence surveys. This blinded survey, in which serologic test results are not linked to identifiable persons, uses neonatal dried blood specimens on filter paper to test for maternal antibodies to HIV. This survey provides relatively unbiased estimates of prevalence of HIV infection in the population of women delivering live children during given survey periods, by month or quarter of delivery, geographic area, and demographic subgroup.
This objective will be met while protecting the integrity and efficient conduct of neonatal screening programs and ensuring patient anonymity. Information from this survey will be used to (a) assess the levels and trends of HIV infection in women and infants, (b) help develop and evaluate prevention programs, and (c) project the number of women and children who will develop HIV infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and will require health care and social services in the future.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allansmith M., McClellan B. H., Butterworth M., Maloney J. R. The development of immunoglobulin levels in man. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):276–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. M., Lee N. C., Schulz S. L., Pappaioanou M., Dondero T. J., Jr, Onorato I. M. Determining HIV seroprevalence among women in women's health clinics. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):130–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Pappaioanou M., Curran J. W. Monitoring the levels and trends of HIV infection: the Public Health Service's HIV surveillance program. Public Health Rep. 1988 May-Jun;103(3):213–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J., Hutchison G. B. Prevalence, incidence and duration. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Nov;112(5):707–723. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., KUMATE J., URRUSTI J., MORALES C. THE SELECTIVITY OF THE HUMAN PLACENTA IN THE TRANSFER OF PLASMA PROTEINS FROM MOTHER TO FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1938–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI105068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon W. H., Lewis D. S., Jones W. K., Powell M. K. A quality assurance program for human immunodeficiency virus seropositivity screening of dried-blood spot specimens. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1989 Jan;10(1):8–13. doi: 10.1086/645908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff R., Berardi V. P., Weiblen B. J., Mahoney-Trout L., Mitchell M. L., Grady G. F. Seroprevalence of human immunodeficiency virus among childbearing women. Estimation by testing samples of blood from newborns. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):525–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. S., Allen D. M., Onorato I. M., Petersen L. R., Dondero T. J., Jr, Pappaioanou M. HIV seroprevalence surveys in drug treatment centers. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):125–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karon J. M., Dondero T. J., Jr, Curran J. W. The projected incidence of AIDS and estimated prevalence of HIV infection in the United States. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(6):542–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray E., Onorato I. M., Miller B. I., Dondero T. J., Jr, Bloch A. B. Estimating HIV levels and trends among patients of tuberculosis clinics. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):135–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick L. F., Berns D., Stricof R., Stevens R., Pass K., Wethers J. HIV seroprevalence in newborns in New York State. JAMA. 1989 Mar 24;261(12):1745–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato I. M., McCray E., Pappaioanou M., Johnson R., Aral S., Hardy A. M., Dondero T. J., Jr HIV seroprevalence surveys in sexually transmitted disease clinics. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappaioanou M., Dondero T. J., Jr, Petersen L. R., Onorato I. M., Sanchez C. D., Curran J. W. The family of HIV seroprevalence surveys: objectives, methods, and uses of sentinel surveillance for HIV in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):113–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. R., Dodd R., Dondero T. J., Jr Methodologic approaches to surveillance of HIV infection among blood donors. Public Health Rep. 1990 Mar-Apr;105(2):153–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


