Abstract
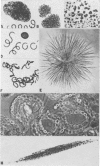
Unialgal cultures of several species and strains of blue-green algae, including those most suspected of causing animal deaths, have been grown and found to vary greatly in toxicity. At least four toxic factors have been recognized. One produces fast deaths and is algal in origin. The others produce slow deaths and are bacterial in origin. The fast-death factor (FDF) is an endotoxin that so far has been encountered only with strains of Microcystis aeruginosa Kütz. emend. Elenkin. Its production is genetically and physiologically controlled. An FDF-producing strain of M. aeruginosa has been cultured on a large scale and the cells shown to be toxic when administered orally to sheep, calves, and smaller animals. FDF isolated from these cells has been identified as a quite stable cyclic polypeptide having an intraperitoneal LD50 for white mice of 0.47 mg. per kg. body weight. The slow-death factors may also contribute to the toxicity of waterblooms. It is concluded that a complex of interdepedent variables determines the degree and kind of toxicity that a waterbloom can develop.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth C. T., Mason M. F. Observations on the Pathological Changes Produced by a Toxic Substance Present in Blue-Green Algae (Microcystis aeruginosa). Am J Pathol. 1946 Mar;22(2):369–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP C. T., ANET E. F., GORHAM P. R. Isolation and identification of the fast-death factor in Microcystis aeruginosa NRC-1. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Mar;37(3):453–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. G., REIF C. B. Cutaneous sensitization to blue-green algae. J Allergy. 1953 Sep;24(5):452–457. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(53)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT G. A., HUGHES E. O. Development of toxicity in blue-green algae. Can J Public Health. 1953 Sep;44(9):334–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. O., GORHAM P. R., ZEHNDER A. Toxicity of a unialgal culture of Microcystis aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Jun;4(3):225–236. doi: 10.1139/m58-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEOD J. A., BONDAR G. F. A case of suspected algal poisoning in Manitoba. Can J Public Health. 1952 Aug;43(8):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'donoghue J. G., Wilton G. S. Algal Poisoning in Alberta. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1951 Aug;15(8):193–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART A. G., BARNUM D. A., HENDERSON J. A. Algal poisoning in Ontario. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1950 Jun;14(6):197–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINBERG G. G. Toksicheskii fitoplankton. Usp Sovrem Biol. 1954 Sep-Oct;38(2):216–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]