Abstract
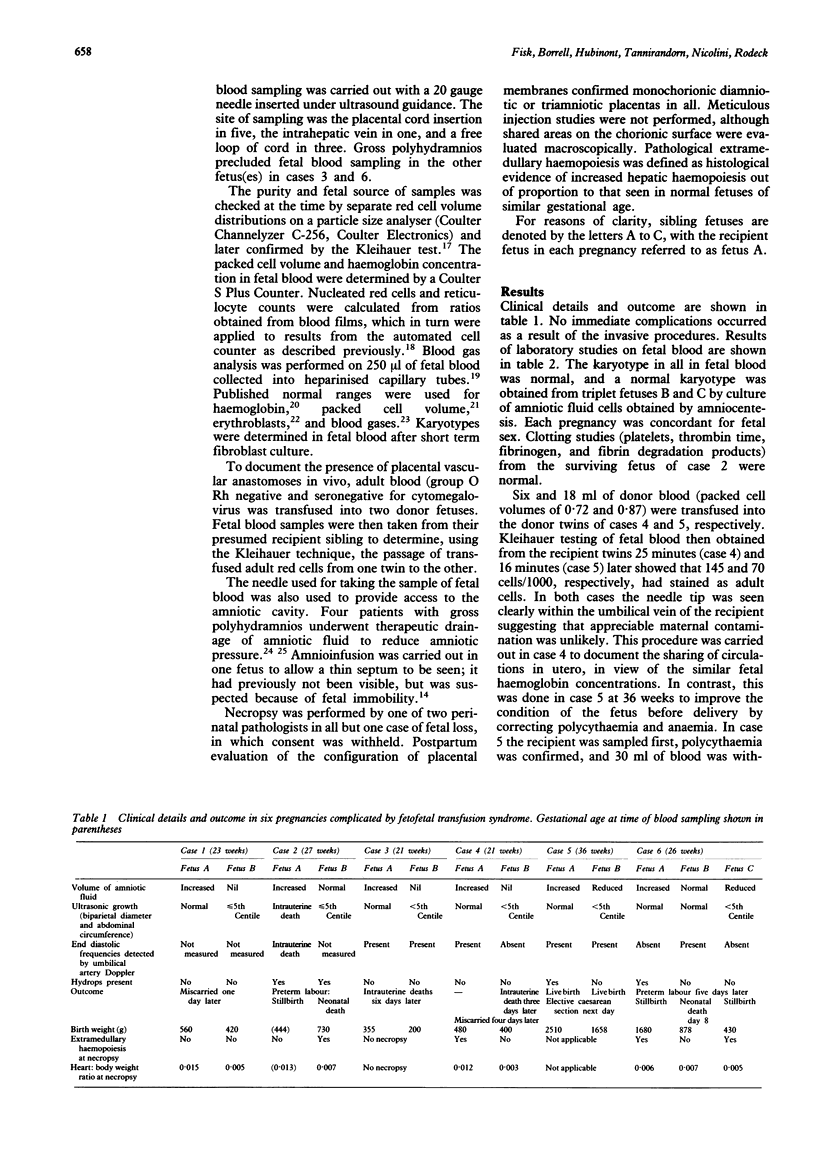
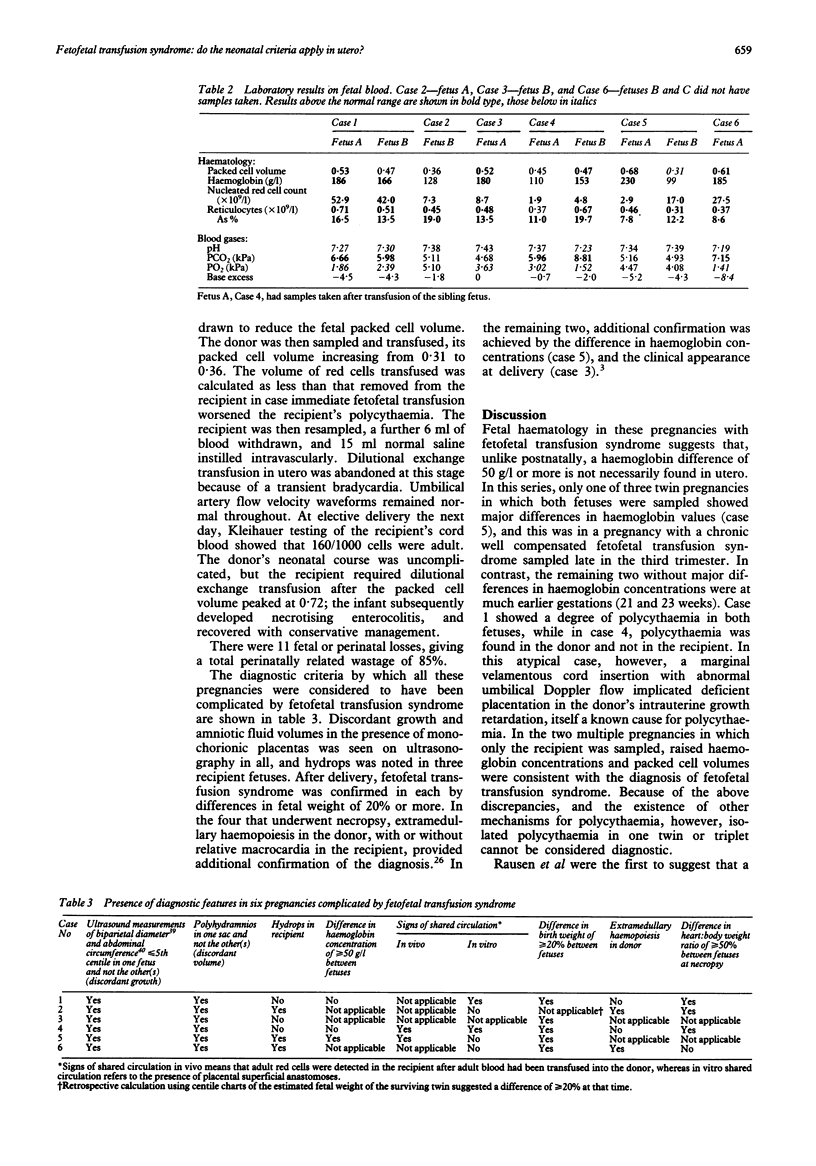
Thirteen fetuses (five twin, one triplet) were compromised by fetofetal transfusion syndrome in six pregnancies, five in the mid trimester, and one in the third trimester. This diagnosis, which was suspected because of ultrasound findings of discordant growth, discordant amniotic fluid volumes, concordant external genitalia, and monochorial placentation, was confirmed postnatally in each. Nine fetuses underwent blood sampling to aid diagnosis and assessment of fetal wellbeing. In contrast to fetofetal transfusion syndrome investigated postnatally, a difference in haemoglobin concentration of 50 g/l or more in utero was found in only one pregnancy, which was near term, although all had fetal erythroblastaemia and a difference in weight of 20% or more. In vivo confirmation of shared circulation was achieved in two pregnancies by transfusing adult Rh negative red cells into the smaller fetus and then detecting them by Kleihauer testing in blood aspirated from the larger. Invasive procedures also yielded information on fetal blood gas measurements (acidaemia in four and hypoxaemia in six) and amniotic pressure (raised in two). We suggest that comparison of haemoglobin concentrations is inaccurate in fetofetal transfusion syndrome in utero, the diagnosis of which may necessitate detection of a shared circulation using a marker such as adult red cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aherne W., Strong S. J., Corney G. The structure of the placenta in the twin transfusion syndrome. Biol Neonat. 1968;12(3):121–135. doi: 10.1159/000240099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebbington M. W., Wittmann B. K. Fetal transfusion syndrome: antenatal factors predicting outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Apr;160(4):913–915. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benirschke K., Kim C. K. Multiple pregnancy. 1. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 14;288(24):1276–1284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306142882406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan J. N., Diwan R. V., Rosen M. G., Bellon E. M. Fetofetal transfusion syndrome: prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis. Radiology. 1982 May;143(2):535–536. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.2.7071360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Benson C. B., Driscoll S. G., Doubilet P. M. Twin-twin transfusion syndrome: sonographic findings. Radiology. 1989 Jan;170(1 Pt 1):61–63. doi: 10.1148/radiology.170.1.2642349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Newman G. B. Growth of the fetal biparietal diameter during normal pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1971 Jun;78(6):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1971.tb00309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Wilkin D. Ultrasonic measurement of fetal abdomen circumference in the estimation of fetal weight. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1975 Sep;82(9):689–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1975.tb00708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chescheir N. C., Seeds J. W. Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios in twin gestations. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jun;71(6 Pt 1):882–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox W. L., Daffos F., Forestier F., Descombey D., Aufrant C., Auger M. C., Gaschard J. C. Physiology and management of intrauterine growth retardation: a biologic approach with fetal blood sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jul;159(1):36–41. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox W. L., Forestier F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Daffos F. Fetal blood sampling in twin pregnancies. Prenatal diagnosis and management of 19 cases. Fetal Ther. 1987;2(2):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danskin F. H., Neilson J. P. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome: what are appropriate diagnostic criteria? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Aug;161(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLia J. E., Cukierski M. A., Lundergan D. K., Kochenour N. K. Neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser occlusion of rhesus placental vasculature via fetoscopy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Feb;160(2):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley D. K., D'Alton M. E. Single fetal death in twin gestation. Semin Perinatol. 1986 Jan;10(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold M., Cetrulo C. L., Newton E. R., Weiss J., Shakr C., Shmoys S. Serial amniocenteses in the treatment of twin to twin transfusion complicated with acute polyhydramnios. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1986;35(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1017/s0001566000006310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisk N. M., Tannirandorn Y., Santolaya J., Nicolini U., Letsky E. A., Rodeck C. H. Fetal macrocytosis in association with chromosomal abnormalities. Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Oct;74(4):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galea P., Scott J. M., Goel K. M. Feto-fetal transfusion syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Oct;57(10):781–783. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.10.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshon B., Moise K. J., Jr, Wasserstrum N., Ou C. N., Huhta J. C. Influence of short-term indomethacin therapy on fetal urine output. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jul;72(1):51–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe J. G., Ingomar C. J. The fetoplacental circulation during parturition illustrated by the interfetal transfusion syndrome. Pediatrics. 1972 Jan;49(1):112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange I. R., Harman C. R., Ash K. M., Manning F. A., Menticoglou S. Twin with hydramnios: treating premature labor at source. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Mar;160(3):552–557. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(89)80024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macafee C. A., Fortune D. W., Beischer N. A. Non-immunological hydrops fetalis. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1970 Mar;77(3):226–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1970.tb03511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony B. S., Filly R. A., Callen P. W. Amnionicity and chorionicity in twin pregnancies: prediction using ultrasound. Radiology. 1985 Apr;155(1):205–209. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.1.3883418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar D. S., Davis L. R., Rodeck C. H., Nicolaides K. H., Mibashan R. S. Normal blood cell values in the early mid-trimester fetus. Prenat Diagn. 1985 Nov-Dec;5(6):367–373. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. M., McAdams A. J., Sutherland J. Intrauterine disseminated intravascular coagulation: a syndrome of multiple pregnancy with a dead twin fetus. J Pediatr. 1969 Apr;74(4):523–528. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAEYE R. L. THE FETAL AND NEONATAL DEVELOPMENT OF TWINS. Pediatrics. 1964 Apr;33:546–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides K. H., Soothill P. W., Clewell W. H., Rodeck C. H., Mibashan R. S., Campbell S. Fetal haemoglobin measurement in the assessment of red cell isoimmunisation. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1073–1075. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91896-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolini U., Fisk N. M., Talbert D. G., Rodeck C. H., Kochenour N. K., Greco P., Hubinont C., Santolaya J. Intrauterine manometry: technique and application to fetal pathology. Prenat Diagn. 1989 Apr;9(4):243–254. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970090404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolini U., Santolaya J., Fisk N. M., Hubinont C., Kochenour N. K., Greco P., Rodeck C. H. Changes in fetal acid base status during intravascular transfusion. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Jul;63(7 Spec No):710–714. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.7_spec_no.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius D. H., Manchester D., Barkin S., Parker S., Nelson T. R. Doppler ultrasound of twin transfusion syndrome. J Ultrasound Med. 1988 Mar;7(3):117–124. doi: 10.7863/jum.1988.7.3.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSEN A. R., SEKI M., STRAUSS L. TWIN TRANSFUSION SYNDROME. A REVIEW OF 19 CASES STUDIED AT ONE INSTITUTION. J Pediatr. 1965 Mar;66:613–628. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. G., Neer K. J. Placental injection studies in twin gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Sep 15;147(2):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill P. W., Nicolaides K. H., Rodeck C. H., Campbell S. Effect of gestational age on fetal and intervillous blood gas and acid-base values in human pregnancy. Fetal Ther. 1986;1(4):168–175. doi: 10.1159/000262264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. L., Tan R., Tan S. H., Tan A. M. The twin transfusion syndrome. Clinical observations on 35 affected pairs. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1979 Feb;18(2):111–114. doi: 10.1177/000992287901800206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter K., Schneider K. T. Iatrogenous remission of twin transfusion syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;158(1):221–221. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90826-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner C. P. Diagnosis and treatment of twin to twin transfusion in the mid-second trimester of pregnancy. Fetal Ther. 1987;2(2):71–74. doi: 10.1159/000263286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir P. E., Ratten G. J., Beischer N. A. Acute polyhydramnios--a complication of monozygous twin pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 Nov;86(11):849–853. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann B. K., Farquharson D. F., Thomas W. D., Baldwin V. J., Wadsworth L. D. The role of feticide in the management of severe twin transfusion syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Nov;155(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


