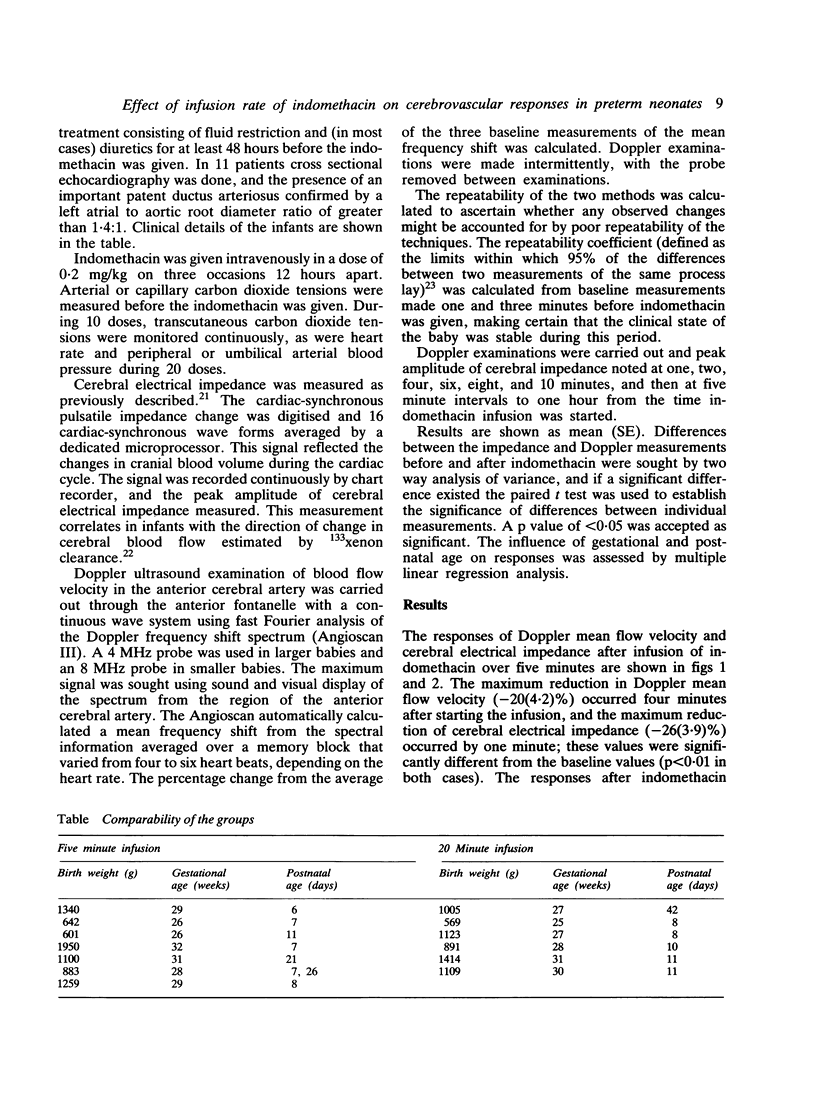
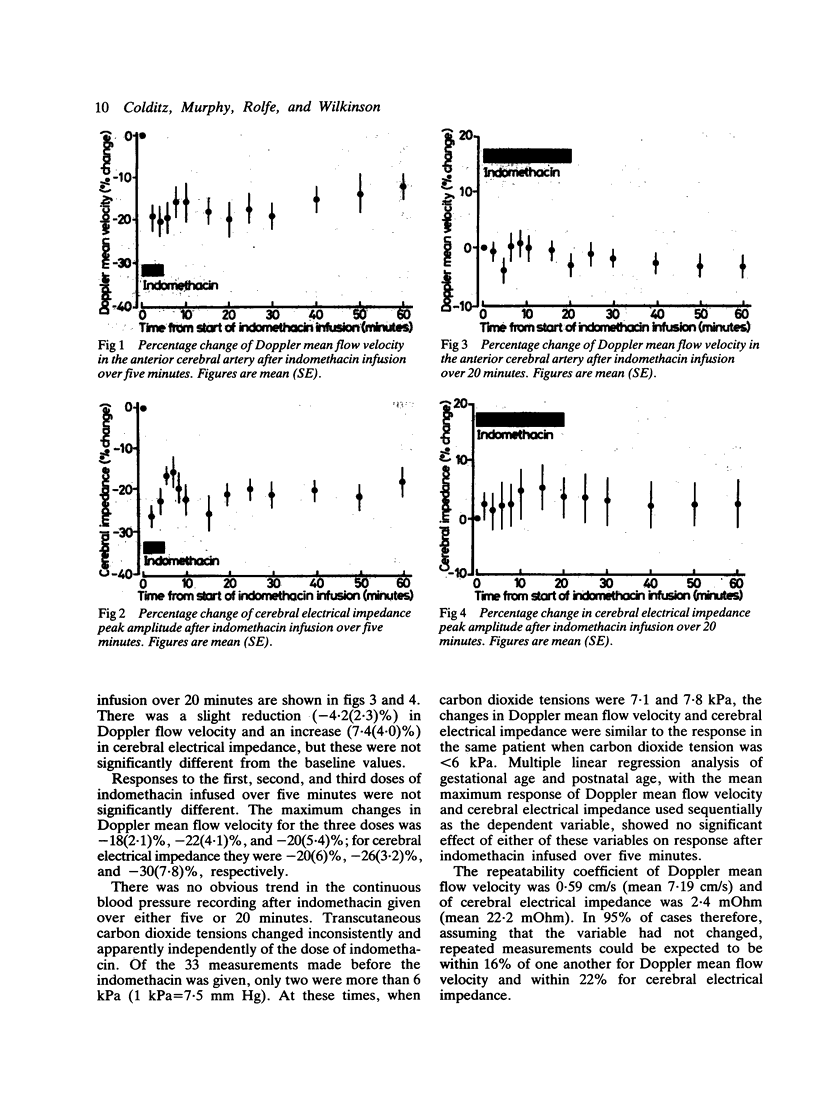
Abstract
Cerebrovascular responses were studied in preterm infants by Doppler ultrasound and cerebral electrical impedance for one hour after intravenous indomethacin infusion for patent ductus arteriosus. Indomethacin in a dose of 0.2 mg/kg body weight was infused over five minutes in one group of infants (20 doses) and over 20 minutes in a second group of infants (16 doses). There were no significant differences between the two groups in birth weight (mean = 1068 g, range 569-1950), gestational age (mean 28.4 weeks, range 25-31), or postnatal age (mean 18.1 days, range 6-42). There was a significant reduction in both the Doppler mean flow velocity in the anterior cerebral artery (mean (SE) -20 (4.2)%) and peak amplitude of cerebral electrical impedance (-26 (3.9)%) within two minutes of starting the indomethacin infusion over five minutes. There was no significant change after the infusion over 20 minutes. There were no significant changes in blood pressure or carbon dioxide tensions after infusion at either rate. The results suggest that infusion of indomethacin over five minutes caused a potentially deleterious reduction in cerebral blood flow. No such reduction occurred when it was infused over 20 minutes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. J., Berl T., McDonald K. M., Schrier R. W. Prostaglandins: effects on blood pressure, renal blood flow, sodium and water excretion. Kidney Int. 1976 Sep;10(3):205–215. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash A. R., Hickey D. E., Graham T. P., Stahlman M. T., Oates J. A., Cotton R. B. Pharmacokinetics of indomethacin in the neonate. Relation of plasma indomethacin levels to response of the ductus arteriosus. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):67–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busija D. W., Heistad D. D. Effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow during hypercapnia in cats. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):H519–H524. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.4.H519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan F. Indomethacin, patent ductus arteriosus, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80398-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockard A., Iannotti F., Ladds G. Cerebrovascular effects of prostaglandin inhibitors in the gerbil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1982;2(1):67–72. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1982.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren N., Siesjö B. K. Effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in barbiturate-anesthetized Normocapnic and hypercapnic rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):109–115. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusting G. J., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins, their intermediates and precursors: cardiovascular actions and regulatory roles in normal and abnormal circulatory systems. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1979 May-Jun;21(6):405–430. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(79)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Hagenfeldt L., Law D., Patrono C., Pinca E., Wennmalm A. Effect of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors on basal and carbon dioxide stimulated cerebral blood flow in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Feb;117(2):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Levene M. I., Archer L. N. The effect of indomethacin on cerebral blood-flow velocity in premature infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1987 Dec;29(6):776–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1987.tb08823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. J. Response of the patent ductus arteriosus to indomethacin treatment. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Mar;141(3):250–250. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460030028016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisen G., Johansen K., Ellison P. H., Fredriksen P. S., Mali J., Friis-Hansen B. Cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant: comparison of Doppler ultrasound and 133xenon clearance. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen A. A., White R. P., Robertson J. T. Synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxane B2 by cerebral arteries. Stroke. 1979 May-Jun;10(3):306–309. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.3.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohimer A. R., Richardson B. S., Bissonnette J. M., Machida C. M. The effect of indomethacin on breathing movements and cerebral blood flow and metabolism in the fetal sheep. J Dev Physiol. 1985 Aug;7(4):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Busija D. W. Arachidonate metabolism on the cerebral surface of newborn pigs. Prostaglandins. 1985 Nov;30(5):811–817. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Busija D. W. Arachidonic acid metabolites and perinatal cerebral hemodynamics. Semin Perinatol. 1987 Jan;11(1):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Busija D. W., Beasley D. G. Effect of therapeutic dose of indomethacin on the cerebral circulation of newborn pigs. Pediatr Res. 1987 Feb;21(2):188–192. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198702000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony L., Caldwell R. L., Girod D. A., Hurwitz R. A., Jansen R. D., Lemons J. A., Schreiner R. L. Indomethacin therapy on the first day of life in infants with very low birth weight. J Pediatr. 1985 May;106(5):801–805. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch J., Kelly P. A., Grome J. J., Pickard J. D. Local cerebral circulatory and metabolic effects of indomethacin. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):H416–H423. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.3.H416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Stewart W. B., Duncan C. C., Scott D. T., Lambrecht R. Beagle puppy model of intraventricular hemorrhage. Effect of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow. J Neurosurg. 1983 Jun;58(6):857–862. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.58.6.0857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham G. J., Miettinen O. S., Ellison R. C., Kraybill E. N., Gersony W. M., Zierler S., Nadas A. S. Clinical course to 1 year of age in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: results of a multicenter randomized trial of indomethacin. J Pediatr. 1984 Aug;105(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard J., Tamura A., Stewart M., McGeorge A., Fitch W. Prostacyclin, indomethacin and the cerebral circulation. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 22;197(2):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryds O., Greisen G., Johansen K. H. Indomethacin and cerebral blood flow in premature infants treated for patent ductus arteriosus. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;147(3):315–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00442705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie J. M., Doyle J., Cooke R. W. Early administration of indomethacin to preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Mar;61(3):233–238. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.3.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakabe T., Siesjö B. K. The effect of indomethacin on the blood flow-metabolism couple in the brain under normal, hypercapnic and hypoxic conditions. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Nov;107(3):283–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyberth H. W., Knapp G., Wolf D., Ulmer H. E. Introduction of plasma indomethacin level monitoring and evaluation of an effective threshold level in very low birth weight infants with symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Dec;141(2):71–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00496793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silove E. D. Pharmacological manipulation of the ductus arteriosus. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):827–829. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe S. J., Friedman W. F., Rogers D., Lang P., Ragni M., Saccar C. The disposition of indomethacin in preterm babies. J Pediatr. 1980 Dec;97(6):1001–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh T. F., Luken J., Raval D., Thalji A., Carr I., Pildes R. S. Indomethacin treatment in small versus large premature infants with ductus arteriosus. Comparison of plasma indomethacin concentration and clinical response. Br Heart J. 1983 Jul;50(1):27–30. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


